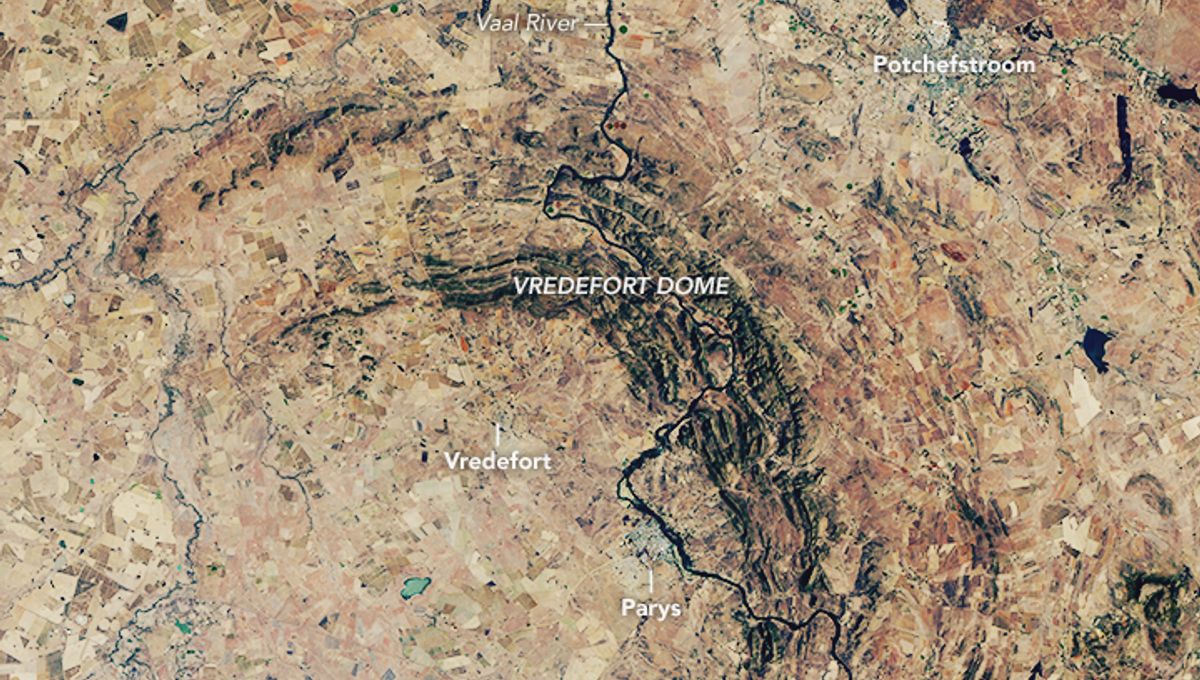
Back before trees existed, when Earth was inhabited solely by single-celled organisms, the largest asteroid to ever hit our planet touched down near what we now know as Johannesburg, South Africa, forming the Vredefort crater.
With an estimated crater size of between 250-280 kilometers (155-174 miles) upon first impact, the size of the asteroid was originally calculated to be around 15 kilometers (9.3 miles) in diameter. However, new research from the University of Rochester suggests the recalculated size is closer to a whopping 25 kilometers (15.5 miles).
The team used a shock physics program called Simplified Arbitrary Langrangian Eulerian (iSALE) to calculate the size of asteroid needed to create an impact on the scale of the Vredefort crater.
They found that the original diameter estimate would produce an impact site measurement of around 172 kilometers (106.8 miles). To get to the actual figure of 250-280 kilometers (155-174 miles), the impactor would have to of been much larger.
Estimations of the effect this impact may have had on Earth’s environment can be drawn from what we already know about the aftermath of the Chicxulub crater impact.
Thought to be the cause of the dinosaurs’ mass extinction, the Chicxulub crater was created by a 10-kilometer (6.2-mile) asteroid that wiped out 75 percent of plant and animal species on Earth 66 million years ago.
Lucky for all living things, there weren’t many around 2 billion years ago. Despite not being the cause of a mass extinction event, it’s thought that the Vredefort impact would have had a greater effect on the global climate than the Chicxulub impact.
The copious amounts of disturbed dust created by the asteroid’s collision would have blocked out the sun, anywhere from hours to decades. This dusty sunscreen would have caused the surface temperature of Earth to cool considerably. As the dust settled, carbon dioxide emitted from the impact would have, in turn, caused the planet’s temperature to rise by several degrees.
Impacts of this size and from this time period are significant in furthering our understanding of the geographical layout of Earth 2 billion years ago.
By studying the ejected material from the Vredeford crater, researchers were able to match samples to those gathered from present-day Karelia, Russia. They estimated the distance of the two landmasses to be around 2,000–2,500 kilometers (1,242-1,553 miles) apart at the time of impact.
As well as helping us better understand what the planet looked like 2 billion years ago, the information gathered from impacts of this size enables researchers to study the effects of other large planetary impacts and estimate potential effects of future collisions.
The study was published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets.
Source Link: The Largest Asteroid To Ever Hit Earth Was 25 Kilometers Wide