What came first, the chicken or the egg? If we’re talking about eggs in general, then the latter, but a new study of an ancient single-celled organism suggests the genetic tools to “create” eggs may have been about before animals were even a thing.
The study, carried out by researchers at the University of Geneva, focused on pinpointing the evolutionary origins of embryogenesis, the process of development that sees a single-celled fertilized egg (zygote) turn into an embryo made up of multiple cells.
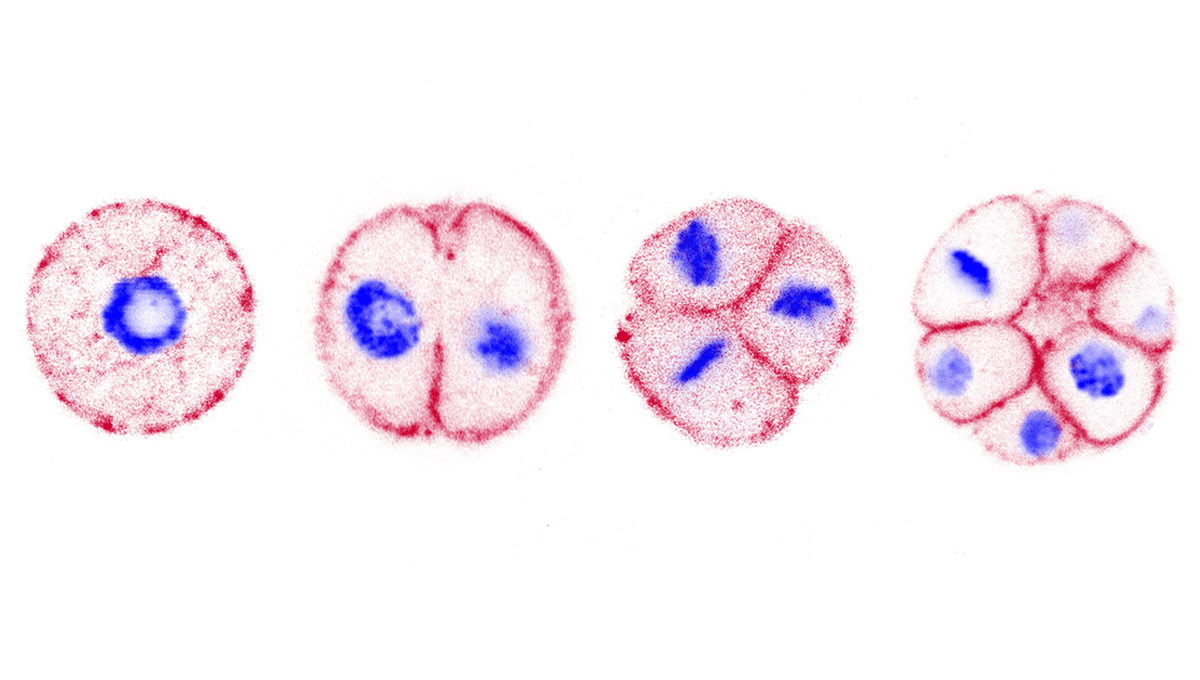
The first step in this process is called cleavage, where the zygote undergoes cell division, but doesn’t grow. This stage, and the other key elements of embryogenesis, are features that have remained well-conserved throughout animal evolution.
Despite this, scientists know little about how embryogenesis came to be. Life on Earth started out unicellular – so how did we end up with a process that transforms a single cell into a multicellular animal?
The team looked to a recently discovered, distant relative of ours: Chromosphaera perkinsii, a unicellular protist that, over a billion years ago, branched off from the evolutionary path leading to animals.
In the lab, the researchers observed the development of C. perkinsii in real-time, using a technique called long-term brightfield live imaging. From this, they discovered that, much like the cleavage stage of animal embryogenesis, C. perkinsii cells grow for around 65 hours, before dividing into a multicellular colony without growing anymore.
The team also looked deeper into the kinds of genes that were being expressed, and the biomolecules produced as a result, during this stage. Again, they found similarities to animal embryogenesis – and even a molecular toolkit with a resemblance to that seen in the maturation of animal eggs.
“[B]efore the first division, C. perkinsii produces and accumulates key cellular components such as proteins and lipids in a manner reminiscent of oocyte maturation,” the team writes in the study.
‘‘Although C. perkinsii is a unicellular species, this behaviour shows that multicellular coordination and differentiation processes are already present in the species, well before the first animals appeared on Earth,” said Omaya Dudin, who led the study, in a statement.
What the study’s findings mean for the evolution of embryogenesis, and cleavage in particular, is up for debate – does the process seen in C. perkinsii share an evolutionary pathway with that seen in animals, or did similar things just so happen to evolve independently of each other?
Regardless, “It’s fascinating, a species discovered very recently allows us to go back in time more than a billion years,” concluded first author Marine Olivetta.
The study is published in Nature.
Source Link: The Chicken Or The Egg? We Might Need To Change The Question