Fancy a trip to see the stars? Don’t worry if you haven’t got a rocket – to see the stars we’re talking about, you only need a passport, some flip-flops, and a Japanese phrasebook.
Our destination is right down in the south of Japan, on the three islands of Iriomote, Hatoma, and Taketomi. Scoop up some sand on their beaches, take a closer look at it, and you’ll see not only the usual fragments of shell and rock, but tiny cream-colored stars.
At a glance, it might look like someone took a stroll on the shore throwing about a bag of pastina, or perhaps a baby sea star convention, but these little stars are in fact the remnants of a species called Baclogypsina sphaerulata.
First described in 1860 under a different name, they’re a member of an ancient group of protozoans – widespread, single-celled organisms that nibble on organic matter – called Foraminifera. B. sphaerulata is only one of an estimated 4,000 living forams, although the group is thought to have been around since the early Cambrian period, around 540 million years ago.
As organisms in this group drift about in the sea, they collect calcium carbonate and use it to build shells or “tests” with a whole host of different shapes, from the rather more blob-like to intricate spirals and, of course, stars.
When forams die, these shells remain and settle on the seafloor, and in the case of B. sphaerulata, eventually wash up on Okinawan beaches.
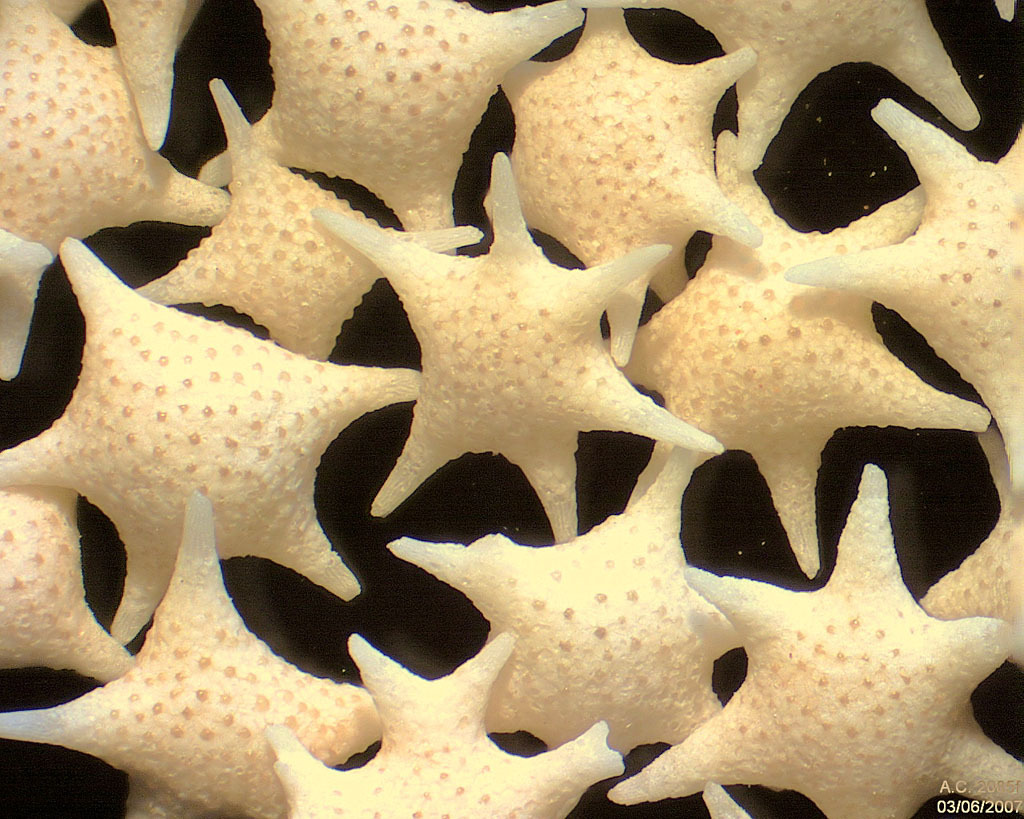
Upon closer inspection, the stars are also covered in dots.
Japanese folklore, however, tells a different story. According to legend, the star-shaped sands are the result of the Southern Cross and the North Star getting jiggy with it and making a bunch of little star babies.
Their offspring were said to live in the sea off the coast of the Okinawan islands, but were killed by a giant sea serpent, with only their skeletons remaining. With time, their remains ended up on the beaches.
The idea of stomping along a baby star cemetery might take away some of the excitement of finding them in the sand, though perhaps it’ll put people off taking them away from the beach (which is very much not allowed).
But if it’s any consolation, these cosmic offspring leave behind a very helpful legacy. Foraminifera can be used by scientists to figure out what the Earth was like millions of years ago, giving clues about the age of rocks and ancient climates.
Thanks, little stars.
Source Link: Rare Star-Shaped Sand Can Be Found On These Japanese Beaches