Our tiny swimmers are not lone wolves as we once thought – sperm cells tend to clump together so they can easily traverse vaginal fluid, a new study has found.
It has always been portrayed that the strongest and fittest individual sperm is the one that beats all others in the fertilization race. That may be true, but the amount of cooperation with its fellow spermy cohorts has surprised scientists.
New research now shows that the sperm (aka spermatozoa) team up together to navigate the treacherous female reproductive tract in a large range of mammalian species. Previously, it was puzzling to scientists why sperm seem to naturally clump together without attaching when swimming in the reproductive system.
The reproductive fluid found in the cervix, uterus, and oviduct (where the egg is fertilized) can be a difficult one to maneuver – imagine it as trying to swim through a vat of melted cheese. It was found the lonely swimmers do not outrun the packs in these settings. This seems to be so beneficial that the wood mouse’s sperm heads actually has a hook for attaching to their neighbors. This can help form huge “sperm trains” that may contain hundreds to thousands of individual sperm cells.
To investigate this clumping trait even further, the researchers had to develop a system that was not as 2D as the normal microscopic slide. They used bovine sperm (as it was a good model to compare against human sperm) and had a device that was used to mimic the female tract. The researchers looked at the sperm clusters in different flow scenarios.
When there was no flow, the sperm clusters swam in a straighter line and turned less frequently than individuals. In the mild flow they seemed better aligned, like a school of salmon heading upstream. When there was a high flow rate, the sperm tend to stick together to prevent being washed away by the strong current.
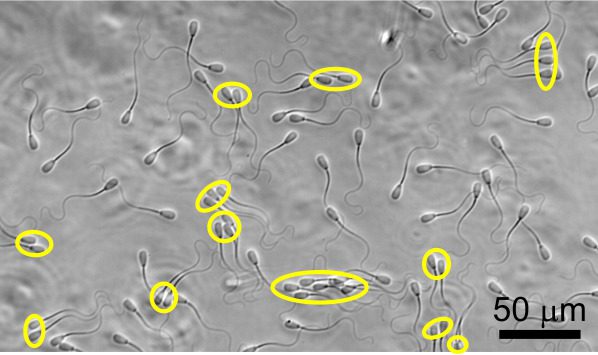
Coexistence of individually swimming and clustered sperm. Clustered sperm are labeled with yellow ovals. Scale bar: 50 μm. Image credit: S Phuyal, SS Suarez, C-K Tung
“In general, I would say that identification of motility advantages that are not speed enhancement is not usual, and therefore significant. In some ways we open new avenues for examination of sperm performance,” Dr Chih-kuan Tung, co-author of the study, noted in a statement.
Tung came up with an amazing analogy when it came to the heavy-flow individuals. “This may resemble the peloton formation in biking, although the fluid mechanics for sperm is drastically different from the bikers. We would certainly want to know more about this.”
This study is incredibly important. Understanding the complex physics of one of the oldest races known – sperm hurrying to to the egg – can help fertility treatments in the future.
“In the longer term, our understanding may provide better selection of sperm used for intervention such as in vitro fertilization or other assisted-reproduction technologies,” Tung said. “This may be needed as [these methods] typically skip some or all of the selection mechanisms present in the female tract and yield less favorable results.”
You never know, maybe one day sperm racing will be a sport.
This study was published in the Journal of Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.
Source Link: Teams of Sperm Clump Together Like A Cyclist Pack To Fight Against Vaginal Fluid