Sediments at the bottom of the Baltic Sea cut anything buried in them off from sunlight and oxygen. That’s fatal to many lifeforms, but others slip into dormancy, waiting for conditions to improve. Some scientists decided to give some of them a helping hand, exposing microorganisms from the sediments to light and air. Their work bore fruit, with one species becoming easily the most ancient sediment dwellers to recover.
ADVERTISEMENT
The capacity to shut down the functions of life until conditions are more suitable exists among animals, plants, and various microorganisms, but some are better at it than others. Phytoplankton are among the better performers. Incapable of moving themselves, if these photosynthesizing organisms lose access to the sunlight from which they draw their energy, they shut down until it returns.
This makes it common for phytoplankton to be buried in sediment while still capable of life. The lack of oxygen there can be a benefit, preventing some of the chemical reactions that would normally cause decay.
“Such deposits are like a time capsule containing valuable information about past ecosystems and the inhabiting biological communities, their population development and genetic changes,” said Dr Sarah Bolius of the Leibniz Institute for Baltic Sea Research in a statement.
Bolius was part of a team that studied the phytoplankton buried at the bottom of the Baltic Sea to learn how the cold body of water has changed over time, and what might be in store for it in the future.
The team then investigated whether they could bring any of the tiny organisms out of dormancy so that they could photosynthesize and reproduce.
“This approach bears the rather unusual name of ‘resurrection ecology’: Dormant stages that can be clearly assigned to specific periods of Baltic Sea history due to the clear stratification of the Baltic Sea sediment are to be brought back to life under favorable conditions, then they are genetically and physiologically characterized and compared with present-day phytoplankton populations,” Bolius explained.
ADVERTISEMENT
More traditional approaches allow the team to assess temperature, salinity, and oxygen levels at the times the sediments were deposited. “By combining all this information, we aim to better understand how and why Baltic Sea phytoplankton has adapted genetically and functionally to environmental changes,” Bolius said.
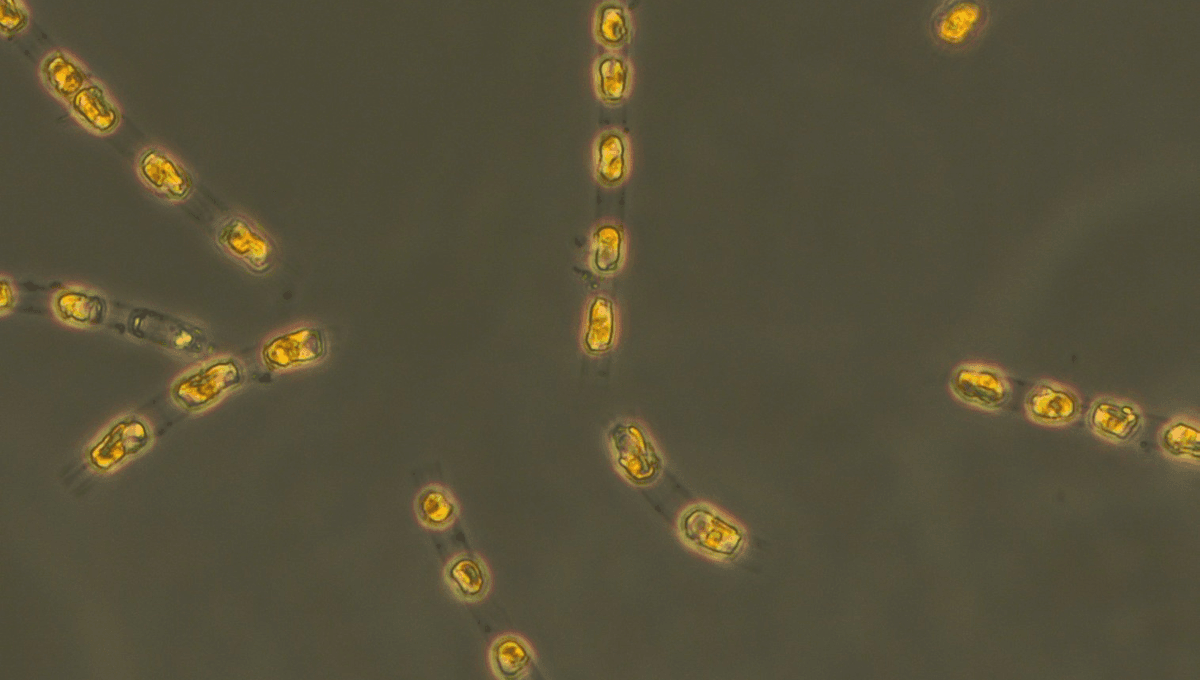
The team collected samples from a dozen layers representing the last 7,000 years and exposed the dormant algae to light and oxygen to wake them up, achieving success in nine of the 12 layers.
In the upper layers, the team revived lifeforms from very different branches of the tree of life. Lower down, the only species to consistently wake up was Skeletonema marinoi, a single-celled organism, which consequently became the focus of the paper Bolius and co-authors published.
The oldest S. marinoi in the sample was 6,871 years old, give or take 140 years. The team assessed the revived organisms’ health by measuring their rate of reproduction and oxygen production. For the earliest S. marinoi, the values were 0.31 cell divisions per day, and 184 moles of oxygen per gram of chlorophyll per hour, both similar to counterparts revived after 2 to 3 years.
ADVERTISEMENT
“It is remarkable that the resurrected algae have not only survived ‘just so,’ but apparently have not lost any of their ‘fitness,’ i. e. their biological performance ability. They grow, divide and photosynthesize like their modern descendants,” Bolius said.
The Baltic seafloor is just 4° C (39 °F), enhancing long-term preservation compared to most other shallow seas.
The productivity of the revived S. mrinoi may not have changed, but their genetics certainly have. Indeed, the team found that at each of the periods they sampled, the S. mrinoi were genetically different from those at other times.
Much older viruses have been revived from permafrost, but whether these count as life is debated. The previous record for a species revived from sediments held by a date palm, was less than a third as old. The aquatic record is even shorter, at 700 years.
ADVERTISEMENT
Photosynthesizing plankton don’t represent an obvious threat to modern ecosystems in the way viruses – or dinosaurs – do. Nevertheless, the work does raise questions about just when it is safe to wake the almost dead.
The study is published in ISME Journal.
Source Link: Prehistoric Algae Dormant For 7,000 Years Set Record For Longest Resurrection