![]() On the largest scales, the Universe is ordered into a web-like pattern: galaxies are pulled together into clusters, which are connected by filaments and separated by voids. These clusters and filaments contain dark matter, as well as regular matter like gas and galaxies.
On the largest scales, the Universe is ordered into a web-like pattern: galaxies are pulled together into clusters, which are connected by filaments and separated by voids. These clusters and filaments contain dark matter, as well as regular matter like gas and galaxies.
We call this the “cosmic web”, and we can see it by mapping the locations and densities of galaxies from large surveys made with optical telescopes.
We think the cosmic web is also permeated by magnetic fields, which are created by energetic particles in motion and in turn guide the movement of those particles. Our theories predict that, as gravity draws a filament together, it will cause shockwaves that make the magnetic field stronger and create a glow that can be seen with a radio telescope.
In new research published in Science Advances, we have for the first time observed these shockwaves around pairs of galaxy clusters and the filaments that connect them.
In the past, we have only ever observed these radio shockwaves directly from collisions between galaxy clusters. However, we believe they exist around small groups of galaxies, as well as in cosmic filaments.
There are still gaps in our knowledge of these magnetic fields, such as how strong they are, how have they evolved, and what their role is in the formation of this cosmic web.
Detecting and studying this glow could not only confirm our theories for how the large-scale structure of the Universe has formed, but help answer questions about cosmic magnetic fields and their significance.
Digging into the noise
We expect this radio glow to be both very faint and spread over large areas, which means it is very challenging to detect it directly.
What’s more, the galaxies themselves are much brighter and can hide these faint cosmic signals. To make it even more difficult, the noise from our telescopes is usually many times larger than the expected radio glow.
For these reasons, rather than directly observing these radio shockwaves, we had to get creative, using a technique known as stacking. This is when you average together images of many objects too faint to see individually, which decreases the noise, or rather enhances the average signal above the noise.
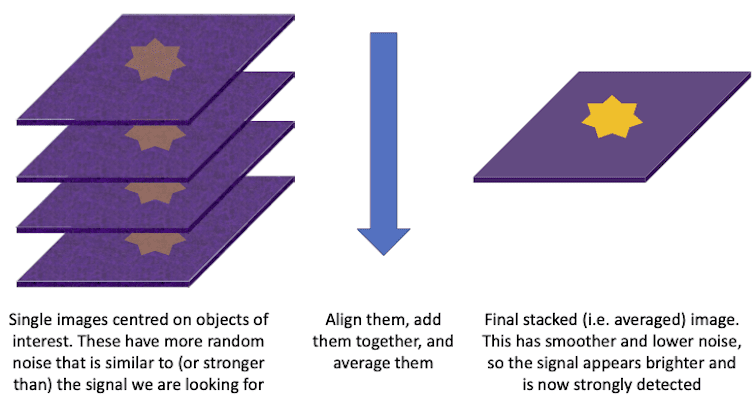
So what did we stack? We found more than 600,000 pairs of galaxy clusters that are near each other in space, and so are likely to be connected by filaments. We then aligned our images of them so that any radio signal from the clusters or the region between them – where we expect the shockwaves to be – would add together.
We first used this method in a paper published in 2021 with data from two radio telescopes: the Murchison Widefield Array in Western Australia and the Owens Valley Radio Observatory Long Wavelength Array in New Mexico. These were chosen not only because they covered nearly all the sky but also because they operated at low radio frequencies where this signal is expected to be brighter.
In the first project, we made an exciting discovery: we found a glow between the pairs of clusters! However, because it was an average of many clusters, all containing many galaxies, it was difficult to say for sure the signal was coming from the cosmic magnetic fields, rather than other sources like galaxies.
A ‘shocking’ revelation
Normally the magnetic fields in clusters are jumbled up due to turbulence. However, these shock waves force the magnetic fields into order, which means the radio glow they emit is highly polarised.
We decided to try the stacking experiment on maps of polarised radio light. This has the advantage of helping to determine what is causing the signal.
Signals from regular galaxies are only 5% polarised or less, while signals from shockwaves can be 30% polarised or more.
In our new work, we used radio data from the Global Magneto Ionic Medium Survey as well as the Planck satellite to repeat the experiment. These surveys cover almost the entire sky and have both polarised and regular radio maps.

We detected very clear rings of polarised light surrounding cluster pairs. This means the centres of the clusters are depolarised, which is expected as they are very turbulent environments.
However, on the edges of the clusters the magnetic fields are put in order thanks to the shockwaves, meaning we see this ring of polarised light.
We also found an excess of highly polarised light between the clusters, much more than you would expect from just galaxies. We can interpret this as light from the shocks in the connecting filaments. This is the first time such emission has been found in this kind of environment.
We compared our results with state-of-the-art cosmological simulations, the first of their kind to predict not just the total signal of the radio emission but the polarised signal as well. Our data agreed very well with these simulations, and by combining them we are able to understand the magnetic field signal left over from the early Universe.
In future we would like to repeat this detection for different times over the history of the Universe. We still do not know the origin of these cosmic magnetic fields, but further observations like this can help us to figure out where they came from and how they have evolved. ![]()
Tessa Vernstrom, Senior research fellow, The University of Western Australia and Christopher Riseley, Research Fellow, Università di Bologna
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Source Link: The Largest Structures In The Universe Are Still Glowing With The Shock Of Their Creation