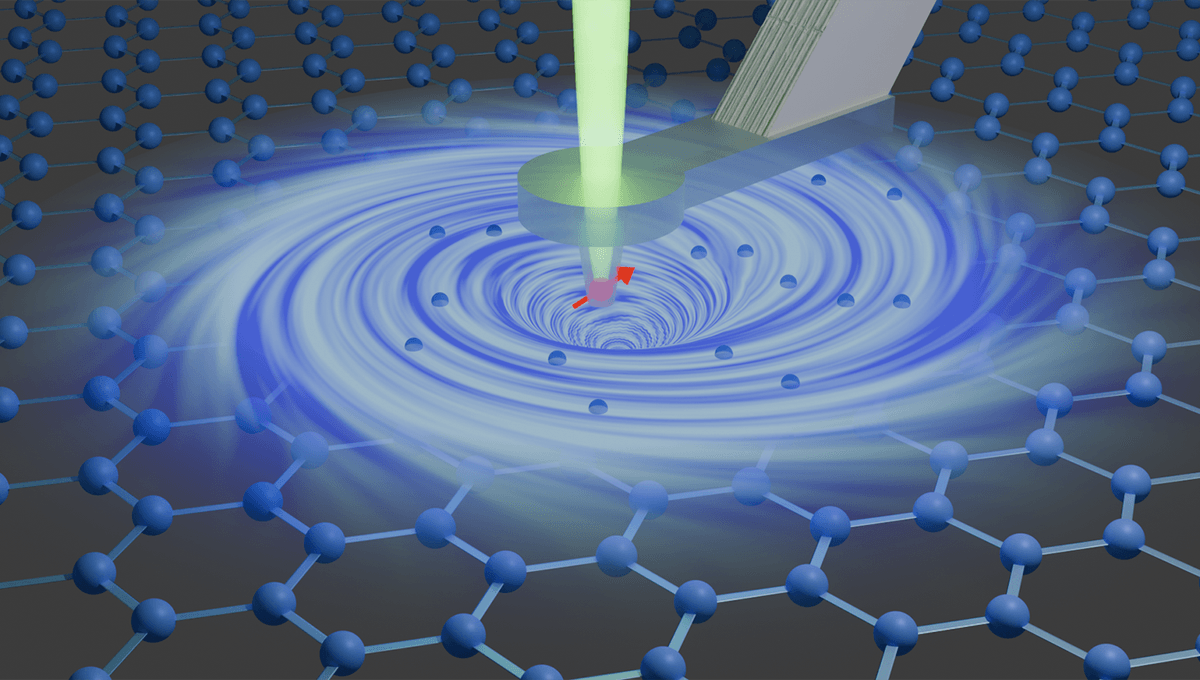
Graphene is a very weird material. It’s a single layer of carbon atoms organized in a honeycomb lattice. It has incredible strength and can conduct heat and electricity in a record-breaking way. The conductivity is based on the fact that electrons in the material behave like a viscous liquid. And like in any liquid, vortices can form.
However, believing that something should happen and seeing it is a whole different thing. Researchers had to use a high-resolution magnetic field sensor. This device allowed them to track the behavior of electrons. The vortices are usually best seen at extremely low temperatures but the device was good enough to spot them even at normal room temperature. Researchers had never seen these electron vortices in graphene before.
Observing the vortices meant observing the movement of the electrons in a detailed way. They tracked the tiny magnetic fields that the electrons flowing in graphene produce.
The test subject was set up as follows: a strip of graphene 1 micron wide was attached to circular disks of either 1.2 microns or 3 microns. Theoretical calculations suggest that vortices will appear in the smaller disk but not in the wider.
“Thanks to our extremely sensitive sensor and high spatial resolution, we didn’t even need to cool down the graphene and were able to conduct the experiments at room temperature,” Dr Marius Palm, from ETH Zurich, said in a statement.
What the team saw was a reversal of the flow of the electrons (typical of how stuff in a vortex moves). As predicted, this effect was only visible in the smaller disk. In the larger one, the electrons flowed with no problem whatsoever.
The magnetic sensor is a diamond needle with a defect at its tip, known as a nitrogen-vacancy. By employing laser beams and microwave pulses, the needle can be extremely sensitive to external magnetic fields. However, they need to be very close to the graphene strip to pick up the magnetic fields of the electrons.
“Because of the tiny dimensions of the diamond needle and the small distance from the graphene layer – only around 70 nanometres – we were able to make the electron currents visible with a resolution of less than a hundred nanometres,” Palm explained.
One hundred nanometers might not seem like an incredible resolution for a strip of one micron (or 1,000 nanometers) across. But it is an important starting point for this work. There is much to find out about the behavior and cause of the vortices but being able to see them is first among the list.
“At this moment, the detection of electron vortices is basic research, and there are still lots of open questions,” added Palm.
A paper on the breakthrough is published in the journal Science.
Source Link: Vortex Of Electrons Seen In Graphene At Room-Temperature For First Time