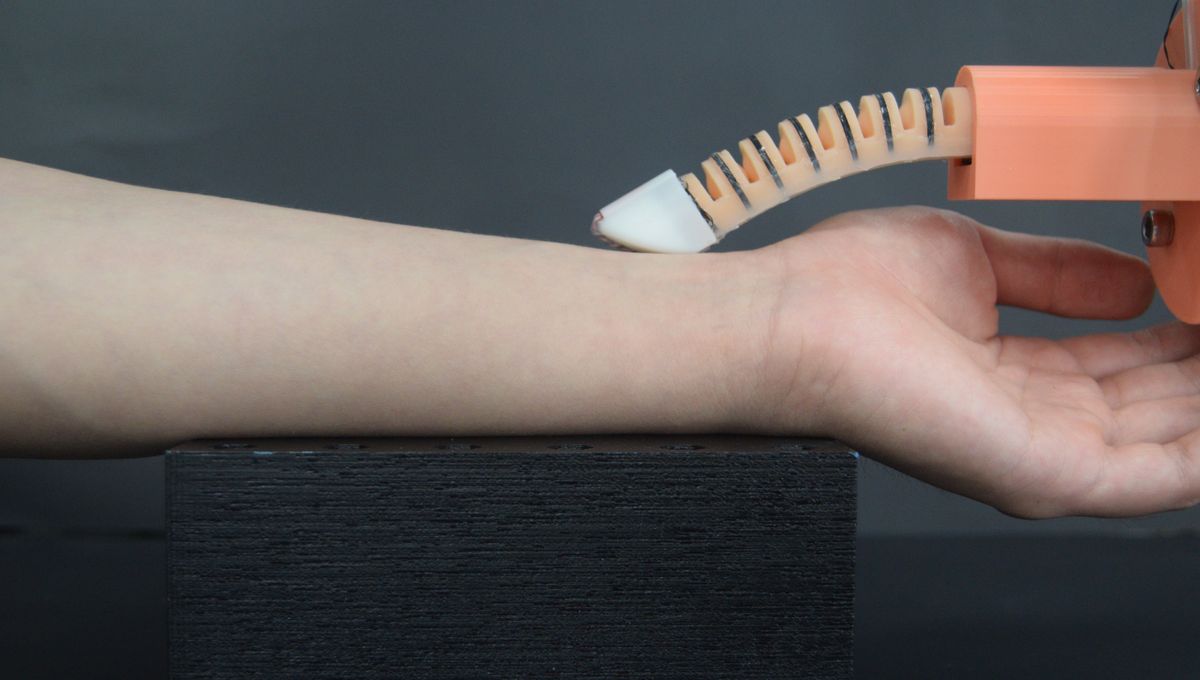
A new ultrasensitive, soft robotic “finger” has been developed by international researchers that can conduct medical tasks, like checking for a pulse and examining patients for lumps. Although robotic hands have been developed before, this new robo-finger has the ability to mimic both the feel and function of human touch.
The hope is that this technology may make it easier for doctors to detect diseases like breast cancer at an earlier stage. This could lead to earlier treatment options but also make otherwise intimidating and invasive physical examinations less uncomfortable for patients.
Most of us probably take our fingers for granted, but these flexible digits are invaluable in our everyday lives. They help us grasp and manipulate objects but also allow us to “feel” the world around us, touch other people and even communicate with one another.
Within the medical context, the sensitivity of human hands, empowered by fine motor control that uses feedback and learning, can be useful for detecting and diagnosing various diseases and conditions. Palpation, a method of feeling with the fingers and hands during a physical examination, is commonly used to identify and screen for abnormalities in a patient’s body. By gently pressing or kneading sensitive areas, doctors can pick up on potential risks, such as cancers, abdominal aneurysms, thyroid nodules and so on.
The problem, however, is that not all doctors are trained sufficiently to carry out these procedures, which can lead to some diseases being missed. At the same time, many patients are not willing to be subjected to a physician’s touch, especially if the doctor is of the opposite sex.
This is where robotic alternatives may be useful, but there are limitations with existing models. For instance, some robo-fingers have been criticized for being too rigid. Some have worried that such hard fingers (it’s difficult to write about these things without it sounding like an innuendo) are not capable of conducting the delicate tasks doctors perform and could even rupture lumps during examinations.
Alternatively, some lightweight robo-fingers have been developed which, while cheaper, can mimic the movements of human hands. However, they’re not overly sensitive and have so far not been able to detect the complex properties of the objects they touch, unlike real fingers.
“Despite the remarkable progress in the last decade, most soft fingers presented in the literature still have substantial gaps compared to human hands,” Hongbo Wang, a sensing technologies researcher at the University of Science and Technology of China, and colleagues explain in their new study.
Essentially, they researchers say, existing robotic fingers can’t get a grip on “real-world scenarios”. But they may have developed a new soft finger that is sensitive enough for these procedures.
“By further development to improve its efficiency, we also believe that a dexterous hand made of such fingers can act as a ‘Robodoctor’ in a future hospital, like a physician,” Wang said in a statement. “Combined with machine learning, automatic robotic examination and diagnosis can be achieved, particularly beneficial for these undeveloped areas where there is a serious shortage in health workers.”
To overcome the restrictions of other robo-fingers, Wang and colleagues developed a device that holds conductive fiber coils with two parts. Firstly, there’s a coil wound on each air chamber of the finger’s actuator (the part that allows it to bend and move), and a twisted liquid metal fiber mounted on the fingertip.
The finger’s electrical flow can be measured, allowing it to bend in real time as it touches objects. The team are then able to monitor the force it applies as it does so. This basically allows the finger to perceive an object’s properties in the same way that a human finger does.
To test its sensitivity, the team started by brushing a feather against its fingertip.
“The magnified view clearly shows the resistance change, indicating its high sensitivity in force sensing,” they explain in their study.
Following this, the team tapped and pushed the fingertip with a glass rod and then bent the finger multiple times to check that the device correctly perceived the type and quantity of force it received.
Then things got really interesting. To assess its ability to perform medical procedures, the team mounted the finger on a robotic arm and watched as it identified three lumps embedded in a large silicone sheet. The robo-finger manipulated the area in a similar way to a doctor. While the finger was mounted on an arm, it also correctly located an artery on a patient’s wrist and measured their pulse.
This ability to move and apply gentle pressure also allowed the artificial finger to type on a keyboard, spelling out the word “hello”.
“We demonstrated that the [robo-finger] can press and ‘feel’ the stiffness of an object and perform safe and accurate robotic palpation similar to that performed by a doctor,” the team explain in their paper.
“These findings highlight the potential of a ‘robodoctor’ to perform physical examinations in the future.”
“We hope to develop an intelligent, dexterous hand, together with a sensorized artificial muscle-driven robotic arm, to mimic the unparalleled functions and fine manipulations of the human hands,” Wang added.
The study is published in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science.
Source Link: “Robodoctor” Finger Can Check Your Pulse And Feel For Lumps – No Human Needed