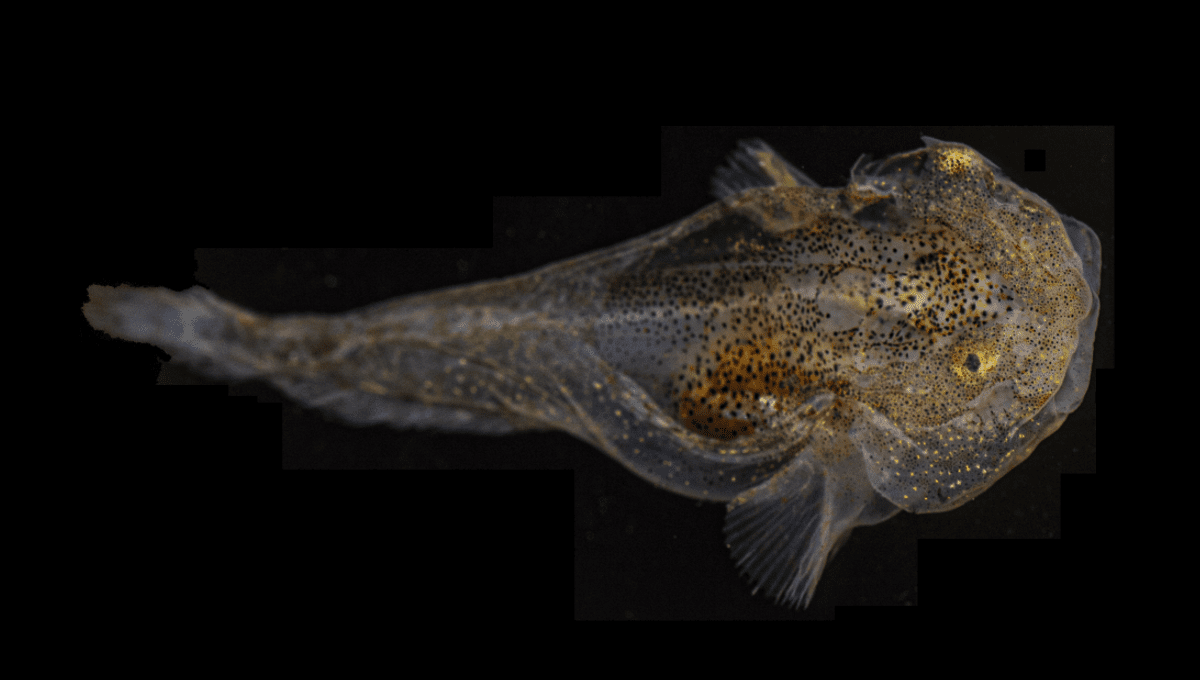
A snailfish positively brimming with antifreeze proteins has stunned scientists studying these animals in the sub-zero waters of their home turf off Greenland. Liparis gibbus, as our frozen-water-friendly fish is known, was first noticed for its flashy bioluminescence, but later revealed it was packing record levels of antifreeze proteins in its tiny body, too.
“Similar to how antifreeze in your car keeps the water in your radiator from freezing in cold temperatures, some animals have evolved amazing machinery that prevent them from freezing, such as antifreeze proteins, which prevent ice crystals from forming,” said David Gruber, a research associate at the American Museum of Natural History and a distinguished biology professor at the City University of New York’s Baruch College, in a statement.
Ice crystals can have a catastrophic effect on the cells of many animals, including humans. That’s why getting yourself cryogenically frozen is less likely to result in you returning to your former glory in the year 3000 than it is to see you squashed against the freezer unit door like a forgotten fish finger (don’t believe us? Check out the Deep Dive into human popsicles in our first ever issue of CURIOUS, IFLScience’s free e-magazine).
While humans and other mammals perish in the cold as a result, some impressive species have overcome the freeze by producing proteins that keep things fluid. And it seems none are packing so many as this little snailfish.
As the only polar fish reported to biofluoresce (they’ve been spotted glowing in green and red), researchers decided to take a closer look at the snailfish and noticed it had two different types of gene families that encoded for antifreeze. In fact, they had the highest expression for antifreeze proteins of any animal ever studied for the trait.
“We already knew that this tiny snailfish, which lives in extremely cold waters, produced antifreeze proteins,” continued Gruber, “but we didn’t realize just how chock-full of those proteins it is – and the amount of effort it was putting into making these proteins.”
The revelation comes from a team of scientists based at the American Museum of Natural History and the City University of New York, who published their findings in the journal Evolutionary Bioinformatics.
As well as being a big day for a little snailfish, the news comes as a sobering warning as to how many creatures will be affected by the oceans’ warming, as once frosty environments become intolerably balmy.
“Since the mid-20th century, temperatures have increased twice as fast in the Arctic as in mid-latitudes and some studies predict that if Arctic Sea ice decline continues at this current rate, in the summer the Arctic Ocean will be mostly ice-free within the next three decades,” said co-author John Sparks, a curator in the Museum’s Department of Ichthyology.
“Arctic seas do not support a high diversity of fish species, and our study hypothesizes that with increasingly warming oceanic temperatures, ice-dwelling specialists such as this snailfish may encounter increased competition by more temperate species that were previously unable to survive at these higher northern latitudes.”
Source Link: Snailfish "Chock-Full" Of Antifreeze Can Stay Limber In Sub-Zero Waters