“We found that sharks follow what’s known as the ‘two-thirds scaling law’ almost perfectly,” explained Joel Gayford, a PhD candidate at James Cook University (JCU) in Australia and lead author on a new study confirming a centuries-old hypothesis about how animals’ volumes scale with their surface area.
“Surface area-to-volume ratios are key inputs in equations used to model how animals respond to climate change, like how fast they regulate their body temperatures or how efficiently they use oxygen,” he said in a statement.
“Confirming it in full-sized animals, not just cells, is a big deal.”
From math to biology
Mathematically, the two-thirds law is a no-brainer. Consider a bog-standard cube: if you increase the length of one side by, say, x times, then the surface area will increase by x2 times and the volume by x3.
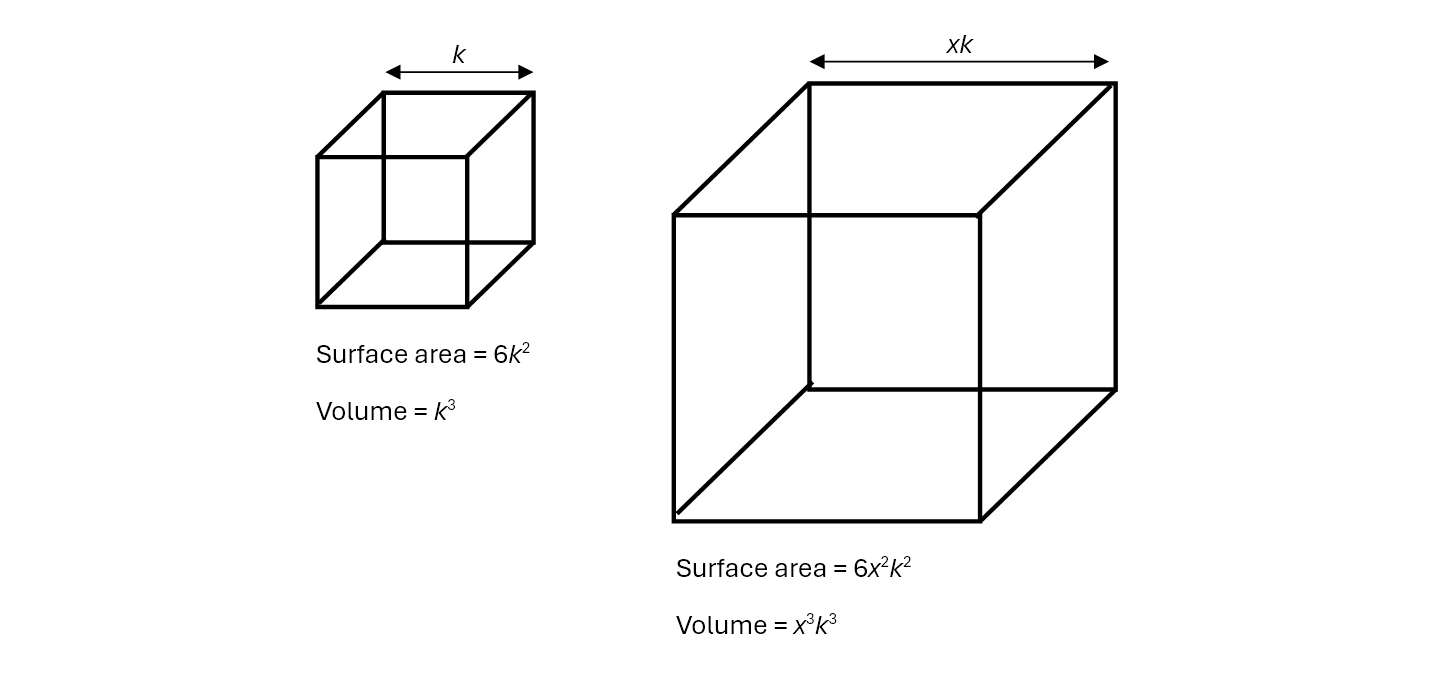
Cubes and sharks both follow the law.
