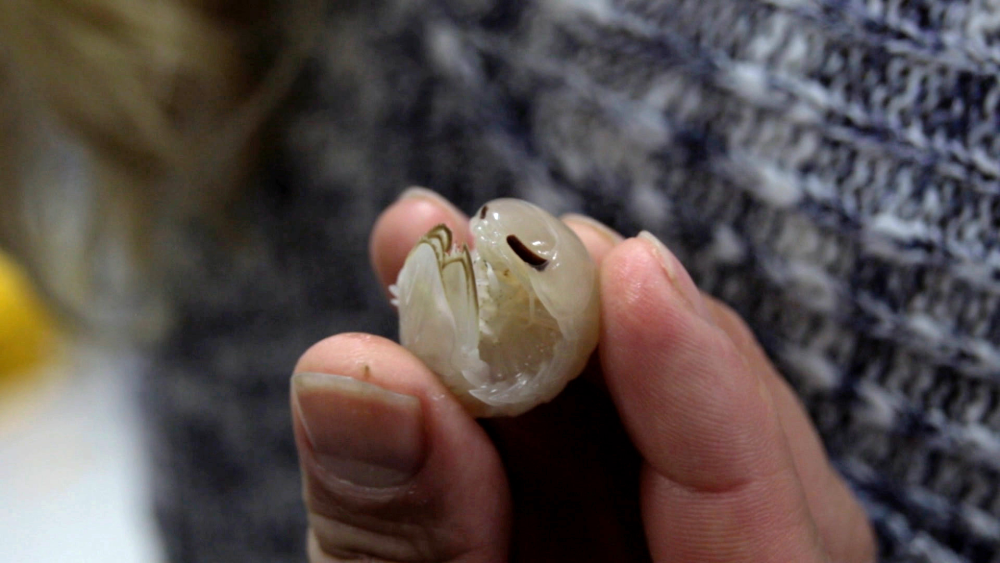
A new species of giant deep-sea isopod has been identified in the Bahamas after researchers with OceanX deployed traps on the seabed. A cousin of the much beloved terrestrial roly-poly pill bugs, they serve a similar ecological role in the nutrient cycle, making them a vital part of the ecosystem.
These alien-like critters have see-through bodies and big buggy eyes that help them search for prey in the gloomy depths. If you’re wondering what a roly-poly on steroids eats 600 meters (1,969 feet) below the sea, they’re partial to sea cucumbers, sponges, and nematodes, but will also scavenge any morsels that rain down from above.
The new species was discovered during a 2019 mission led by OceanX and the Cape Eleuthera Institute that deployed baited eel traps and light traps in the Exuma Sound at depths between 540 and 656 meters (1,172 and 2,152 feet). At sizes between 4 and 6 centimeters (1.5 and 2.4 inches), they’re described as large compared to other species in their genera, most of which are less than 3 centimeters (1.2 inches).
It’s dangerous to go alone! Take this.
Images courtesy of OceanX
The chonky boi has been named Booralana nickorum, named after two family members of study senior author Edward Brooks. It joins two other species from the marine Cirolanidae to be discovered in the Caribbean region since 2010: Bathynomus maxeyorum and Bathynomus yucatanensis.
Its segmented body is protected by a hardened exoskeleton which is white at a push, but nearing translucent. There’s no need for flashy coloration when you live in a habitat that’s almost completely devoid of light.
You can see its guts and things,” study co-author Nicholas Higgs told Live Science. According to Higgs, who is director of research and innovation at the Cape Eleuthera Institute, it was clear to the team that the new species was “definitely different from anything we’ve seen before” when they first observed it onboard the research vessel.
The isopod’s discovery comes as part of an OceanX mission that was focused on identifying both deep-sea and mid-water species, testing 3D models of little-known organisms, investigating the expansion and feeding state of sargassum falls (seaweed on the ocean floor), and satellite tagging bluntnose six-gill sharks at depth.
And if you get a new-to-science species of giant see-through isopod to boot? As they say, there are many benefits to being a marine biologist.
The study is published in Zootaxa.
Source Link: This Freaky Deep-Sea Creature Has Been Hunting In The Dark For 300 Million Years