Hurricanes, cyclones, and typhoons regularly stir up a storm around the tropical stretches of our planet, raising hell wherever they may fall. However, it’s a curious fact that they very rarely approach the equator and – stranger still – never cross it.
First things first, some terms need to be cleared up. Hurricanes, cyclones, and typhoons are all the same phenomenon, but their names differ depending on where on the planet they are occurring: hurricanes in the North Atlantic and northeast Pacific, typhoons in the West Pacific, and cyclones in the Indian Ocean. To make things easier to follow, we’ll simply be calling all of these tropical storms “hurricanes” in this article.
Hurricanes are like a vast spinning turbine fueled by warm, moist air. They tend to form in tropical seas where the waters are above 26°C (79°F).
The air above the sea surface becomes heated by the warm waters, causing it to rise and cool, forming clouds and thunderstorms. The rising of the air also causes a pocket of low pressure to form underneath, which causes air to rush in.
Together with the help of wind, these conditions can cause a storm to enter a spin. Eventually, the mounting clouds above release their rain and dump heat to the surface, further fueling the storm below.
The direction of the wind and the hurricane’s spin is dictated by the Coriolis force, the inertial spinning of an object that’s caused by the rotation of the Earth. In the Northern Hemisphere, the spin of the Earth causes air to be pulled counterclockwise, which results in hurricanes that spin counterclockwise. In the Southern Hemisphere, the opposite happens and they spin clockwise.
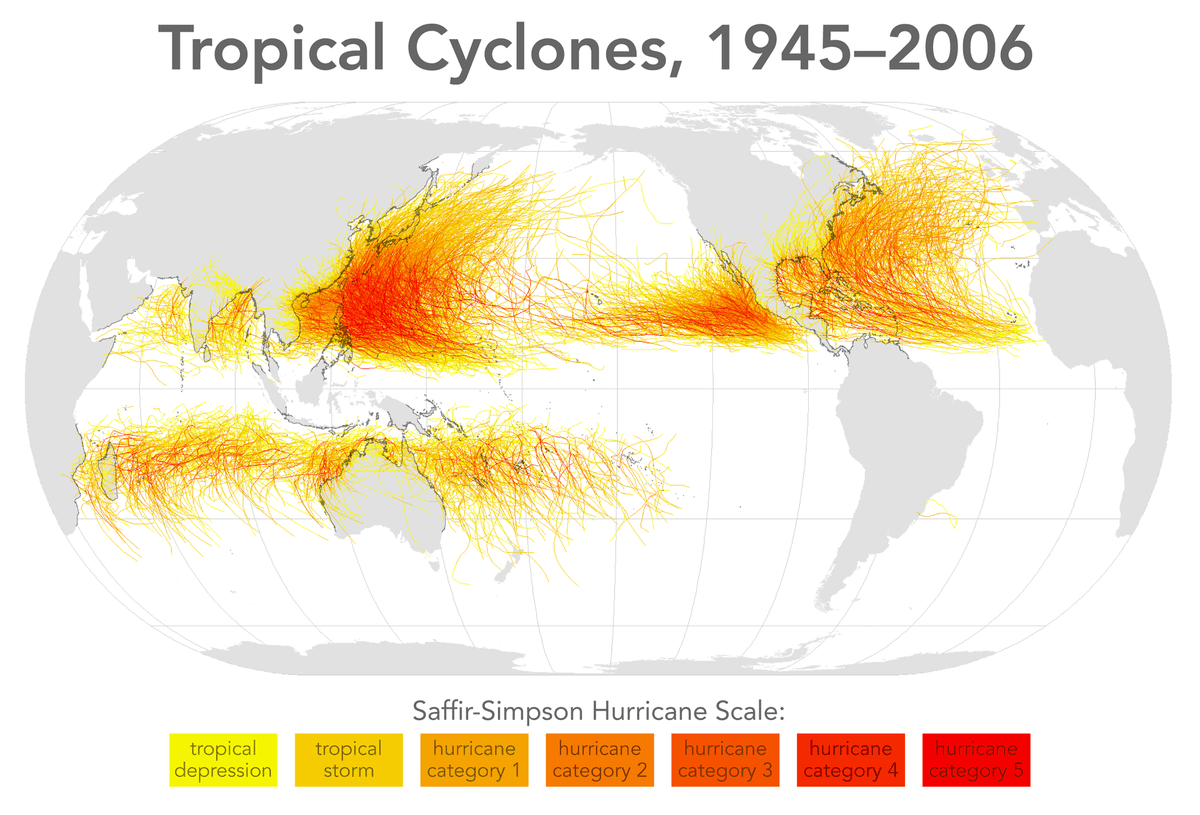
Although they thrive on balmy tropical waters, hurricanes rarely form within 300 kilometers (about 186 miles) of the equator. In 2003, Typhoon Vamei was seen spinning just 150 kilometers (about 93 miles) north of the equator, but that was a real exemption that happens less than once in a century.
They don’t generate near to the equator because there is no Coriolis effect here, meaning patches of stormy weather don’t tend to “spin up” into a hurricane.
Likewise, we don’t see hurricanes cross the equator as it would effectively mean they’d have to stop spinning, reverse direction, and spin in the other direction to continue.
Hypothetically, it might be possible for a hurricane to overcome this. Gary Barnes, Professor of Meteorology at the University of Hawaii, explained that it is theoretically possible for a “well developed storm” to be strong enough to continue its momentum over the relatively weak Coriolis force and push through to the equator.
However, Professor Barnes and others have noted that they have never come across an example of this happening in the real world.
[H/T: Reddit TIL]
Source Link: There's A Weird Reason Why Hurricanes Never Cross The Equator