Ever went caving as a child and were told all about the wonderful structures that form within these epic caverns, only to promptly forget everything the second you saw the sign for the gift shop? Well, wonder no more, as we break down the differences between those pesky cave structures.
Stalactites and stalagmites
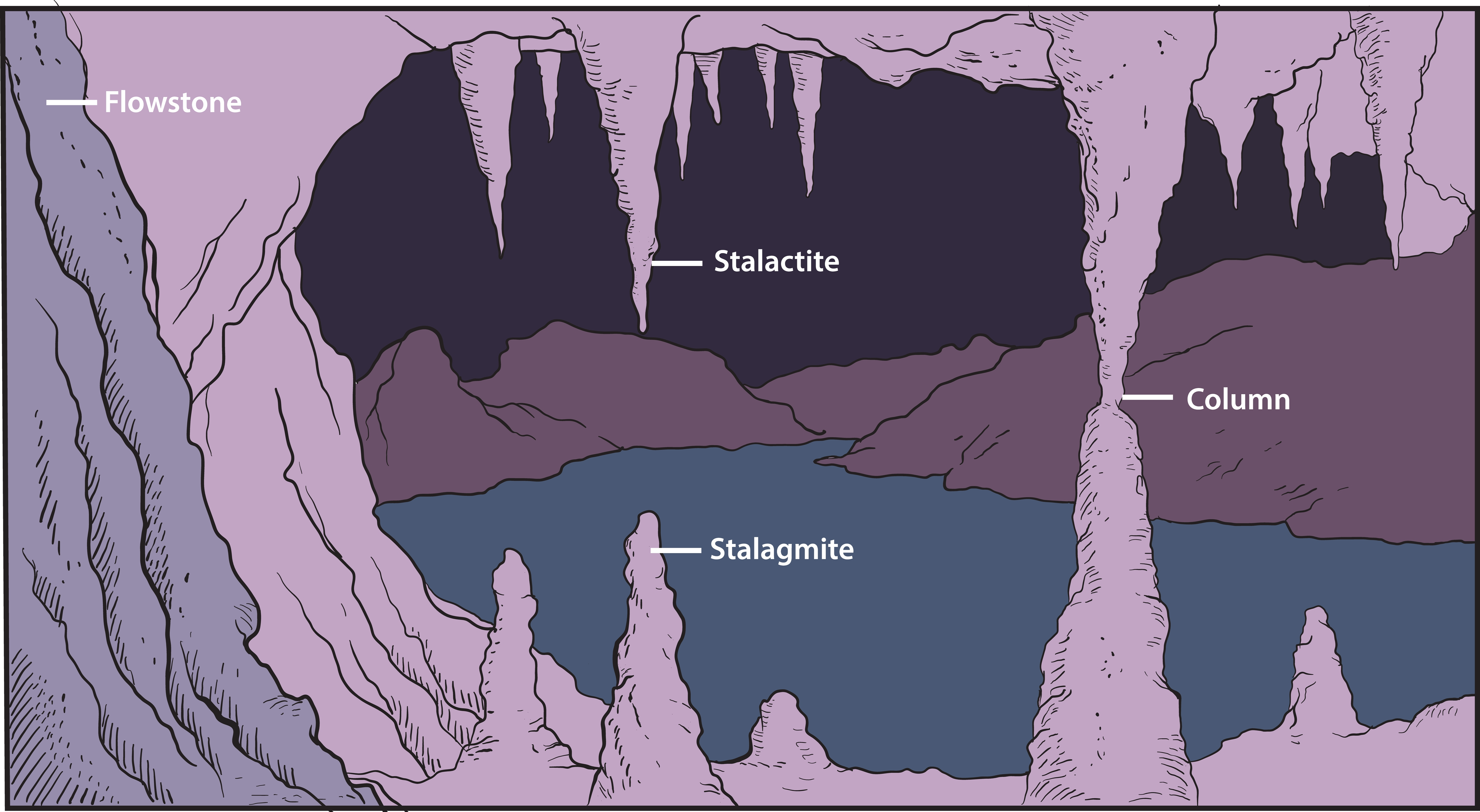
The bread and butter of the mineral formations are undoubtedly stalactites and stalagmites. Formed by mineral deposits building up from precipitation within the cave, stalactites are the icicle-shaped formations that hang from the ceilings. Stalagmites are their upward growing partners that form as water is dripped from the roof onto the floor, creating mineral deposits that form from the ground up, explains NOAA.
There are many fun ways to remember which one is which; some suggest that (stalag)mites crawl up your legs and (stalac)tites fall down, or use the “g” in stalagmites to refer to them growing up from the ground, and the “t” in stalactites as the top of the cave.
Speleothem formation
Both stalactites and stalagmites are types of speleothems, derived from the Greek words spelaion meaning “cave” and thema meaning “deposit”, explains the National Park Service.
Rainwater lands on the ground before seeping into caves via cracks in the rock. Along the way the water picks up carbon dioxide gas, making the water more acidic. This then passes over limestone rocks (sometimes dolomite) dissolving some on the way past. When the water reaches the cave the gas is released, and the calcite is deposited in various forms across the cave drip by drip.
