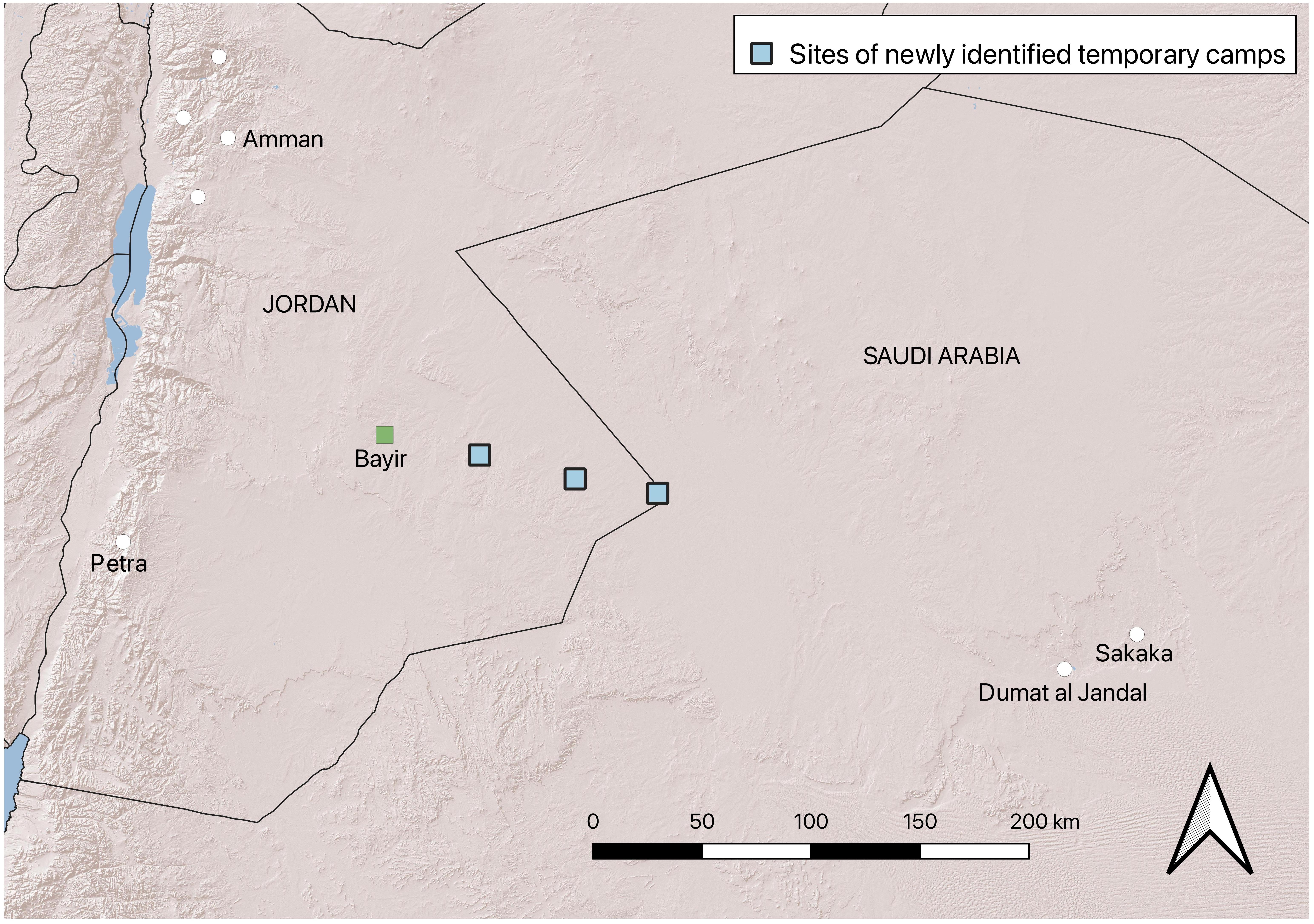
Researchers have spotted three Roman military camps in Jordan that may provide evidence for a previously unknown campaign to conquer a desert kingdom in the second century CE. Identified using Google Earth, the temporary bases rewrite history and suggest that the Roman army marched across Arabia to annex the Nabataean Kingdom, which had its capital at the world-famous city of Petra.
“We are almost certain they were built by the Roman army, given the typical playing card shape of the enclosures with opposing entrances along each side,” explained study author Dr Michael Fradley in a statement. “The level of preservation of the camps is really remarkable, particularly as they may have only been used for a matter of days or weeks.”
The hastily constructed bases were probably built by soldiers as they progressed across the desert on their way to conquer far-off lands. According to the researchers, “the distance between the camps across barren terrain is arguably too far to be crossed by infantry in a day and supports the alternative that the camps were for mounted troops – perhaps with camels.”
Judging by the dimensions of the three camps, the authors say that the westernmost base probably held two cavalry cohorts, while the two smaller structures to the east likely held one cohort each. Noting the route taken by the Roman army, the study authors say that the soldiers were probably headed to the Jawf region in modern-day Saudi Arabia.
Map showing the location of the bases and revealing the route taken by the Roman army. Image credit: EAMENA
“They went along a peripheral caravan route linking Bayir and Dûmat al-Jandal. This suggests a strategy to bypass the more used route down the Wadi Sirhan, adding an element of surprise to the attack,” says Fradley. “It is amazing that we can see this moment in time played out at a landscape scale.”
Attempting to link the camps to known Roman military operations in the region, the authors say the structures are unlikely to have been used in the campaign against the Nabataean kingdom of 62 BCE, as this crusade focused on Petra, which lies far to the west. They therefore conclude that the camps were probably used in a previously undocumented campaign to annex the kingdom, under the command of legendary Emperor Trajan in 106 CE.
This is significant, as written sources from the time describe the handover of the Nabataean kingdom as a peaceful transfer of power. The existence of Roman military camps, however, suggests that the process may have been considerably more violent.
“These marching camps – if we are correct in dating them to the early second century – suggest the Roman annexation of the Nabataean Kingdom following the death of the last king, Rabbel II Soter in AD 106, was not an entirely straightforward affair, and that Rome moved quickly to secure the kingdom,” says study author Professor Andrew Wilson.
The study is published in the journal Antiquity.
Source Link: Roman Military Camps In Arabia Spotted Using Google Earth, Suggesting Desert Conquest