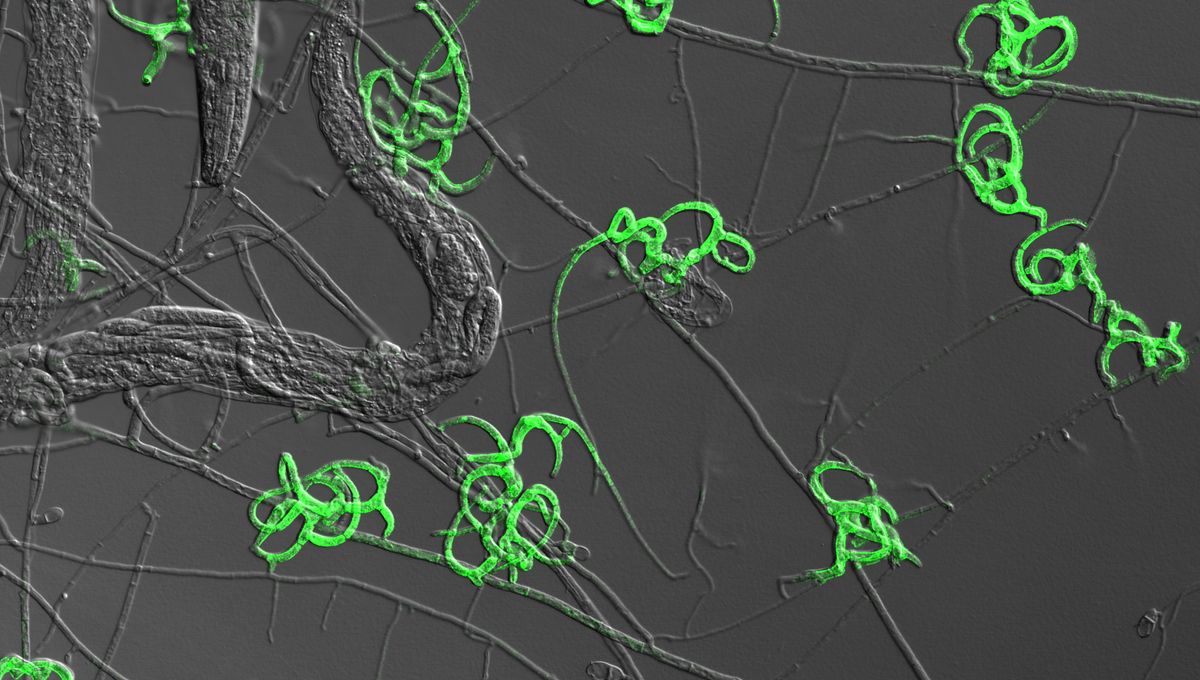
Think fungi can’t be carnivorous? Think again. Arthrobotrys oligospora is a worm-eating species of fungus that has been found to be capable of sensing, trapping, and consuming very small animals. Now, new research has illuminated some of the molecular changes that enable its predatory lifestyle.
First discovered in 1850, Arthrobotrys oligospora isn’t the only worm-eating fungus in the world, but it is the most common. Without the muscle for taking on girthy earthworms, its preferred prey is mini bites like the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, which was volunteered as tribute in a new study into A. oligospora’s feeding strategy.
Most of the time, the fungi’s main source of nutrients is decaying organic matter, but when A. oligospora, it can switch to a carnivorous diet and eat tiny animals. Researchers observed such predation interactions in a series of lab experiments that combined with sequencing techniques revealed some of the molecular underpinnings for the fungi’s diet and activity.
DNA replications and the production of ribosomes (the structures that build proteins in cells) both increase when A. oligospora senses delicious worms nearby. Shortly after, the fungi’s genes get busy increasing the production of proteins that are crucial to worm trapping, such as adhesive nobs and networks that entangle and immobilize nematodes, and a group of “trap enriched proteins”.
Trapping a worm in your fungus prison is one thing, but next a fungi’s gotta eat. Here, researchers observed that A. oligospora uses filamentous structures called hyphae to effectively burrow into the worm and digest it.
The consumption of worms was associated with an uptick in activity for the genes that code for proteases, a group of enzymes that can break down the peptide bonds of proteins. This was particularly true for a group known as the metalloproteases, suggesting these may be crucial for worm digestion.
“Our comprehensive transcriptomics and functional analyses highlight the role of increased DNA replication, translation, and secretion in trap development and efficacy,” concluded the authors. “Furthermore, a gene family that is largely expanded in the genomes of nematode-trapping fungi were found to be enriched in traps and critical for trap adhesion to nematodes. These results furthered our understanding of the key processes required for fungal carnivory.”
It might sound a little savage for a fungus to be eating worms, but nematode-trapping fungi play an important ecological role as one of their natural predators, helping to maintain the balance of microorganism ecosystems and nutrient cycling. Bon appétit, you crazy fungi.
The study is published in the journal PLOS Biology.
Source Link: This Predatory Fungus Sets Deadly Traps When It Senses Worms Nearby