![]() Most diamonds are formed deep inside Earth and brought close to the surface in small yet powerful volcanic eruptions of a kind of rock called “kimberlite”.
Most diamonds are formed deep inside Earth and brought close to the surface in small yet powerful volcanic eruptions of a kind of rock called “kimberlite”.
Our supercomputer modelling, published in Nature Geoscience, shows these eruptions are fuelled by giant “pillars of heat” rooted 2,900 kilometres below ground, just above our planet’s core.
Understanding Earth’s internal history can be used to target mineral reserves – not only diamonds, but also crucial minerals such as nickel and rare earth elements.
Kimberlite and hot blobs
Kimberlite eruptions leave behind a characteristic deep, carrot-shaped “pipe” of kimberlite rock, which often contains diamonds. Hundreds of these eruptions that occurred over the past 200 million years have been discovered around the world. Most of them were found in Canada (178 eruptions), South Africa (158), Angola (71) and Brazil (70).
Between Earth’s solid crust and molten core is the mantle, a thick layer of slightly goopy hot rock. For decades, geophysicists have used computers to study how the mantle slowly flows over long periods of time.
In the 1980s, one study showed that kimberlite eruptions might be linked to small thermal plumes in the mantle – feather-like upward jets of hot mantle rising due to their higher buoyancy – beneath slowly moving continents.
It had already been argued, in the 1970s, that these plumes might originate from the boundary between the mantle and the core, at a depth of 2,900km.
Then, in 2010, geologists proposed that kimberlite eruptions could be explained by thermal plumes arising from the edges of two deep, hot blobs anchored under Africa and the Pacific Ocean.
And last year, we reported that these anchored blobs are more mobile than we thought.
However, we still didn’t know exactly how activity deep in the mantle was driving kimberlite eruptions.
Pillars of heat
Geologists assumed that mantle plumes could be responsible for igniting kimberlite eruptions. However, there was still a big question remaining: how was heat being transported from the deep Earth up to the kimberlites?
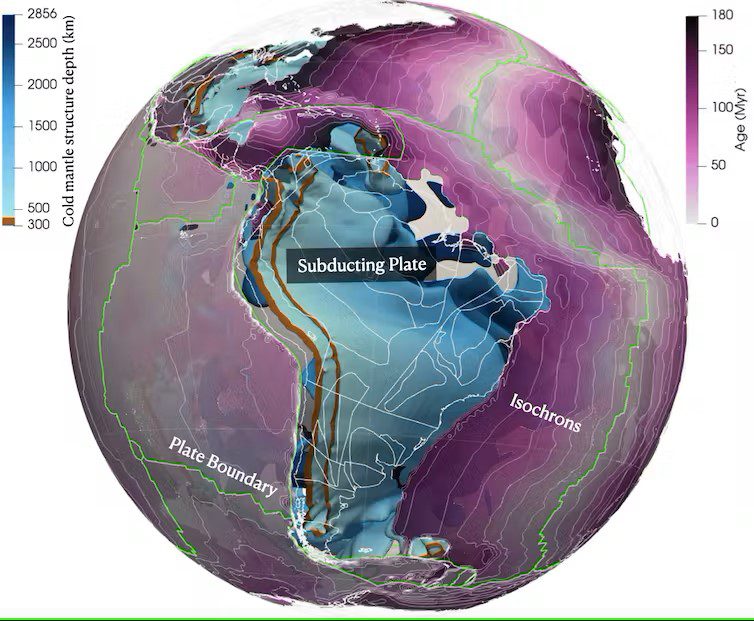
A snapshot of the global mantle convection model centred on subduction underneath the South American plate. Image credit: Ömer F. Bodur, Author provided
To address this question, we used supercomputers in Canberra, Australia to create three-dimensional geodynamic models of Earth’s mantle. Our models account for the movement of continents on the surface and into the mantle over the past one billion years.
We calculated the movements of heat upward from the core and discovered that broad mantle upwellings, or “pillars of heat”, connect the very deep Earth to the surface. Our modelling shows these pillars supply heat underneath kimberlites, and they explain most kimberlite eruptions over the past 200 million years.
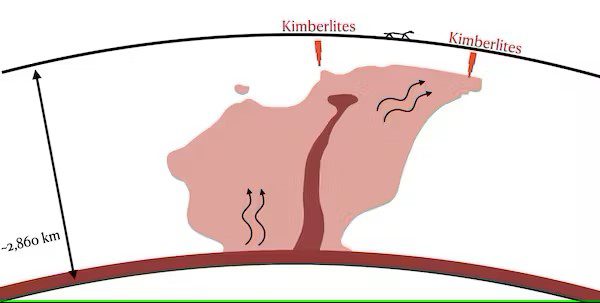
A schematic representation of Earth’s heat pillars and how they bring heat to kimberlites, based on output from our geodynamic model. Image credit: Ömer F. Bodur, Author provided
The model successfully captured kimberlite eruptions in Africa, Brazil, Russia and partly in the United States and Canada. Our models also predict previously undiscovered kimberlite eruptions occurred in East Antarctica and the Yilgarn Craton of Western Australia.
Towards the centre of the pillars, mantle plumes rise much faster and carry dense material across the mantle, which may explain chemical differences between kimberlites in different continents.
Our models do not explain some of the kimberlites in Canada, which might be related to a different geological process called “plate subduction”. We have so far predicted kimberlites back to one billion years ago, which is the current limit of reconstructions of tectonic plate movements.
Ömer F. Bodur, Honorary Fellow, University of Wollongong and Nicolas Flament, Associate Professor, University of Wollongong
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Source Link: Supercomputers Have Revealed The Giant "Pillars Of Heat" Funneling Diamonds Upwards From Deep Within Earth