Early Cambrian fossils reveal how a small, shelled animal evolved to deal with attacks from a predator. The finds confirm a popular hypothesis, until now lacking in clear evidence, about what drove the greatest expansion in biological diversity in Earth’s history.
The Cambrian explosion saw life take on a staggering array of forms around 539 million years ago, a few of which are recognizable as the ancestors of modern branches of the tree of life. Others look so much like the product of a bad acid trip one was even named Hallucigenia. It is thought the explosion was made possible by a flood of nutrients entering the ocean at the end of Snowball Earth, but even if the raw materials were there, some evolutionary impulse must have caused all that experimentation.
“Predator-prey interactions are often touted as a major driver of the Cambrian explosion, especially with regard to the rapid increase in diversity and abundance of biomineralizing organisms at this time. Yet, there has been a paucity of empirical evidence showing that prey directly responded to predation, and vice versa,” said Dr Russell Bicknell of the American Museum of Natural History in a statement.
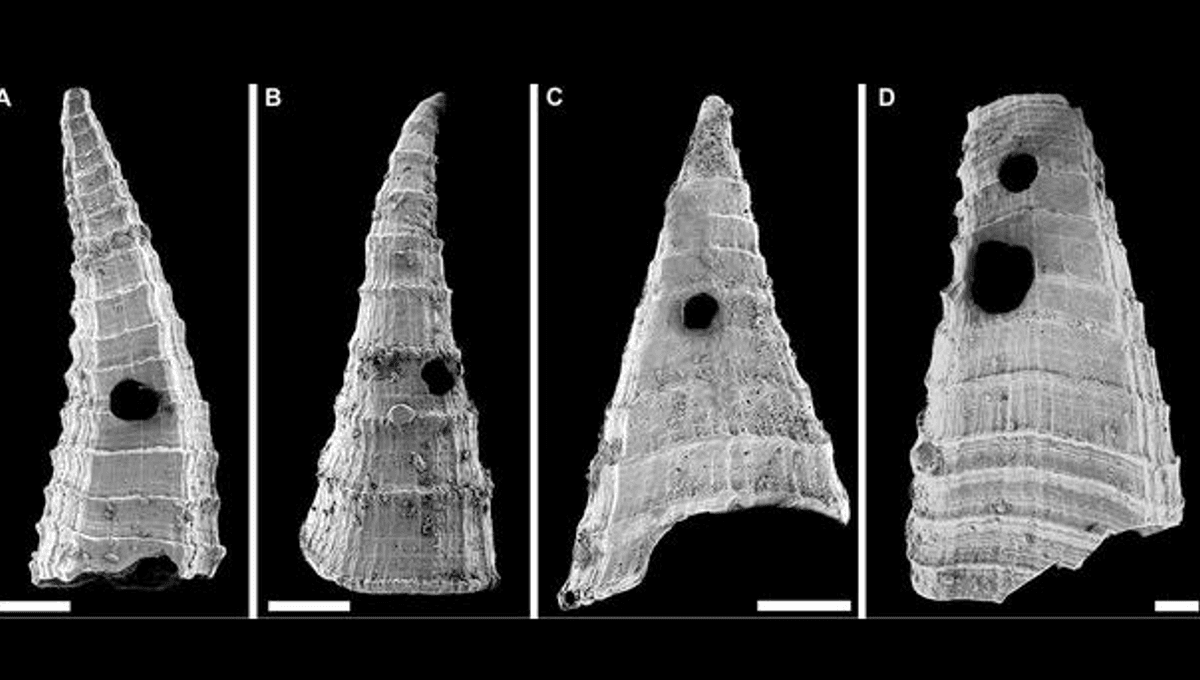
Now, Bicknell and colleagues appear to have found that evidence in the form of holes punched in the shells of Lapworthella fasciculata, a tiny animal distantly related to modern brachiopod bivalves.
Thousands of L. fasciculata shells have been found in a South Australian fossil bed. More than 200 have holes punched in them, thought to be made by a predator that had found a way through their shell. Since all these shells are less than a few millimeters in size, and some barely larger than grains of beach sand, the food available within cannot have been large, but something coveted it nevertheless.
The shells span an unknown time period, are thought to have been deposited slowly, yet covering 14 meters (45 feet), suggesting a long window on Cambrian evolution. Bicknell and co-authors report the shell wall thickness grew over this time, while punched shells increase from 1 to 4 percent of all those found. They conclude that as predatory pressure increased, L. fasciculata gained tougher defenses in a sometimes effective effort to shield itself.
These sturdier walls would have kept out the earliest version of the hole-punching predator, which the team suspect was a mollusk or worm, leading to more powerful punches, capable of penetrating at least some of the toughened walls. Notably, the size of the holes does not change, suggesting their makers grew more powerful, but not larger.
Armored vehicles and drones are doing the same thing today, at a much faster rate.
The Red Queen Hypothesis holds that lifeforms are often driven to evolve by changes in their environment. However, when one species changes, others must as well to maintain their place. It gets its name from Through The Looking Glass, where the Red Queen says it is necessary to run as fast as one can just to stay in the same spot.
An evolutionary arms race is a specific form of the Red Queen’s Race where members of a species with some protection against predators survive when others do not. This leads to stronger versions of the defense becoming more widespread, so the predators have to find ways around it or starve. The prey, in turn, adapt to the new weapons predators develop.
Confirming an arms race requires having many fossils from at least one party in the race over a long period of time, and L. fasciculata was just what was needed.
L. fasciculata was far from the only animal in the early Cambrian to learn that shells offered a level of safety. The authors think the animals that developed enhanced hole-punching capacity would have applied it to other species as well, forcing a more widespread thickening. It’s also possible some shelled creatures developed different approaches to such attacks, potentially encouraging the expansion of animal forms.
“This critically important evolutionary record demonstrates, for the first time, that predation played a pivotal role in the proliferation of early animal ecosystems and shows the rapid speed at which such phenotypic modifications arose during the Cambrian explosion event,” Bicknell said.
The study is published in Current Biology.
Source Link: Predator-Prey Arms Race Revealed In 517-Million-Year-Old Fossils Is World’s Oldest