Unusually powerful disturbances in the Earth’s magnetic field have sparked some stunning red auroras this week, with the rare scarlet glow visible from locations across Europe and North America. Typically, the famous Northern Lights are made up of predominantly green hues, and while flashes or streaks of crimson are sometimes seen, sustained red skies are extremely uncommon.
The fiery display was caused by a massive spew of plasma – known as a coronal mass ejection (CME) – from the Sun. Striking the Earth on September 24, the CME punched a hole in our planet’s magnetic field, enabling highly charged particles to pour through and trigger a G2-class geomagnetic storm.
As these solar particles get channeled towards the poles, they interact with and excite gas atoms and molecules in the Earth’s atmosphere. These excited little guys then have to try and calm themselves down, which they do by releasing photons, thus giving rise to the spectacular light shows known as the aurora borealis (or Northern Lights) and aurora australis (Southern Lights).
If all of this sounds alarming then fear not, because it’s completely normal for charged solar particles to tear little holes in our magnetosphere. These punctures are usually very short-lived and pose no threat to us ground-dwellers.
What makes this latest geomagnetic storm a little different, however, is that the solar particles were able to smash into oxygen atoms high in the Earth’s atmosphere. Typically, solar winds reach an altitude of between 100 and 300 kilometers (60 to 180 miles), where there is a high concentration of oxygen atoms for them to react with. When this occurs, green light is given off, which is why this color tends to dominate the aurora.
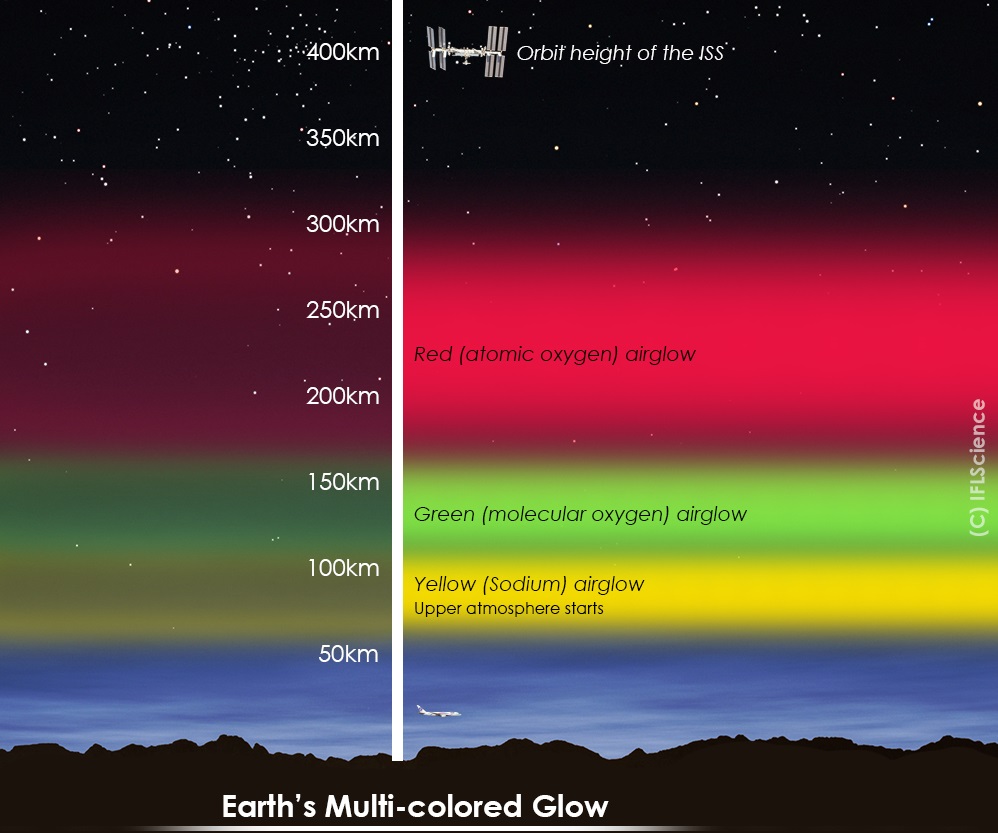
The altitude at which solar winds react with Earth’s atmosphere determines the color of the aurora.
Image credit: © IFLScience
However, on this occasion, the charged particles reached a height of between 300 and 400 kilometers (180 to 240 miles), where oxygen is much less concentrated and requires a higher amount of energy in order to become excited. The result is a brilliant flash of red light, although these ruby auroras are somewhat fragile and can only be observed if the oxygen atoms remain undisturbed for long enough to spit out their red photons.
The human eye is also considerably less sensitive to red light than to green, which is another reason why red auroras are so rarely seen. No such problems this week, though, with Spaceweather reporting that the red lights were visible with the naked eye as far south as France.
With the Sun ramping up its activity as it heads towards the Solar Maximum in July 2025 (or earlier), we should get more and more of these spectacular sky shows.
Source Link: Sun Rips Hole In Earth’s Magnetic Field Sparking Rare Red Auroras