Image credit: (C) IFLScience
The relationship between just the surface area and volume, therefore, is going to be x2/x3 – equivalently written as x2/3. Hence: two-thirds law.
But the natural world rarely works as nicely as pure geometry. There are plenty of examples where observation has seemed to contradict expectation – think whales’ cancer incidences, for instance, or dolphins’ seemingly paradoxical speed through the water. Would the two-thirds law hold up in real life?
The handful of studies that already existed seemed to hint at “yes” – but with a few caveats. Many were based on observations in single cells – not really applicable more generally. Others did look at whole organisms, but only a small selection, or using theoretical rather than directly observed measurements.
Given all those issues, sharks were kind of an ideal group of animals to look at. The 54 species included in the study “spann[ed] a 16-fold increase in body length and an approximately 19,000-fold increase in body mass,” the team points out in their paper. “They exhibit substantial variation in body size, morphology, physiology and ecological lifestyle.”
“Consequently, we might expect to observe variation in surface area to volume […] ratios at any given body size,” they write.
A vindication of a hypothesis
In other words: if any single group of animals is going to show deviation from the two-thirds scaling law, sharks are a pretty good candidate. So, to see whether that was the case, the team modeled the bodies of their chosen shark species using high-resolution 3D images and CT scans of specimens in museums, and compared their surface areas and volumes using a technique known as phylogenetic regression.
First proposed in 1989, phylogenetic regression is a statistical technique specifically designed to compare information across multiple related species. In essence, it allowed the team to treat their chosen sharks as genuinely separate species, rather than a fluid group with an influential shared ancestry. It made the results of their analysis more concrete; more applicable – which is important, especially since it was so definitive.
“The observed scaling coefficient [was] 0.64 for surface area to volume ratios,” the paper reports – a figure which “deviates only 3 percent from the expected 0.66 coefficient.”
“Only the reef-associated ecotype exhibited (relatively minor) statistically significant deviations from the isometric predictions of the 2/3 law,” it notes, “with a scaling coefficient of 0.60.”

Perfect, just like geometry.
JCU
That’s a really, really good vindication of the two-thirds scaling law – and it suggests something far more significant than a simple geometry lesson.
“It’s remarkable,” said Jodie Rummer, a professor in JCU’s department of Marine Biology and co-author on the study. “This suggests sharks have evolved to stick to this ratio, possibly because deviating from it is too costly or constrained by early development.”
Why this matters
Mathematically, the two-thirds law makes sense. But why should it hold up so well in biology?
“This law helps explain how animals exchange heat, energy, and oxygen with their environment,” Gayford said. “Now, we can use those equations with much greater confidence in sharks and other large animals.”
Now, sharks are known for being pretty conservative with their evolution – hell, they’ve barely changed since the Carboniferous, some 359 million years ago, let alone pulling off the rapid-scale diversification of, say, Swedish sea snails. But the list of things that should be constrained by that doesn’t include surface area – that’s why sharks come in such a range of shapes, even if they don’t exhibit, say, vastly different breathing mechanisms.
So the fact that they all seem to follow this two-thirds law pretty closely tells us something important. Deviating from the rule seems to be a difficult thing to do – potentially revealing a clue about how sharks develop individually: “Changing the way tissue is distributed throughout the body might require major changes during early embryonic development,” Gayford explained, “and that’s expensive, energetically speaking.”
More than that, however, confirming this adherence to the two-thirds law may have important real-world implications. Understanding how species’ bodies cope with heat and nutrient uptake can provide a new lens through which to view shark behavior and habitat exploitation, the paper points out; it can also influence how we approach shark conservation in the age of increasingly hot and acidic oceans. Even the simple fact that this method has borne fruit is exciting: it means that the techniques may be applicable to other species and clades, potentially allowing us to confirm the two-thirds rule across the animal kingdom.
“This ratio is fundamental,” Rummer explained. “It underpins how animals breathe, regulate temperature, and process waste.”
“Now, for the first time, we’ve shown it holds true in animals as complex and diverse as sharks.”
Source Link: Sharks Follow A Fundamental Law Of Geometry, And That's A Really Big Deal