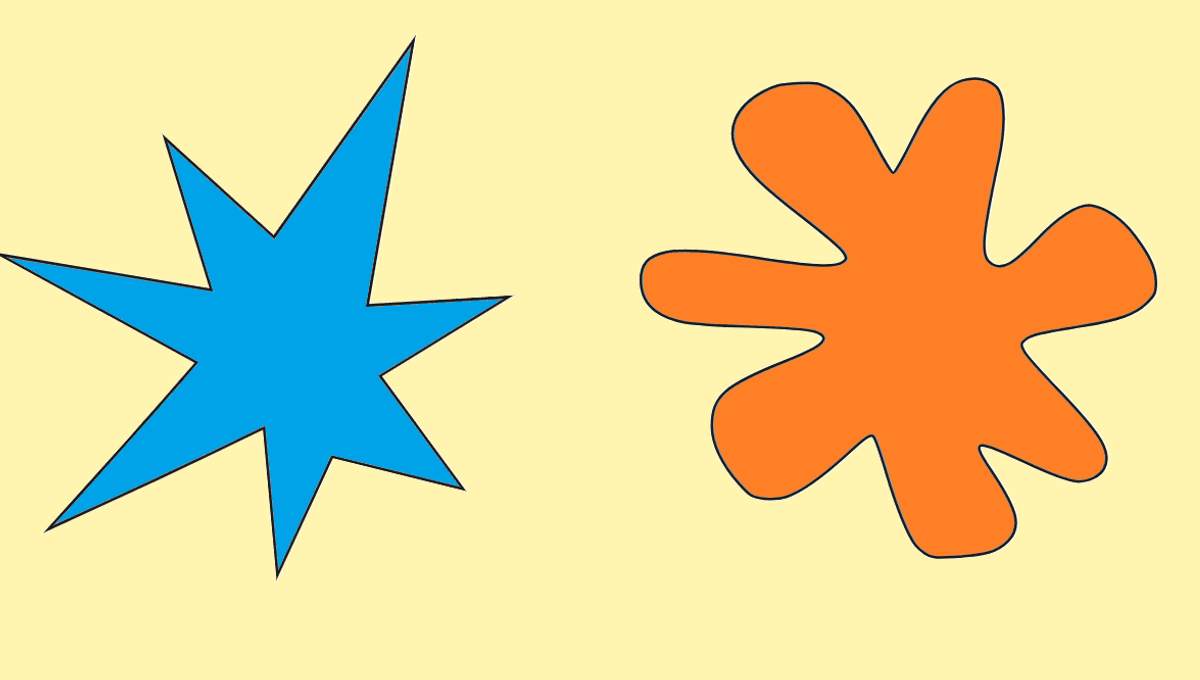
You’d be surprised what you can learn about the human mind from some nonsense words and childlike doodles. Take a look at the two shapes in the image above and ask yourself: which one is called “kiki” and which one is “bouba.” Regardless of your cultural background or mother tongue, there’s an extremely strong chance you’ll think the spikey shape is “kiki,” while the blobby one is “bouba.”
This is known as the bouba-kiki effect, a famous psycholinguistic experiment that provides insight into how the human brain connects abstract sensory experiences.
One of the first people to identify this peculiar effect was German psychologist Wolfgang Köhler in the 1920s, who demonstrated a similar phenomenon with two similar non-words: “baluba” (later “maluma”) and “takete”. Most people believed that the word “takete” was suited to an angular shape with spikes, while “maluma” fits better with a rounded shape.
In the early 2000s, Vilayanur Ramachandran and Edward Hubbard breathed new life into the effect by repeating Köhler’s experiment with the words “kiki” and “bouba”. Testing both American college undergraduates and Tamil speakers in India, they found 95 percent to 98 percent of people in both groups agreed which shapes were “kiki” and which were “bouba.”
It’s possible to play around with this idea using much more than boring abstract shapes. For instance, oranges and lemons: which fruit would you assign to be “kiki” or “bouba”? Sex Pistols and the Beach Boys: which one is “kiki” and “bouba”? What about Buzz Lightyear and Woody?
Indeed, the effect can apply to much more than shapes and words. Some research has indicated that the connection may extend to personality traits, with sharp sounds being linked to intelligence or seriousness and soft sounds to pleasant or foolish traits.
For example, a character that embodies “kiki” characteristics is more likely to be perceived as happy, clever, small, thin, young, unpleasant, and nervous, while a spikey star-shaped figure is often linked to traits like intelligence, slimness, nervousness, unpleasantness, and being upper-class.
The bouba-kiki effect has been repeated several times to see whether the effect remains true regardless of people’s culture, language, personality, age, and so on.
By and large, the bouba-kiki effect seems to hold. Remarkably, similar effects have been demonstrated in people who were born blind, in kids who haven’t learned to read yet, and in some cultures that do not use written language.
That said, researchers have found some languages where the effect is not that significant, including Mandarin Chinese, Turkish, Romanian, and Albanian.
The researchers were unsure why these particular languages don’t follow the trend. Then again, no one has yet presented a convincing explanation for why the effect occurs in the first place.
One idea is that the sounds correlate to the shape of mouths when we’re uttering the words: “bouba” is sounded with rounded lips, while “kiki” force the mouth into a more angular shape.
Alternatively, it could be a case of ideasthesia, a phenomenon where abstract concepts (like ideas or words) activate sensory-like experiences (such as perceptions of shape, color, or size). In terms of the bouba-kiki effect, it might be a form of mental mapping of auditory experiences (the sounds) to visual experiences (the shapes).
Understanding why so many humans have these tendencies to link sound, shape, and other qualities in this fashion could have some profound implications. The bouba-kiki effect might help explain the origin of language because it shows that sound and meaning are not entirely arbitrary.
The effect – if a genuine phenomenon – seems to show there’s a universal connection between certain sounds and qualities, such as shapes or personalities. This could suggest that language evolved within a universal psychological framework that’s ingrained in humans whereby sounds are intrinsically linked to the things they represent, rather than being purely invented or “random.”
Source Link: The Bouba-Kiki Effect Shows A Very Strange Facet Of Language And Human Psychology