An “exceptional” 99-million-year-old tentacle trapped in amber is the first partial body fossil of a tapeworm ever discovered, suggesting the parasites have been wreaking havoc on intestines since at least the mid-Cretaceous.
Despite being found in nearly all marine, freshwater, and terrestrial ecosystems, tapeworms (Cestoda) are rarely preserved in the geological record. In fact, the only widely accepted example before the Quaternary are eggs discovered in fossilized shark poop from the Permian.
“The fossil record of tapeworms is extremely sparse due to their soft tissues and endoparasitic habitats, which greatly hampers our understanding of their early evolution,” Bo Wang, the lead researcher of a study describing the latest discovery, said in a statement. But now, his team have “reported the first body fossil of a tapeworm,” he added.
Not only that, but the find is also arguably the most convincing body fossil of a flatworm ever discovered.
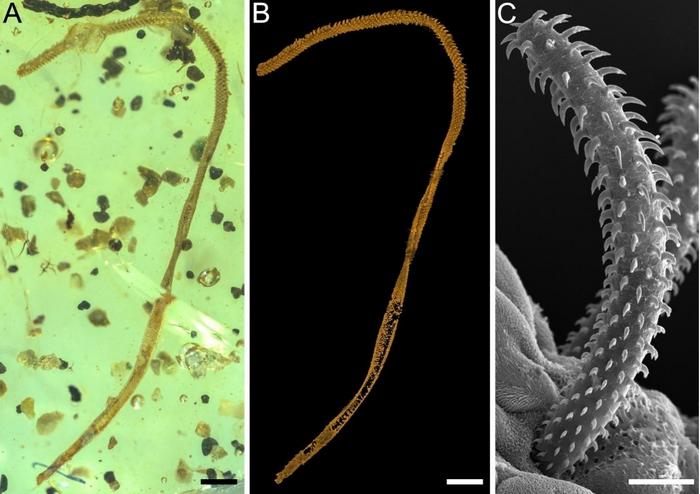
The fossilized tapeworm (A/B), compared to a modern tapeworm (C).
Image credit: NIGPAS
The prehistoric parasite, preserved in mid-Cretaceous Kachin amber from northern Myanmar, bears resemblance to tapeworms that are around today and infect elasmobranch fish like rays and sharks. The researchers, therefore, think that this little critter likely did the same, which begs the question: how did a marine parasite end up caught in amber?
While they don’t know for sure, the team does propose one possible explanation.
Tapeworms are what’s known as endoparasites, meaning they live inside their hosts. Trypanorhynchs – the group to which the newly discovered worm belongs – are intestinal interlopers, clinging to their hosts’ guts and absorbing nutrients. As the specimen was found in a near-shore environment, it could be assumed that it was lurking in the bowels of an elasmobranch that was stranded by a tide or storm.
The unfortunate fish may then have been scavenged upon by a land-based predator – perhaps a dinosaur if the paleoart is anything to go by – which ripped its tentacle free, and allowed it to get trapped in resin.
It’s a purely speculative scenario, the study authors note: “the truth may be far beyond our imagination.”
“No matter how unlikely the preservation of this tapeworm in amber, our study highlights that amber has the potential to capture unexpected life details in deep time,” the authors conclude, referencing their discovery that resin is capable of preserving the internal structures of parasitic worms too.
“Our study not only provides a remarkable example of a marine endoparasite preserved in amber, but also highlights the importance of amber research in paleoparasitology.”
The study is published in the journal Geology.
Source Link: Tapeworms Have Been Upsetting Stomachs For At Least 99 Million Years, First Fossil Suggests