For humanity to expand into space, we need to know how reproduction and gestation will happen in microgravity. From reproduction to birth, we do not know what is safe for parents and offspring in such conditions. But new research is slowly challenging our ignorance on the subject – a recent experiment on the International Space Station (ISS) shows, for the first time, that mammal embryos can grow in microgravity without harmful effects.
The embryos in question were mice and were sent to the ISS in August 2021 as frozen fertilized cells. While on the ISS, they were thawed and kept in a special setup at body temperature. Over the course of four days, the zygotes were allowed to grow and develop, becoming blastocysts – the assembly of cells that would normally develop into a fetus and placenta.
There was a control sample on board the space station, which was placed in a centrifuge to simulate an Earth-like artificial gravity, as well as a control sample on Earth. The developmental stages were the same for all three setups, but the survival rates were significantly lower in space compared to Earth.
In the past, researchers had demonstrated, also in mice, that going to space did not affect the fertility of male mice or the health of the offspring that they conceived when back on Earth. This new work is the first to show that mammal embryos can develop healthily in microgravity.
“The embryos cultured under microgravity conditions developed into blastocysts with normal cell numbers, inner cell mass, trophectoderm, and gene expression profiles similar to those cultured under artificial-1 g control on the International Space Station and ground-1 g control which clearly demonstrated that gravity had no significant effect on the blastocyst formation and initial differentiation of mammalian embryos,” the researchers wrote in the paper.
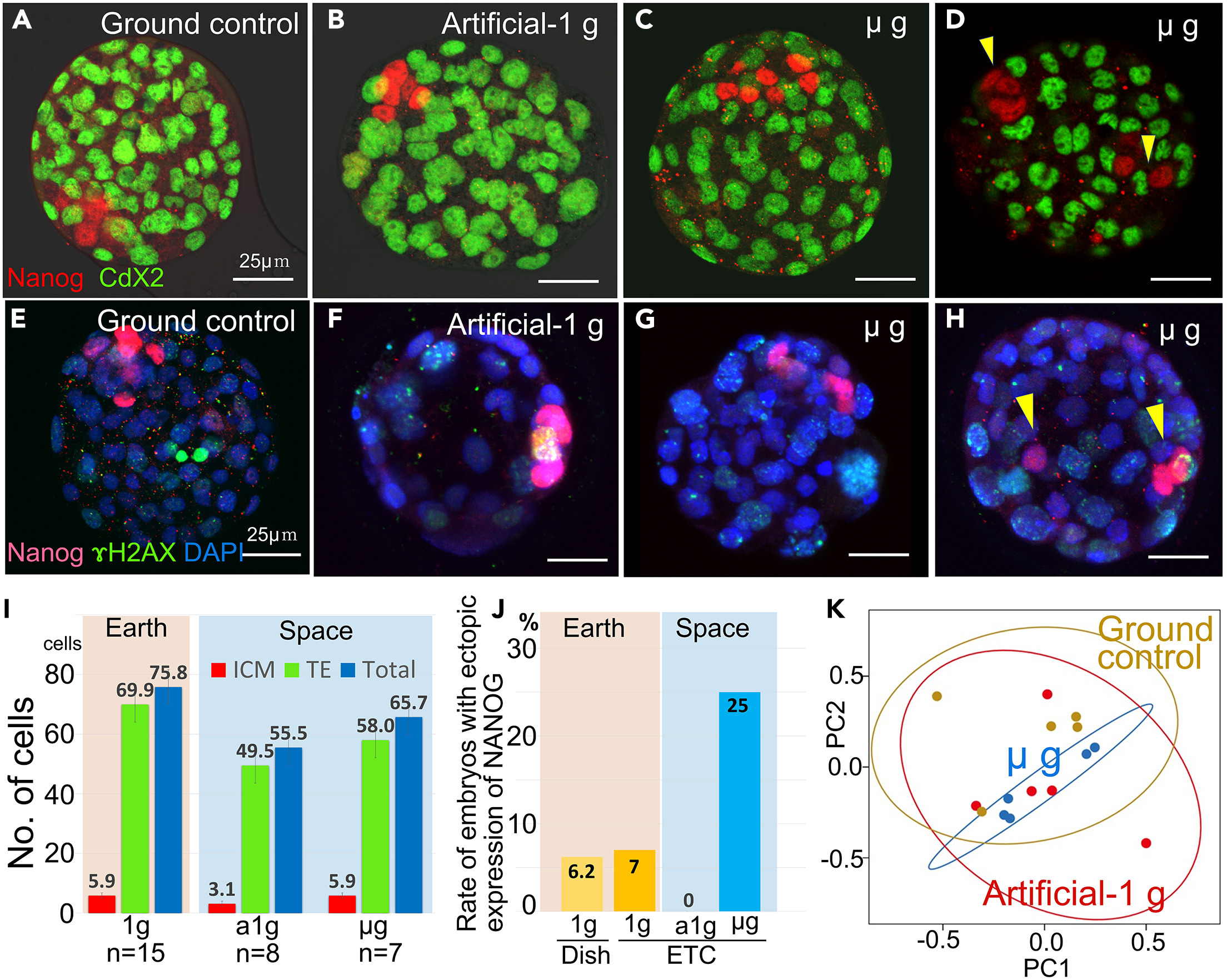
The image shows comparisons between the controls and the microgravity blastocysts.
The findings are intriguing, but moving from the blastocyst stage to a viable pregnancy, there’s a lot that needs to happen and a relatively long time for things to go wrong. The blastocyst stage is before implantation – in human terms, that would be up to three weeks after fertilization. One space shuttle-based experiment kept pregnant mice for several days in microgravity and that led some of the offspring to have several health complications – but it did show that it was not impossible to have healthy mice pups that have developed partially in space.
Astronauts exercise a lot to stave off the effects that not having gravity does to their bones and muscles, but even the most active pregnant astronaut cannot pass those benefits to a fetus. There is a lot more work needed to understand what fetal development in space might be like; the team is interested in performing further studies in this field, looking at implanting those blastocysts developed in space here on Earth.
The study is published in iScience.
An earlier version of this article was published in October 2023.
Source Link: The First Mammal Embryos Have Been Grown In Space