The internet is full of hacks and tips on how to best pack your suitcase for a vacation, but what about those of us who crave chaos? Is there a way to rationally and systematically fill a space in the worst way possible? The answer is yes – and thanks to a recent proof, we’re getting closer to figuring out exactly how.
“We use[d] optimal control theory to prove that the most unpackable centrally symmetric convex disk in the plane is a smoothed polygon,” explained Thomas Hales, Professor of Mathematics at the University of Pittsburgh and co-author of a new book containing the proof, in a May blog post.
“Our book proves what [renowned mathematician Kurt] Mahler set out to prove: Mahler’s First conjecture on smoothed polygons,” he wrote. While not yet peer-reviewed, initial reactions from other mathematicians seem to be positive regarding the result’s validity.
So what does all that mean? Well, let’s start with some terminology.
First, we have “most unpackable”, which sounds awkward af, we know. It’s a technical term, though: the more unpackable a shape is, the less dense a packing of it is able to be. To put it another way, one shape is more “unpackable” than another if a tessellation of it will leave more space uncovered.
Then we have “centrally symmetric convex disk.” This describes the shapes we’re considering – the most important bit is the “convex disk” bit, which specifies that any two points inside the shape can be connected by a straight line that’s also contained entirely within the shape. Without this detail, we could create all kinds of weird Taskmaster-style workarounds that leave virtually all of the space uncovered, and that – well, that’s cheating, isn’t it?
Centrally symmetric, meanwhile, means that a point is located inside the shape if and only if its reflection through the center is also. It’s not a necessary condition for the problem – it’s just a way to reduce the number of possible shapes, making the question easier to tackle.
That’s an important point, by the way: this is, despite its glib appearance, an incredibly difficult problem. “I knew this problem was hard going into it, but there was always more structure that you could unravel,” Koundinya Vajjha, co-author of the book along with Hales and now an engineer at Intel, told Quanta.
“It was always the case that there was just six months more,” he said. “We could never know when this problem would fight back and stay unresolved for another century.”
In fact, the pair took so long on this potentially unsolvable problem that Vajjha progressed from grad student to employed engineer before a conclusion was reached. But then, Hales had an epiphany: they may not be close to proving the original problem they had set out on, but they were almost there on a related one – namely, that conjecture by Mahler, which posited that the worst such shape would be a smoothed polygon.
“A smoothed polygon is a polygon whose corners have been rounded in a special way by arcs of hyperbolas,” Hales explained in his blog. Or, more evocatively:
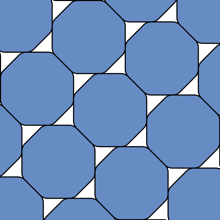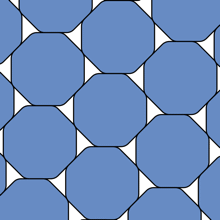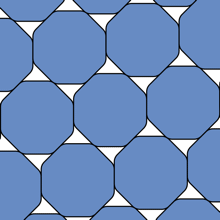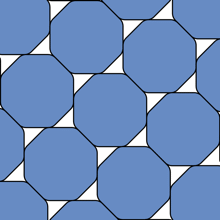
A smoothed octagonal packing.
By reformulating a theorem by Minkowski regarding the geometry of numbers, the pair was able to apply it to their packing problem by investigating one particular aspect of the statement: “To improve Minkowski’s theorem, it was natural to ask how much the constant of Minkowski’s theorem might be improved to a smaller constant,” Hales wrote.
“There is no improvement if K is a parallelogram or centrally symmetric hexagon, because these polygons tile the plane,” he explained. “What choice of K gives the constant improving Minkowski’s theorem by the most? […] We prove that in dimension 2, the constant d(K) is minimal for some smoothed polygon K.”
In other words, Mahler was right: the most unpackable shape is a smoothed polygon. But which one?
Well, people have made guesses. The mathematician Karl Reinhardt showed in 1934 that circles weren’t as unpackable as a smoothed octagon – the latter covering at maximum 90.24 percent of a surface, while the former reaches the heady heights of 90.69 percent – and he, along with Mahler, believed this to be the answer.
Many other mathematicians agree: “I’ve always believed that Reinhardt is probably right but that the theory was not there to attack this problem,” mathematician Henry Cohn, who was not involved in the research, told Quanta. But “were we ever going to see a proof? Probably not in my lifetime,” he added.
And, so far, he’s correct. While the book makes a big leap towards solving the problem of how worst to pack a suitcase, the question is still only half answered.
“Reinhardt’s conjecture asserts that the smoothed octagon is the centrally symmetric convex K with the property that its densest lattice packing is the least,” Hales concluded.
“This problem is still unsolved in general,” he wrote, “but our result gives the best known result in this direction.”
The new book, currently not peer-reviewed, can be read on the ArXiv preprint server.
Source Link: The Worst Way To Pack A Suitcase, According To Math (Is Actually Still A Mystery)