A red giant star has been spotted in an unexpected location. Once the astronomers who found it got over their surprise, they realized that what has happened once could happen twice – including to us. If a star like this happened to pass quite close to the Sun at the right time, it would have affected the Earth in ways that could explain features such as plate tectonics. Although it’s still speculative, such an event could have made the Earth suitable for creatures like us.
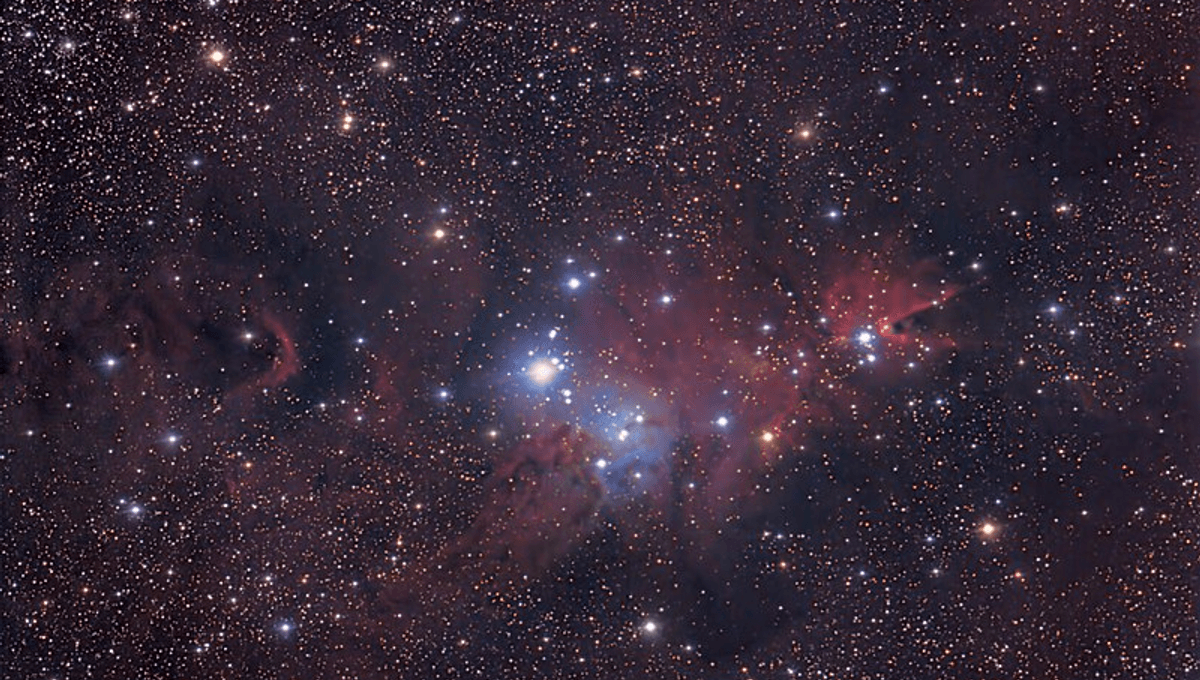
Stars, almost certainly including the Sun, coalesce in star-forming regions like the Orion Nebula, before dispersing through the galaxy. These regions are predominantly made up of stars of a similar age, but occasionally older stars that have long since left their own star-forming region wander into new ones.
The Gaia satellite has made it much easier to distinguish when this occurs from the older star passing between us and the star-forming region so that it’s in the same field of view. Dr Richard Parker of the University of Sheffield and Dr Christina Schoettler of Imperial College London have been looking for these interlopers in the Gaia data. They found an unexpected example of an evolved asymptotic giant branch (AGB) star in the NGC 2264 star-forming region, also known as the Christmas tree cluster.
Most stars’ passage near other stars could cause gravitational disruption, unleashing comets on the inner planets or possibly even pulling the planets themselves out of their orbits. AGB stars, however, can have an effect much earlier in the process. AGB stars shed a lot of radioactive elements, particularly aluminium-26 and iron-60, through their stellar winds.
Both isotopes are thought to have played a crucial role on Earth. Their presence has previously been attributed to nearby supernovas, but the timing seems out. Parker and Schoettler raise the possibility that an AGB star could be responsible for their initial abundance instead.
If so, this star did humanity an incalculable favor. Radioactivity from the two isotopes raised the temperature of the early Earth’s interior significantly, and that extra heat may be the reason Earth has plate tectonics. The constant slow refreshment that plate tectonics gives to the planet not only provides nutrients to the soil that would have long since degraded otherwise, but it also keeps our atmosphere breathable by recycling carbon dioxide and releasing nitrogen.
Without plate tectonics, Earth would probably still have life, but may have never got past single-celled organisms. Iron-60 and aluminum-26’s contribution to this is still speculative, and their source in a retired AGB star even more so: further research may confirm or refute either of these. The pair plan to start by investigating how common it is for highly evolved stars to pass through star-forming regions. Complicating matters, the AGB star in NGC 2264 has about 1.5 solar masses, too low to have shed enough iron-60 and aluminum-26 for Earth. However, its presence suggests somewhat more massive stars could end up in similar places.
If Parker and Schoettler are right, however, it may imply a universe where life is common, but multi-celled organisms are restricted to those planets whose star-forming region had an AGB star pass at the right time. If so, such planets might be rare indeed, which would provide an answer to the Fermi Paradox.
“Until now, researchers have been sceptical that these old, evolved stars could ever meet young stars that are forming planets, so this discovery reveals much more about the dynamics, relationships and journeys of stars,” Parker said in a statement. “By showing that AGB stars can meet young planetary systems, we have shown that other sources of Aluminum-26 and Iron-60, such as the winds and supernovae of very massive stars, may not be required to explain the origin of these chemical elements in our solar system.”
AGB stars have been known for a while to have made a contribution to Earth’s composition. The question of why we seem to have inherited more of some of their elements than Mars or the asteroid belt has been explored. However, the role Parker and Schoettler are proposing is much larger.
The study is published open access in The Astrophysical Journal Letters
Source Link: Surprise Discovery Of Older Interloper In Star-Forming Region Could Explain Earthly Mystery