For the first time ever, you can watch a virus enter a cell and infect it. Scientists from Harvard Medical School captured the live footage of engineered viruses doing their thing as they bound to living cells, and later injected their genomes into them.
Their findings are published in the journal PNAS.
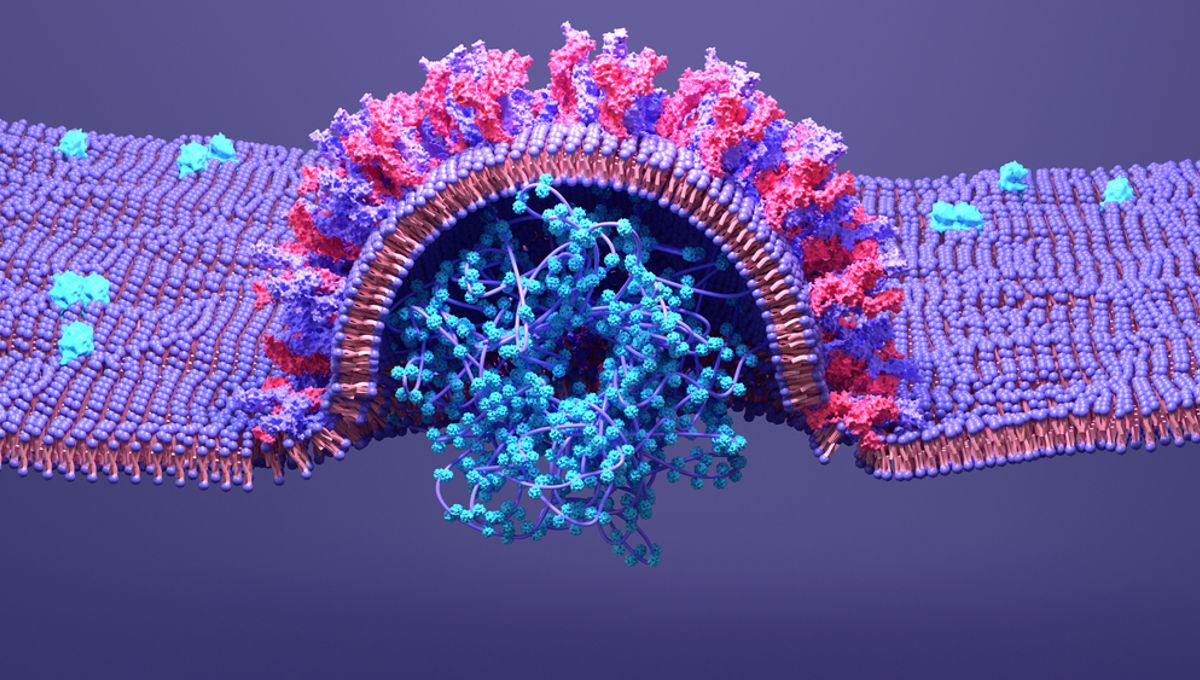
Viruses infect cells by releasing their genetic material (RNA) into the cytosol – a semi-fluid substance inside cells. The RNA can then enter the nucleus, where it is replicated before being translated to viral proteins outside of the nucleus by ribosomes. These proteins can then assemble to form a new viral particle, which is released from the cell and can go on to infect other cells in the body.
However, before this can happen, the virus needs to enter the cell in the first place. It does this via a process called endocytosis. First, the virus binds to its target cell, before it is engulfed by the membrane, forming a new cellular compartment called an endosome. It’s from the endosome that the RNA is released into the cell.
Now, we can watch these two processes in action.
In the first half of the video, you can see the virus (labeled pink) fusing to the cell membrane, which then forms an endosome. As the virus binds to the endosome membrane, you can see it injecting its RNA (labeled in blue) into the cytosol. These are the first steps of viral infection, seen for the first time in real-time and in three dimensions.
In the second half of the video, you can see several of the pretty pink viruses chilling inside the cell.
To achieve this, the researchers engineered viruses to express SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins – the part of the virus responsible for COVID-19 that allows it to enter cells. They also modified the virus so that the spike protein (labeled “S” in the video) could be tracked separately to the viral contents, which were themselves labeled with a fluorescent protein (“P” in the video).
The whole process was filmed using lattice light sheet microscopy – an advanced imaging technique.
On top of this impressive feat, the researchers also discovered that viruses only fuse with membranes and release their genomes under specific environmental conditions. They require a slightly acidic environment, between pH 6.2 and 6.8, similar to the pH of saliva and urine. Endosomes are also known to be similarly acidic, as is the human nose, the team discovered.
These acidic environments allow enzymes in endosomes or at the cell surface to cut the spike protein from the virus, which can then fuse to a membrane. This, the researchers suggest, is happening inside the nose, where COVID-19 infections often begin.
“Amusingly enough, measuring the pH of the nostril cavity has rarely been done before,” the paper’s co-senior author Tomas Kirchhausen remarked in a statement,
Source Link: Watch A Virus Infecting A Cell Caught On Video For The First Time Ever