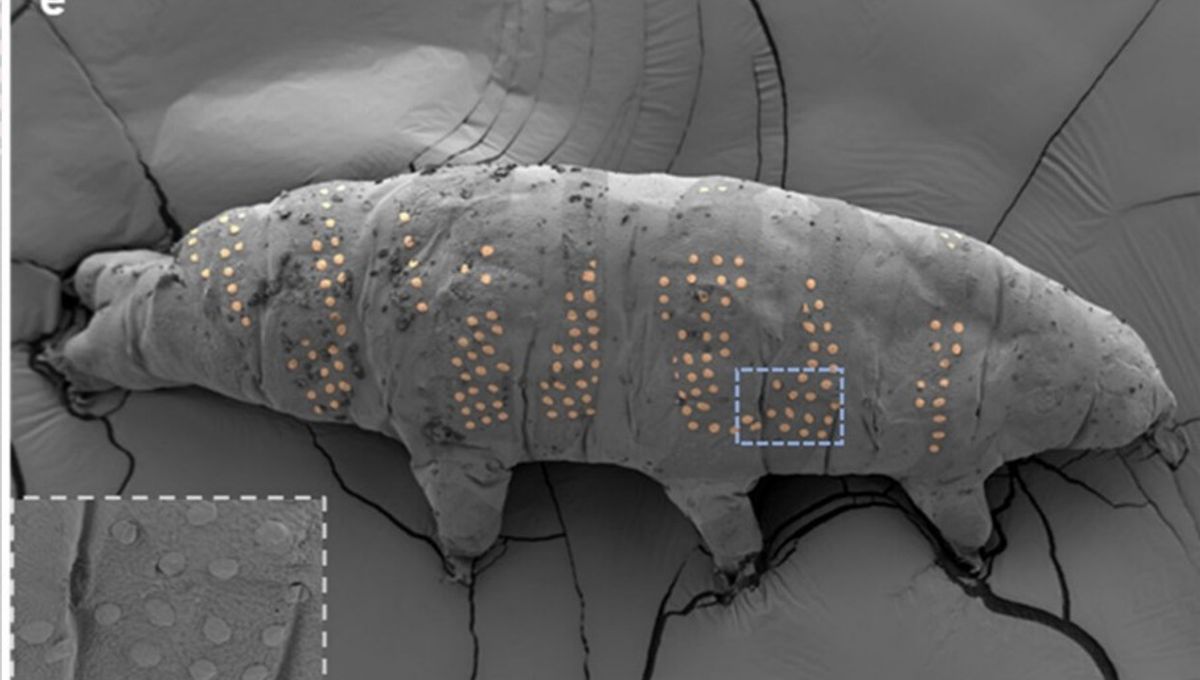
At half a millimeter long (0.02 inches) tardigrades are so small they’re hard to see without a microscope. However, these adorable eight-legged creatures still have room for tattoos on their bodies, scientists have demonstrated, and the work could lead to medical applications, much as it may sound like the product of bored minds.
Tardigrades, also known as water bears for their ursine appearance, have achieved a cult following in recent years in recognition of their exceptional survival capacity. When bad times come, tardigrades can enter a cryobiotic state, called a tun, which allows them to survive extremes of heat and cold, immense pressures and vacuums, and high doses of radiation. Makes you want to be a water bear.
Tardigrades’ survival capacity has seen them sent into space, and now scientists have found another way to use them to advance research. A team at Westlake University have placed tiny tattoos on tardigrades to test the capacity to build biocompatible devices on the tiniest scales.
The team deprived the water bears of water until they were dehydrated, causing them to become tuns. Individual tardigrade tuns were then placed on carbon composite paper and cooled to -143°C (-226°F) and covered the with organic compound anisole.
An electron beam was then focused on the tardigrades. The anisole protected them from damage, as long as the beam was 2 kiloelectronvolts or less, but formed a sticky compound that attached itself to the tardigrades’ equivalent of skin where the beam had touched. So long as the anisole layer was less than 200 nanometers thick, it protected the tardigrade from radiation damage without causing charge accumulation.
When the tardigrades were returned to room temperature the remaining anisole escaped as gas. Providing the tardigrades with water saw them return to life, none the worse for wear, but carrying sick new tattoos, which retained their original shape despite the stretching as tardigrades revived. Rinsing and drying did not remove the tattoos.
Electron beams can be focused so tightly (making lines just 72 nanometers wide) that even with the tiny space to work with, the tardigrades could sport complex shapes – even the university’s logo got an outing.
Although tardigrades go through cycles of dehydration in the wild quite frequently, around 60 percent died during the process, but the team hope to get that number down with adjustments. Those who survived were described as behaving normally for water bear, aside – one presumes – from proudly showing off their ink to others.
The authors note that nanoengineering has become so precise we can engrave the Encyclopedia Britannica on the head of a pin, but until now the techniques used have been incompatible with microscopic life.
The purpose of the work is to serve as a stepping-stone to combine biosensors with living organisms that could providing warnings of cancer cells or infections. Further down the track, it could lead to tiny cyborgs capable of performing operations such as eliminating these dangers.
“Through this technology, we’re not just creating micro-tattoos on tardigrades – we’re extending this capability to various living organisms, including bacteria,” said Dr Ding Zhao in a statement.
The study is published in the journal Nanoletters.
Source Link: Scientists Are Tattooing Tardigrades Because Why Not