Fear is very useful for survival – but so is being able to control it. It’s wise to be scared of the unfamiliar, especially when it resembles a known threat. However, once you realize that thing lying by the door is actually just a draught excluder and not a reticulated python, you can safely set that fear aside. Scientists have just discovered how the brain helps us do this, by uncovering for the first time a brain circuit in mice that can override instinctual fear.
ADVERTISEMENT GO AD FREE
“We wanted to understand whether a specific brain area, the ventrolateral geniculate nucleus (vLGN), could play a role in learning to overcome fear responses,” Professor Sonja Hofer and Dr Sara Mederos, lead authors of the new study, told IFLScience. “Previous findings from our lab showed that the vLGN can strongly modulate instinctive fear responses and suggested that its activity tracks prior knowledge of threats. This led us to investigate whether the vLGN is involved in the learned suppression of fear and how this learning occurs.”
The team, from the Sainsbury Wellcome Centre at University College London, designed an experiment to test escape behavior in mice.
It is rare to achieve such a deep understanding of a brain function.
Professor Sonja Hofer and Dr Sara Mederos
When faced with a threatening visual stimulus, mice will instinctively flee to find shelter. In this experiment, the mice were presented with expanding black dots projected towards them, representing a looming threat – but, crucially, they weren’t able to escape. Over time, they learned that the stimulus posed no real threat and stopped trying to flee.
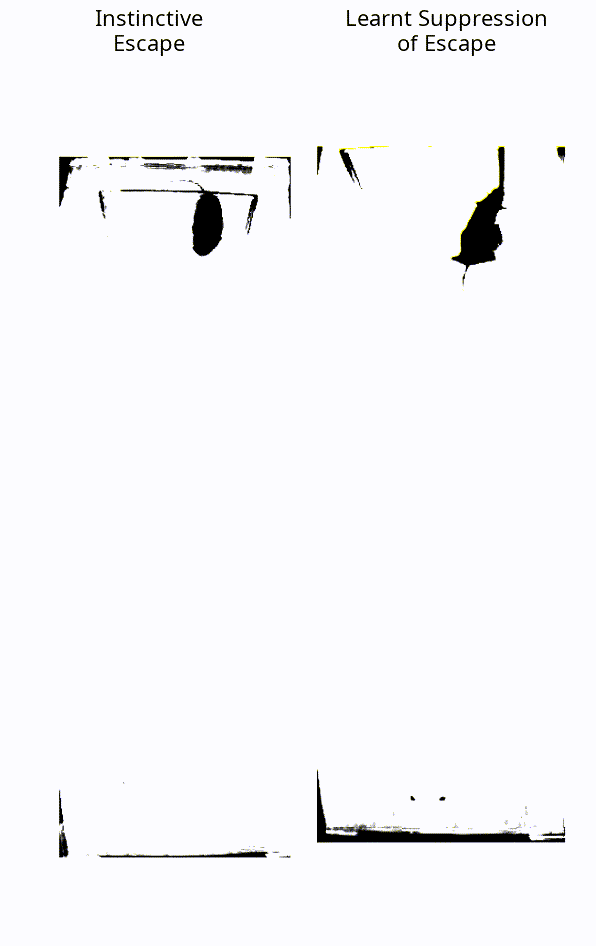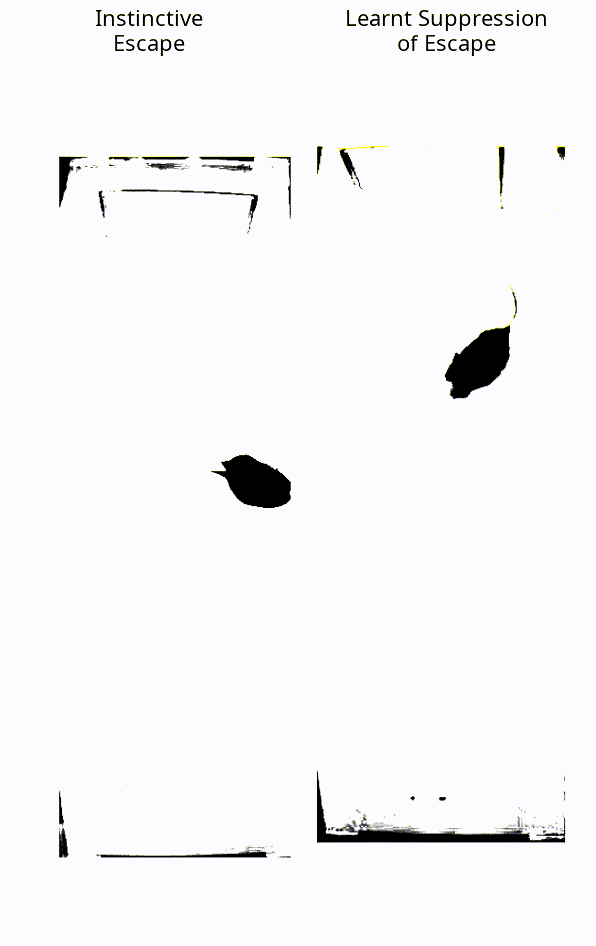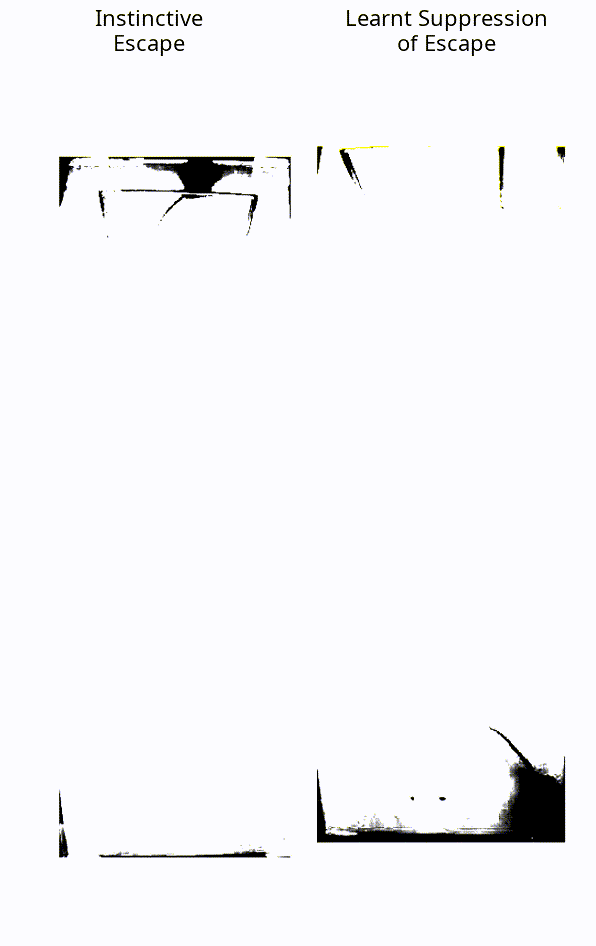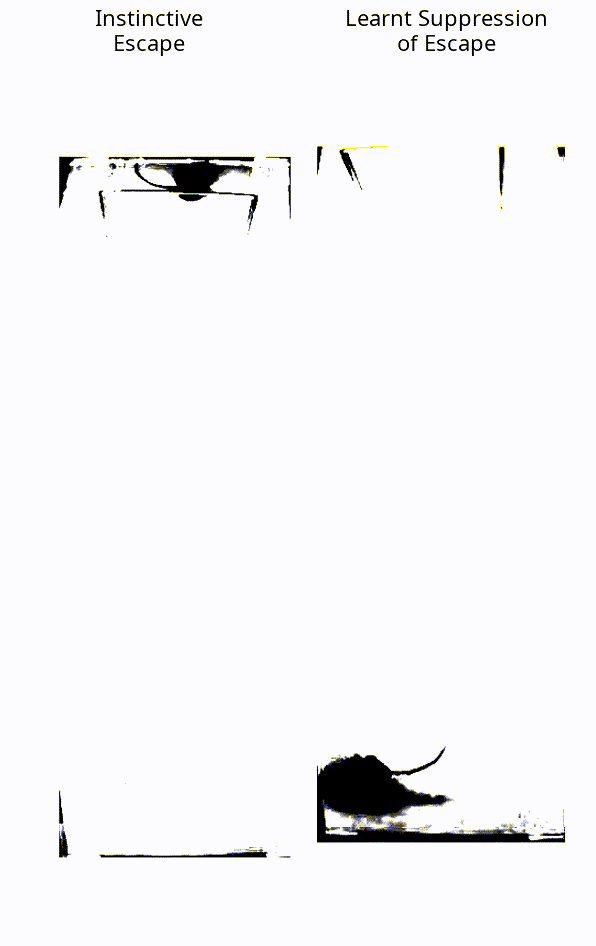
The instinctive reaction of a mouse, vs a mouse that has learned to suppress this fear.
