Mauna Loa erupted for the first time in nearly 40 years on the Big Island of Hawai’i on Sunday night, releasing a flurry of red-hot lava that trickled down its side. This spectacular sight has since been captured from the vantage point of low-Earth orbit by satellites.
Maxar Technologies captured the shots on Monday night at around 22:30, showing a long trail of lava flow moving along the Northeast Rift Zone.
Along with the lava flow, there have been reports of lava fountains measuring up to 40 meters (148 feet) in height.
“Heightened unrest began in mid-September 2022 as recorded by an increase in earthquakes below Mauna Loa summit (from 10-20 per day to 40-50 per day), an increased rate of inflation recorded by GPS stations, and inflation recorded on the MOK tiltmeter. The unrest was caused by renewed input of magma into Mauna Loaʻs summit reservoir system”, said the United States Geological Survey (USGS).
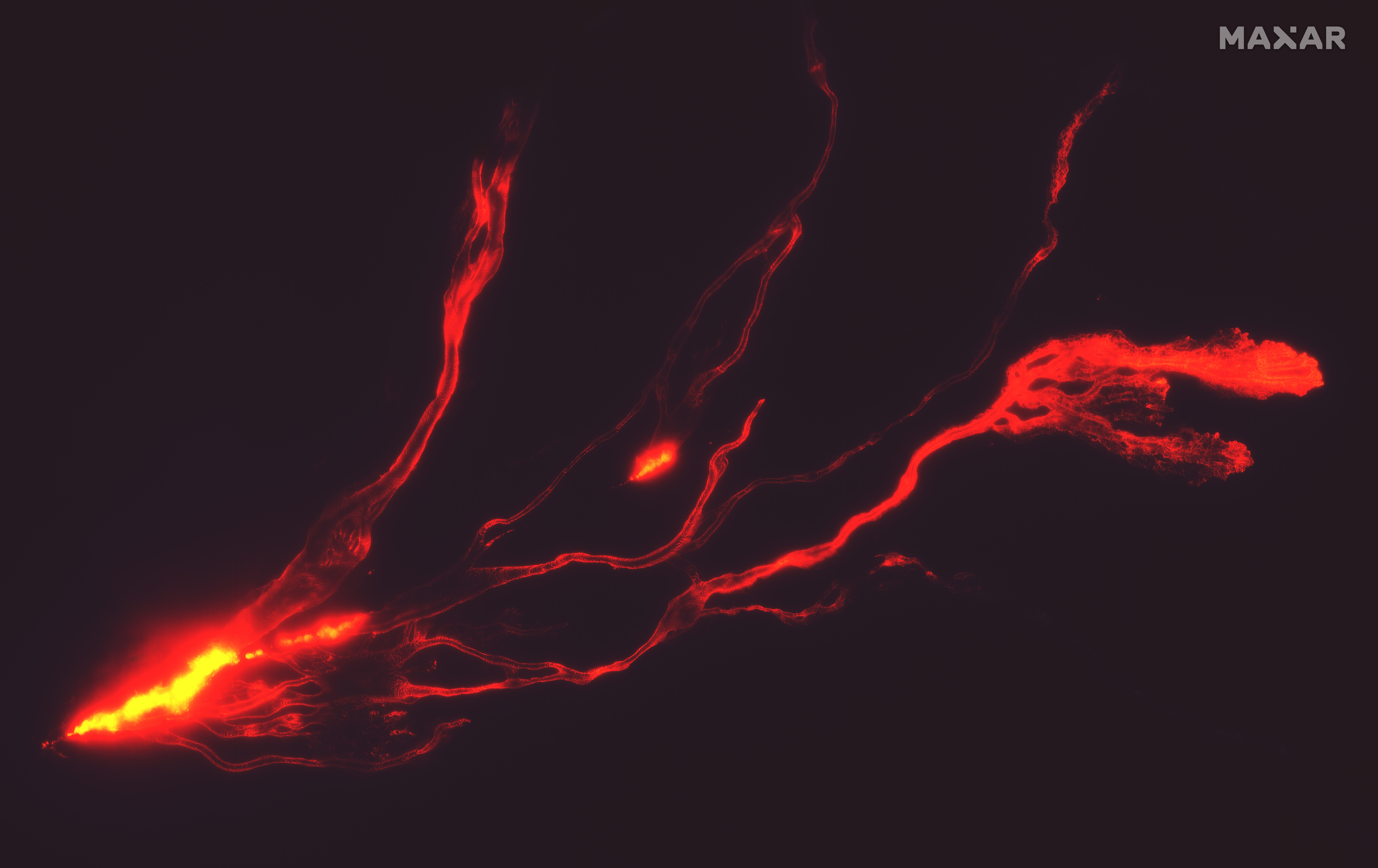
Satellite image of the eruption on November 28 2022. Image credit: Satellite image ©2022 Maxar Technologies
Mauna Loa is the world’s largest active volcano. It has previously erupted 33 times since modern record-keeping began in 1843, according to the USGS. The volcano’s last eruption was in 1984, when a lava flow came within 7.2 kilometers (4.5 miles) of Hilo, the island’s largest population center.
As it stands, there is no immediate risk to populated areas, although the USGS has designated the eruption as a “code red”, meaning “hazardous eruption is underway or suspected with significant emission of volcanic ash into the atmosphere.”
It has already been causing a fair bit of disruption though. The area is home to the Mauna Loa Observatory which has been monitoring the concentration of carbon dioxide in Earth’s atmosphere for over 60 years. . Researchers at Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego, which manages the observatory, have said that their equipment lost power on Monday and is not currently recording data. The situation is so severe they are looking into relocating the measurement equipment.
“It’s a big eruption and it’s in a bad place,” said Scripps Oceanography geoscientist Ralph Keeling, son of Charles David Keeling who invented the famous Keeling Curve, the daily record of global atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration.
Source Link: The Mauna Loa Volcano Eruption Looks Formidable From Space