The Mississippi River Delta is under siege – a multi-pronged attack of sediment erosion, rising sea levels, and flooding is putting immense strain on the wetlands between the Mississippi River and the Gulf of Mexico, threatening the wildlife and millions of humans that call the region home.
The disappearance of Louisiana’s coastal wetlands is being driven by both natural and human-caused factors, encompassing both acute and chronic stresses.
Vast swathes of swampy wetlands are being lost to the sea as increased flooding, storms, and rising sea levels accelerate sediment erosion. Meanwhile, human activities upstream on the Mississippi River – such as dam construction, agriculture, and fossil fuel infrastructure – are preventing the natural replenishment of the marshes with sediments and disrupting the balance of nutrients.
Intertwined with this issue, the river deltas are seeing a significant die-back of plant life, namely the gently swaying “walls” of grass-like reeds, that can help the wetlands resist the impacts of flooding.
One of the most harshly impacted regions is the Bird’s Foot Delta. Mead Allison, a coastal geologist at Tulane University, recently told Science that it’s perhaps “one of the most threatened places in America if not the Earth.”
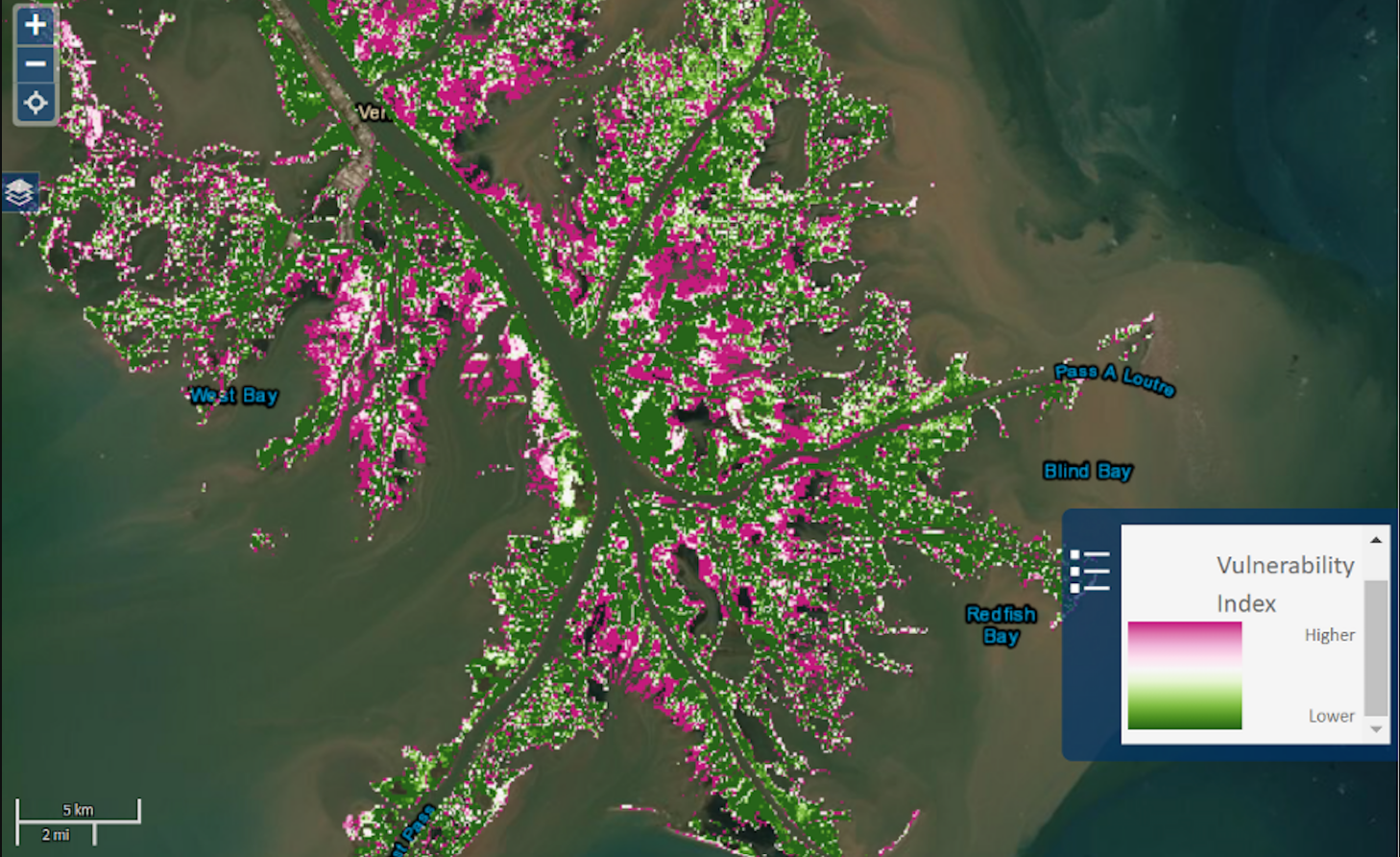
Map showing the severity of vegetation loss in the Mississippi River Birdfoot Delta.
Image credit: USGS (Public Domain)
The problem is also not wholly new. Since the 1930s, Louisiana has lost over 5,179 square kilometers (2,000 square miles) of land – an area roughly the size of Delaware. However, the situation is reaching crunch time. Today, it’s estimated that a football field of land becomes open water every 100 minutes in Louisiana.
It’s all too clear what’s at stake if the Mississippi River Delta is allowed to continue deteriorating. Almost half of the Louisiana population – over 2 million people — lives near the state’s coastal zone, and these people rely on the wetlands for recreation and their livelihoods, not to mention storm protection.
The region is also an economic hub, responsible for a huge amount of tourism, fishing, cargo shipping, and crude oil production.
Along with human life, the Mississippi River Delta is home to an abundance of wildlife, including 400 species of birds, as well as countless other fish, mammals, amphibians, and smaller organisms that are crucial for the wider ecosystem.
If the delta continues to shrink, much of this could be lost. Fortunately, scientists and policymakers are taking action to resist its demise. With the support of a $22 million federal grant, researchers from Louisiana State University (LSU) and Tulane are embarking on a multiyear investigation to uncover the challenges facing the delta and devise solutions to curb its deterioration.
“The very specific objective for this is to determine what the future holds for the geomorphic landmass that constitutes the Bird’s Foot under our present management strategies for the river,” Sam Bentley, professor in the LSU Department of Geology and Geophysics and co-director of the project, said in a statement.
“It’s very exciting work and really meaningful. And it’s going to have a combination of direct and some indirect insights that can be applied to other river deltas around the world.”
Source Link: The Largest River Delta In USA Could Soon Be Lost To The Sea