Between 120,000 and 60,000 years ago, Neanderthals embarked on a second wave of major migrations from Eastern Europe to southern Siberia and Central Asia. Using supercomputers, anthropologists have now managed to track the path of that journey with incredible precision.
It’s known that Neanderthals made this journey based on archaeological sites in Eastern Europe dating to around 120,000 years old and others in the Altai Mountains of Mongolia from about 60,000 years ago. However, the vast region between these areas is marked by rugged mountain terrain, glacial barriers, and a notable absence of archaeological evidence from that period, leaving the exact migration route uncertain.
To find out more, two researchers from New York University and the University of Algarve attempted to identify a possible route using computer simulations that modelled the terrain, climate, and ancient river systems of the region. Their model essentially looked to find the path of least resistance, revealing where ancient travelers were most likely to have made the mass exodus.
The findings showed that Neanderthals could have used river valleys as natural highways to traverse the region. By following these river corridors via a northern route, it’s possible they moved around 3,250 kilometers (2,000 miles) from the Caucasus Mountains to Siberia in less than 2,000 years.
This rapid migration likely took place during warmer periods when environmental conditions were more favorable and glaciers no longer blocked the mountainous river routes. Based on the climatic data, this could have occurred during one of two ancient time periods: either around 125,000 years ago or approximately 60,000 years ago.
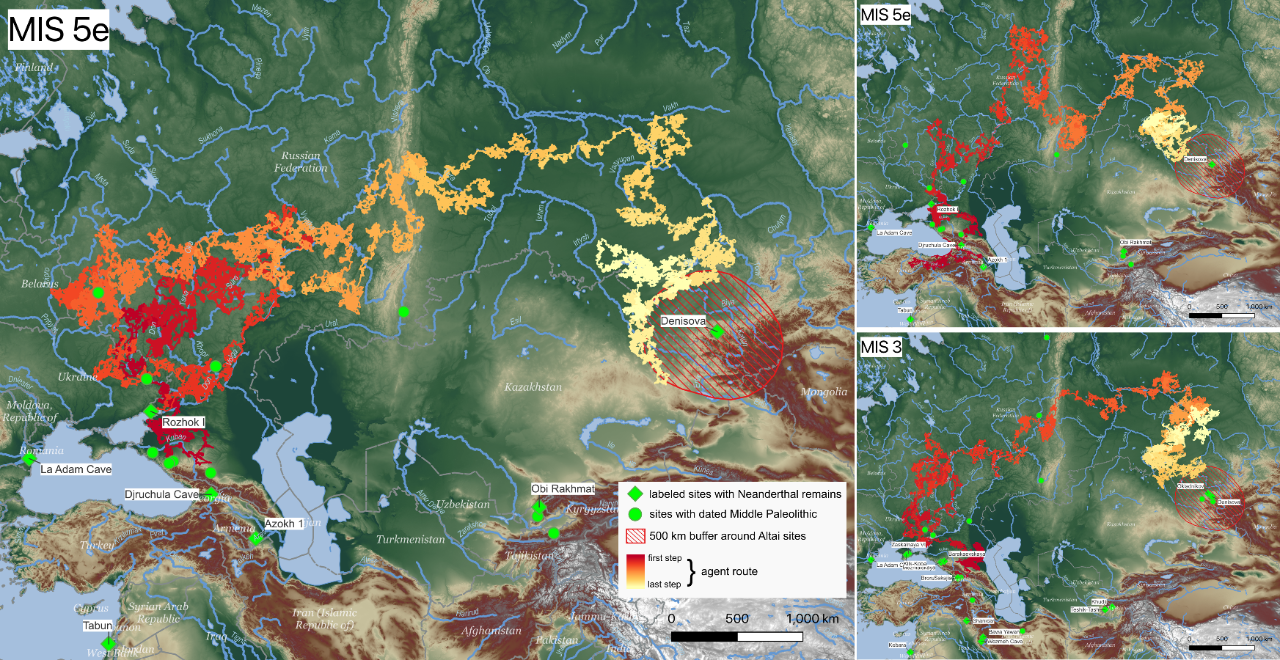
Computer simulations show Neanderthals could have reached Siberia’s Altai Mountains within 2,000 years during warm periods – either around 125,000 (MIS 5e) or 60,000 years ago (MIS 3) – via one of three possible routes.
Image credit: Emily Coco/Radu Iovita
“Our findings show that despite obstacles like mountains and large rivers, Neanderthals could have crossed northern Eurasia surprisingly quickly,” study author Emily Coco, who began the study as a New York University doctoral student and is currently a postdoctoral researcher at Portugal’s University of Algarve, said in a statement.
“Others have speculated on the possibility of this kind of fast, long-distance migration based on genetic data, but this has been difficult to substantiate due to limited archaeological evidence in the region. Based on detailed computer simulations, it appears this migration was a near-inevitable outcome of landscape conditions during past warm climatic periods,” added fellow author Radu Iovita, an associate professor at New York University’s Center for the Study of Human Origins.
This marked the easternmost extent of Neanderthal expansion before their extinction around 40,000 years ago. They inhabited a vast range across Europe, possibly reaching as far north as the Arctic, but their range in Asia ended around the Altai region, the modern-day intersection of Russia, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan.
However, archaeological evidence shows that Neanderthals did not just inhabit the northern route above the Caucasus Mountains. South of the Caspian Sea, another very important part of the Neanderthal story unfolded. In the Zagros Mountains of modern-day Iran and northern Iraq, Neanderthals prolifically interbred with prehistoric Homo sapiens, leaving a genetic legacy that still be seen today in most people with European or Asian heritage.
The study is published in the journal PLOS One.
Source Link: We Finally Know The Route Of Neanderthals’ Massive Migration Across Eurasia