These cave formations take a long time to build up, sometimes several thousand years.
Image credit: zombiu26/Shutterstock.com
Other formations
While stalactites and stalagmites are referred to as dripstones, because they are formed by dripping water, many other types of cave formations also occur. Columns are created when stalactites and stalagmites join up together, while the bizarre “cave popcorn” is formed when water comes through pores in the rocks, forming rounded bumps that resemble popcorn and in some cases trapping skeletons inside forever.
In the Eastern United States, a vast expanse of stalactites and stalagmites have formed the world’s biggest musical instrument.
Funky flowstones can also occur when the water travels over the walls in sheets, creating longer layers. These can contain different colored mineral deposits, earning the nickname “cave bacon” due to their streaky appearance.
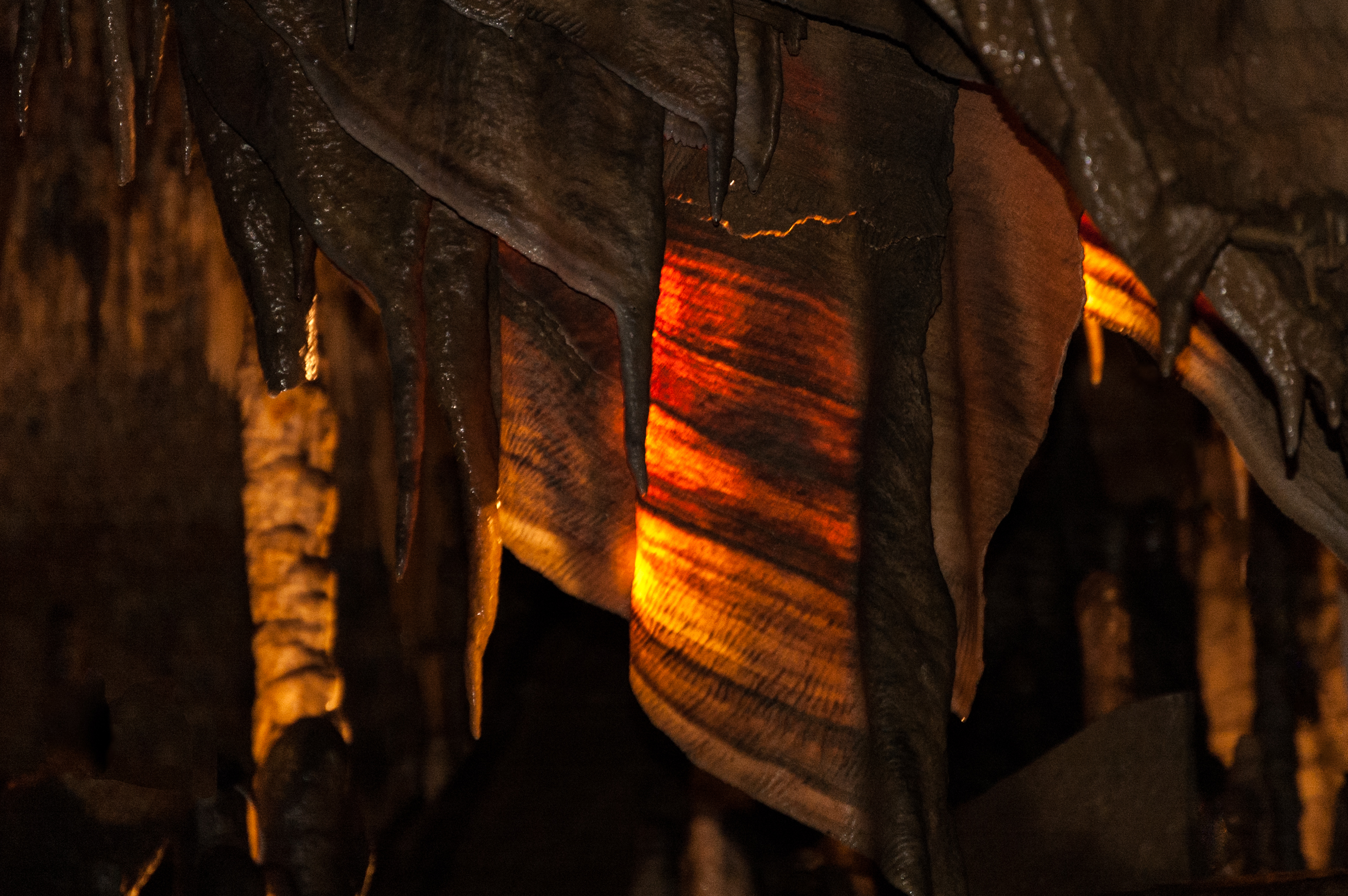

Don’t eat the forbidden cave bacon!
Image credit: Winning Image Photography/Shutterstock.com
These cave formations take a long time to form, sometimes over millions of years, while others have been painted by Neanderthals and can even help trace ancient wildfires.
Source Link: Stalactites And Stalagmites: What’s The Difference?