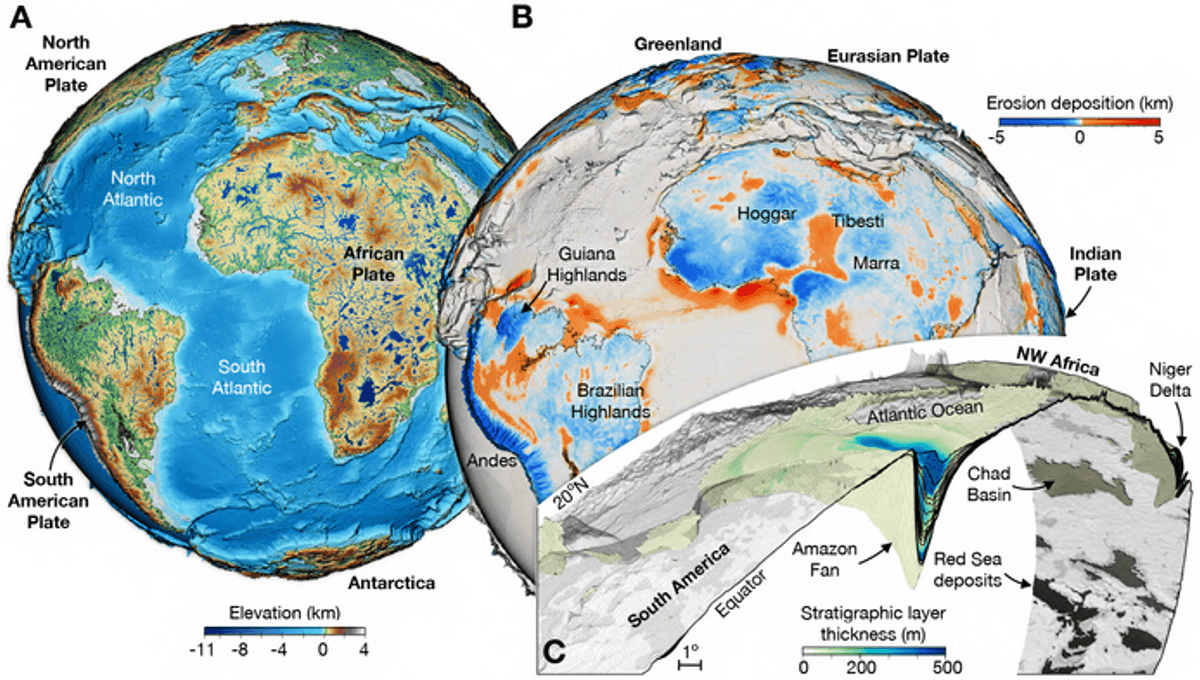
A new geological model, the most detailed yet, has enabled us to peer back in time over the past 100 million years of the Earth’s surface. As you might expect, a lot has changed in that time, the details of which will further our understanding of the Earth’s geophysical landscape as we know it today and may even reveal what’s in store for our planet in the future.
“To predict the future, we must understand the past,” lead author Dr Tristan Salles, from the University of Sydney School of Geosciences, said in a statement. “But [existing] geological models have only provided a fragmented understanding of how our planet’s recent physical features formed.”
The new model rectifies that: it provides the first-ever high-resolution understanding of the complex interplay between plate tectonics, climate, and time that has shaped the face of our planet. It also factors in the roles of river basins, global-scale erosion, and sediment deposition, which previous models have failed to account for in such detail, Salles added.
“This is a big advance.”
The model has achieved an “unprecedented” resolution of about 10 kilometers (6 miles) over the last 100 million years, broken down into million-year increments, as you can see above. This will allow geoscientists a “more complete and dynamic understanding of the Earth’s surface,” according to second author Dr Laurent Husson from Institut des Sciences de la Terre.
“Critically, it captures the dynamics of sediment transfer from the land to oceans in a way we have not previously been able to.”
This “transfer” refers to the millions of tonnes of eroded sediment that have been swept into the oceans from mountaintops over millions of years. The flow of debris plays a role in regulating the Earth’s carbon cycle and climate fluctuations, so getting to grips with its past variation is imperative if we want to better understand past and predict future climate change.
“Given that ocean chemistry is changing rapidly due to human-induced climate change, having a more complete picture can assist our understanding of marine environments,” Salles said.
It will also allow scientists to test out hypotheses as to how the Earth’s surface will respond to future climatic or tectonic changes, as well as to investigate other features of the Earth system, including biogeochemical cycles or biological evolution.
The study was published in the journal Science.
Source Link: "Unprecedented" Model Provides Most Detailed Glimpse Yet Of Earth's Last 100 Million Years