Pseudocraters or rootless cones are peculiar volcanic formations with an explosive origin. They do not form from magma coming from deep underground. They are caused by lava covering a water-rich layer, which causes the explosive reaction. To fully understand the mechanism of their formation, scientists have devised an experiment with simple cooking ingredients not too dissimilar from the basic soda volcano you might have made in school.
ADVERTISEMENT GO AD FREE
These rootless cones might not be very common but our need to understand their formation stretches beyond Earth. Iceland has many of these craters ranging from several meters to several hundred meters in diameter. Some are found around the Big Island’s coast in Hawai’i, but it is on Mars that these geological features have their greatest numbers. Vast fields of them have been seen from orbit.
The real scenario has lava with a temperature of more than 1,000°C (1,800°F) covering rivers, lakes, or some other water-rich resource. The lava boils the water very quickly, and the pressure of the water vapor increases to the point that it can’t do anything but push the lava apart in an explosion.
This might not be your typical school experiment, but the researchers used the same crucial ingredient you might have: baking soda AKA sodium bicarbonate. In the traditional volcano setup, the foaming is achieved with the use of an acid (vinegar/lemon juice). The chemical reaction releases carbon dioxide in that foamy way. Baking soda can also release carbon dioxide at high temperatures, which is why it is used as a leavening agent in cakes and cookies.
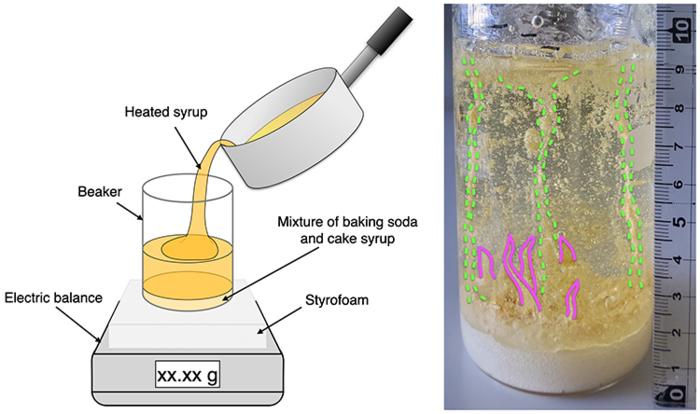
A schematic of the experiment and one of the beakers with the rootless cones formed.
Image Credit: Niigata University
The team used the approach of making karumeyaki (Japanese honeycomb toffee), which is similar in principle to how honeycomb candy is made across the world. They used a mixture of starchy syrup and baking soda as the water equivalent. On top of that, they poured hot syrup. The baking soda breaks apart, liberating carbon dioxide and creating little explosions. By varying the thickness of the layer of hot syrup, the team created various scenarios.
The distribution of the rootless cones depended on what the study called conduit competition. More conduits between the water layer and the surface mean a larger chance that they would fail to reach the surface. This is consistent with what is seen on Mars – where the lava is thicker, there are fewer pseudocraters.
“We observed that conduits often failed to maintain their structure because they were disrupted by nearby forming conduits,” explained Associate Professor Rina Noguchi in a statement.
ADVERTISEMENT GO AD FREE
A paper describing the results is published in the Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research.
Source Link: Twist On The Volcano Experiment You Did In School Reveals Something Important About Mars