Just a few years ago, archeologists in China unearthed a 300,000-year-old hominin jawbone with a curious shape not quite like modern humans, but unlike most ancient hominins seen before. Somewhat sensationally, they speculate this strange individual may be an undescribed “sister lineage” in the human family tree.
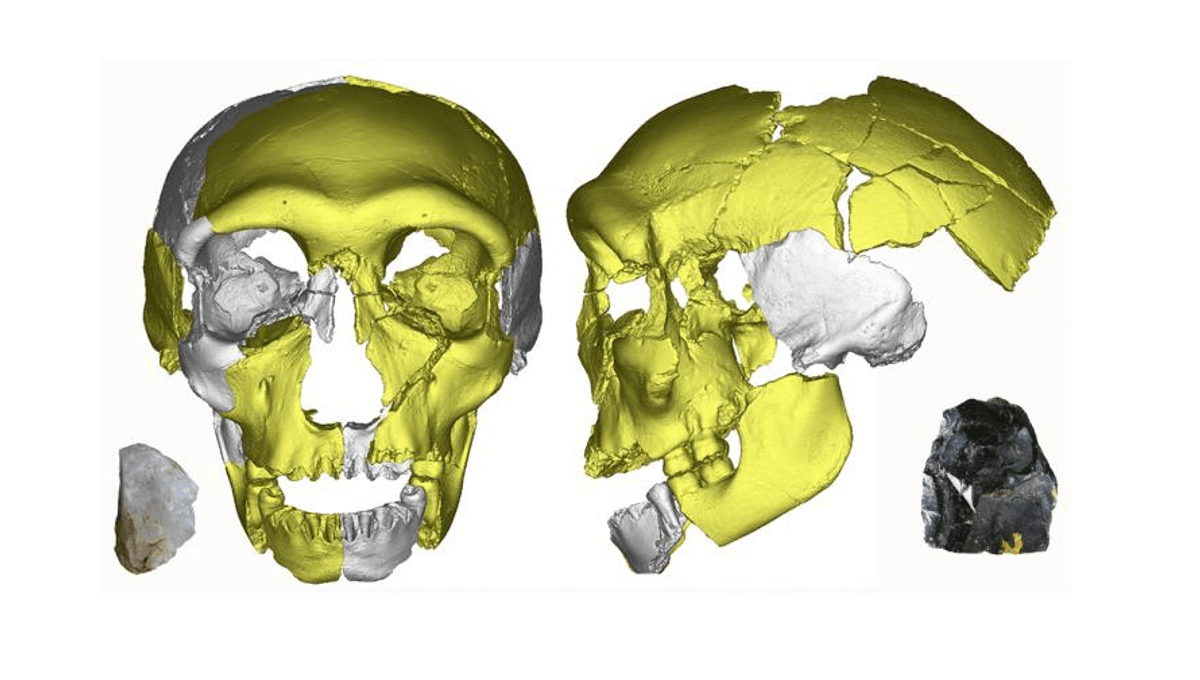
The skeletal remains were discovered at Hualongdong cave in Anhui province of eastern China. Among the 16 hominin fossils found here, one in particular caught the eye of the researchers: Hualongdong 6, aka HLD6. The remains of this individual consisted of a nearly complete jawbone, as well as a partial skull and a few leg bones.
Describing the individual in a 2019 paper, the Chinese researchers note that the skull bears many similarities to modern humans, but it doesn’t appear to have a true chin – a key feature of Homo sapiens – which suggests it looked more akin to older archaic hominin relatives. The skull also dates to 300,000 years ago, before the emergence of modern humans in East Asia.
In sum, HLD6 has a “mosaic” of traits that are typical of both H. sapiens and ancient hominins, making it a very unusual individual that potentially foreshadows later modern human forms.
“Even though the predominantly modern human-like morphological features in the […] facial bones suggest that [the specimen] bears similarities to modern humans, the mosaic morphological pattern of the […] mandible revealed in the present study supports the complicated morphological diversity that existed in the late Middle Pleistocene hominin record in East Asia,” the researchers wrote in 2019.
Can we consider them a new species of human relative, though?
Other skulls with “mosaic morphologies” found in China have previously been attributed to Denisovans, a mysterious “sister species” of humans that ranged from Siberia to Southeast Asia, in some parts overlapping with H. sapiens and Neanderthals.
Given HDL6’s unique blend of features, however, the researchers write that they may belong to “a third lineage that is neither H. erectus nor Denisovan but one that is phylogenetically close to H. sapiens.”
“In general terms, the HLD hominin fossils described here and elsewhere could potentially belong to the ‘nonerectus’ Asian Middle Pleistocene group, given the lack of distinctive classic H. erectus traits, but exhibit more derived, modern human-like and Neanderthal-like features,” the study authors write.
“This possibility accords with a recently proposed scenario that envisages the origin of the last common ancestor for both H. sapiens and Neanderthals in Southwest Asia and a later expansion into all continents, including Asia,” they added.
For now, there’s unfortunately not enough evidence to make a concrete conclusion. To place the Hualongdong hominin in the human family tree, archeologists will need further research and, better still, the discovery of more similar fossils.
Source Link: Skull Found In China May Be A New "Third Lineage" Of Human