Psychedelic satellite imagery shows the world’s largest piedmont glacier, located on the southeast edge of Alaska, in all its colossal glory. This vast natural monument may look still and steady, but the images highlight how the ice giant is in a state of flux.
As explained by NASA’s Earth Observatory, the image shows Alaska’s Malaspina Glacier primarily located in Wrangell-St. Elias National Park on the southeast coast of Alaska.
It’s known as Sít’ Tlein in the Tlingit language spoken by the Indigenous people in the area, which means “big glacier” – and it is, indeed, very big. The glacier takes up an area of 4,350 square kilometers (1,680 square miles), making it the largest piedmont glacier on the planet.
A piedmont glacier simply describes a glacier where the ice has spread out into a flat, lowland area, as opposed to a valley glacier that flows down the mountainside.
The false-color image (yep, unfortunately, it’s not that color to the naked eye) was taken by the OLI-2 (Operational Land Imager-2) onboard the Landsat 9 satellite on October 27, 2023.
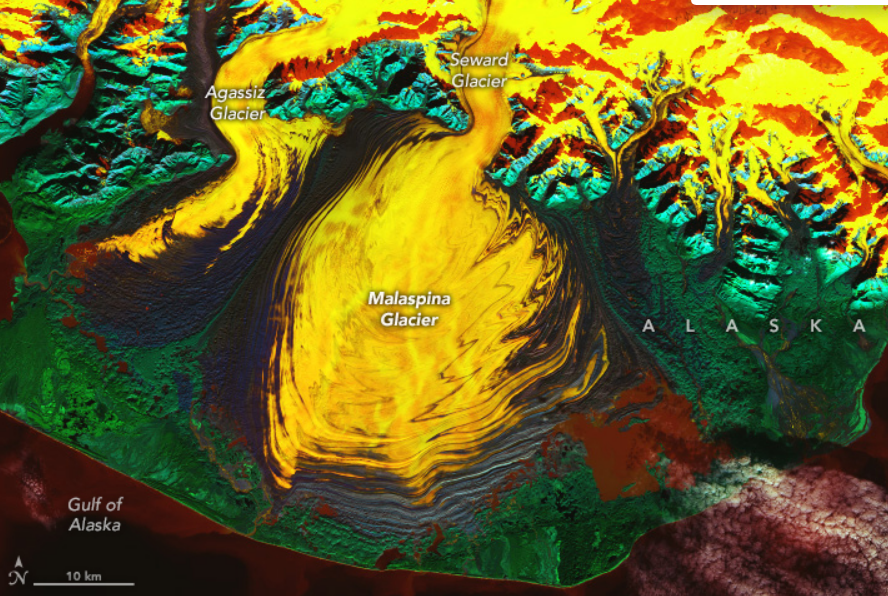
A labeled version of the image above.
Image credit: Wanmei Liang/Landsat 9/NASA Earth Observatory
To our human eyes, the Malaspina Glacier of Alaska would appear icy blue and white, with intermittent specks of grey rock. However, we’re able to gain a deeper perspective thanks to the OLI-2, which captures the scene using infrared radiation. This shows the ice as yellow, red, and orange colors, the water as red, the rock as blue, and the vegetation as green. The dark blueish-purple lines on the ice are moraines, areas where rocky soil has been scooped up by the glacier and dumped on its edges.
The ripples that you can see in the main body of the Malaspina Glacier show how ice is periodically edging forward in a multi-year process, creating moraines that fold and compress with the surge.
You’ll also notice a thin strip of land between the large glacier and the Gulf of Alaska, which eventually leads to the Pacific Ocean. NASA explains that a watery lagoon system has been forming along this “barrier” in recent decades, which you can see in the rusty red-colored pools.
Some of this water is very salty, indicating that the relatively warm ocean water is making contact with the ice. If this continues, it could be enough to calve a significant chunk of ice from the main body, accelerating the glacier’s retreat.
Source Link: Psychedelic Colors Reveal Hidden Beauty Of Alaska's Giant Glacier