Image courtesy of the Sainsbury Wellcome Centre
Using a variety of different methods, including optogenetics to silence specific brain areas and electrophysiological recordings of the activity inside cells, the team were able to determine that a group of brain regions in the visual cortex called the posterolateral higher visual areas (plHVA) are vital for the initial learning phase. However, once the mouse has learned to suppress its instinctive fear of the stimulus, this memory appears to be stored in the vLGN.
“One very exciting thing about the study is that the combination of many different methodologies enabled us to describe the detailed mechanisms of how the brain learns to overcome fear, from brain areas and neural pathways all the way down to the necessary neurons, synaptic connections and molecular plasticity mechanisms,” Hofer and Mederos said. “It is rare to achieve such a deep understanding of a brain function.”
ADVERTISEMENT GO AD FREE
“There are also two key findings from our study that we found particularly exciting. First, we discovered that higher visual areas in the cerebral cortex play a crucial role in instructing learning during the experience of a threat, enabling the suppression of fear, but this brain region is not necessary anymore once learning has occurred. This led to our second key finding: that this form of learning and the associated memory relies on subcortical circuits. This is surprising, as plasticity has been extensively studied in the neocortex and hippocampus but not in subcortical circuits.”
While the study focused on mice, the team believe there’s a good chance that something similar is going on in the human brain too, as the same brain pathway exists in us.
“There is therefore a chance that our findings could have implications for the treatment of anxiety disorders and PTSD, where fear responses become exaggerated and maladaptive,” Hofer and Mederos said. These disorders are estimated to affect over 300 million people worldwide, they told us.
ADVERTISEMENT GO AD FREE
“By identifying key brain areas involved in fear suppression, we highlight potential targets for therapeutic interventions, such as deep brain stimulation (DBS), focused ultrasound, or pharmacological approaches targeting endocannabinoid receptors.”
Fundamental research is about expanding what we know, which is essential for any real progress in science and medicine.
Professor Sonja Hofer and Dr Sara Mederos
It will be exciting to see what potential clinical applications come out of these findings; but for Hofer and Mederos, the importance of this study also lies in the very fact that its aim was not necessarily to identify a specific treatment for a specific condition, but simply to teach us more about how the brain works.
“Even if not immediately linked to clinical applications, uncovering the core mechanisms that drive behavior is essential for progress in science and medicine. Many of the breakthroughs that have shaped modern treatments came from basic research that initially had no clear practical goal,” they told us.
ADVERTISEMENT GO AD FREE
“This basic understanding is what eventually helps us recognize when these processes aren’t working properly, leading to new ways of thinking about brain disorders and how to treat them. Fundamental research is about expanding what we know, which is essential for any real progress in science and medicine.”
The study is published in the journal Science.
Source Link: Scary Or Safe? New Brain Pathway Quashes The Instinct To Flee From Danger