Feathers, scales, spines, and hair are all examples of keratinized skin appendages developed by vertebrates. They are very different from each other, but they share early developmental processes during the embryonic stages. Researchers at the University of Geneva have now worked out that it is surprisingly easy to grow feathers where there should be scales, just by affecting one gene’s expression.
All the keratinized skin appendages develop from a localized thickening on the skin surface and the expression of particular genes. An important one has a silly name: Sonic hedgehog (Shh). The name came from the discovery that a mutation on it gives drosophila larvae multiple points, a bit like the spines of a hedgehog. When activated this pathway, allows chickens to grow feathers where they usually do not.
‘‘Our results indicate that an evolutionary leap – from scales to feathers – does not require large changes in genome composition or expression. Instead, a transient change in expression of one gene, Shh, can produce a cascade of developmental events leading to the formation of feathers instead of scales,’’ corresponding author Dr Michel Milinkovitch said in a statement.
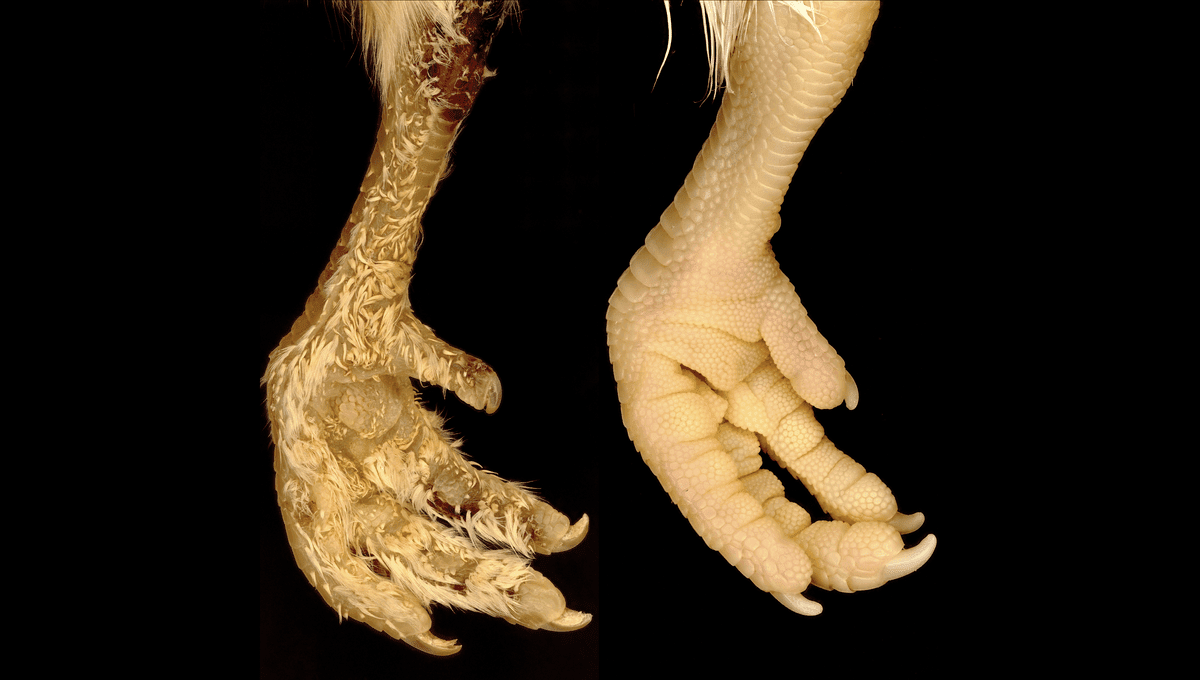
There are some chicken varieties with feathers on their feet but it is not a common trait. And why some have it and most don’t is not exactly fully understood. The researchers observed that a single treatment on chicken embryos when they are still in the egg is enough to trigger the formation of feathers on their feet.
“We used the classic technique of ‘egg candling’, in which a powerful torch illuminates blood vessels on the inside of the eggshell. This allowed us to precisely treat chicken embryos with a molecule that specifically activates the Shh pathway, injected directly into the bloodstream,’’ explained first author Dr Rory Cooper, a post-doctoral researcher in Michel Milinkovitch’s laboratory.
The two scientists also treated embryos with a control solution that did not activate the Shh pathway. RNA analysis showed that in the group that got the Shh-activating molecule, the pathway was activated immediately and persistently, creating feathers like those on the rest of the body. These are regenerated when lost and automatically replaced when the chick becomes an adult.
The work shows that the Shh pathway is key to the transformation of scales into feathers. The diversity of the various skin appendages in nature, as well as the evolution of birds from avian dinosaurs, likely pass through this pathway.
The work was published in the journal Science Advances.
Source Link: Turning Scales Into Feathers Is A Lot Easier Than We Thought