The ancestor of all four-limbed creatures crawled out of the ocean around 400 million years ago. Then, 350 million years later, the ancestors of today’s whale species crawled back in. Its descendants that swim through Earth’s waters might be some of the largest and most talked about ocean species, with seriously impressive hunting techniques and an interesting modern history to boot, but how did they become the majestic ocean creatures they are today? We wind back the clock and explore the mysteries of whale evolution.
ADVERTISEMENT GO AD FREE
Surprisingly, the closest living relative to whale species is the hippopotamus, even they look nothing alike and have pretty different habitats, diets, and distributions. Despite their semi-aquatic lifestyle, how did one large land mammal come to be so closely related to the largest mammals of all?
Well, hippos are thought to have evolved from a non-aquatic group called the anthracotheres about 15 million years ago. Whales, on the other hand, evolved over 50 million years ago from creatures that lived on land. Somewhere way back in evolutionary history, hippos and whales would have shared a common ancestor that was also terrestrial.
One of the earliest terrestrial whale ancestors was an animal known as Pakicetus, known as the “first whale” or one of the first cetaceans. This was a creature that walked on four limbs, and is thought to have eaten both meat from land animals and fish. It was first discovered in 1983 and would have lived at the edge of the Tethys Sea in what is now Pakistan and India. The fossil revealed that it has a similar ear bone to modern-day whales, with a unique structure that could even have led Pakicetus to be able to hear underwater.
After Pakicetus evolved creatures that moved further into the water, adapting to this new environment. One of these was Ambulocetus, which lived roughly 50 to 48 million years ago. It had a long tail for swimming, spent time on both land and in the water, and still possessed four limbs.
After Ambulocetus, dorudontids and basilosaurids emerged around 40 to 33 million years ago. Basilosaurids had tiny hind limbs and their nostrils were further back, possibly an intermediate step between a snout and blowhole. Dorudon was a five-meter-long (16-foot) animal with tiny hind legs and flippers, that spent all of its time in the water, including while giving birth. There are other species that have been discovered to have lived during this time period too, such as this early whale from Senegal.
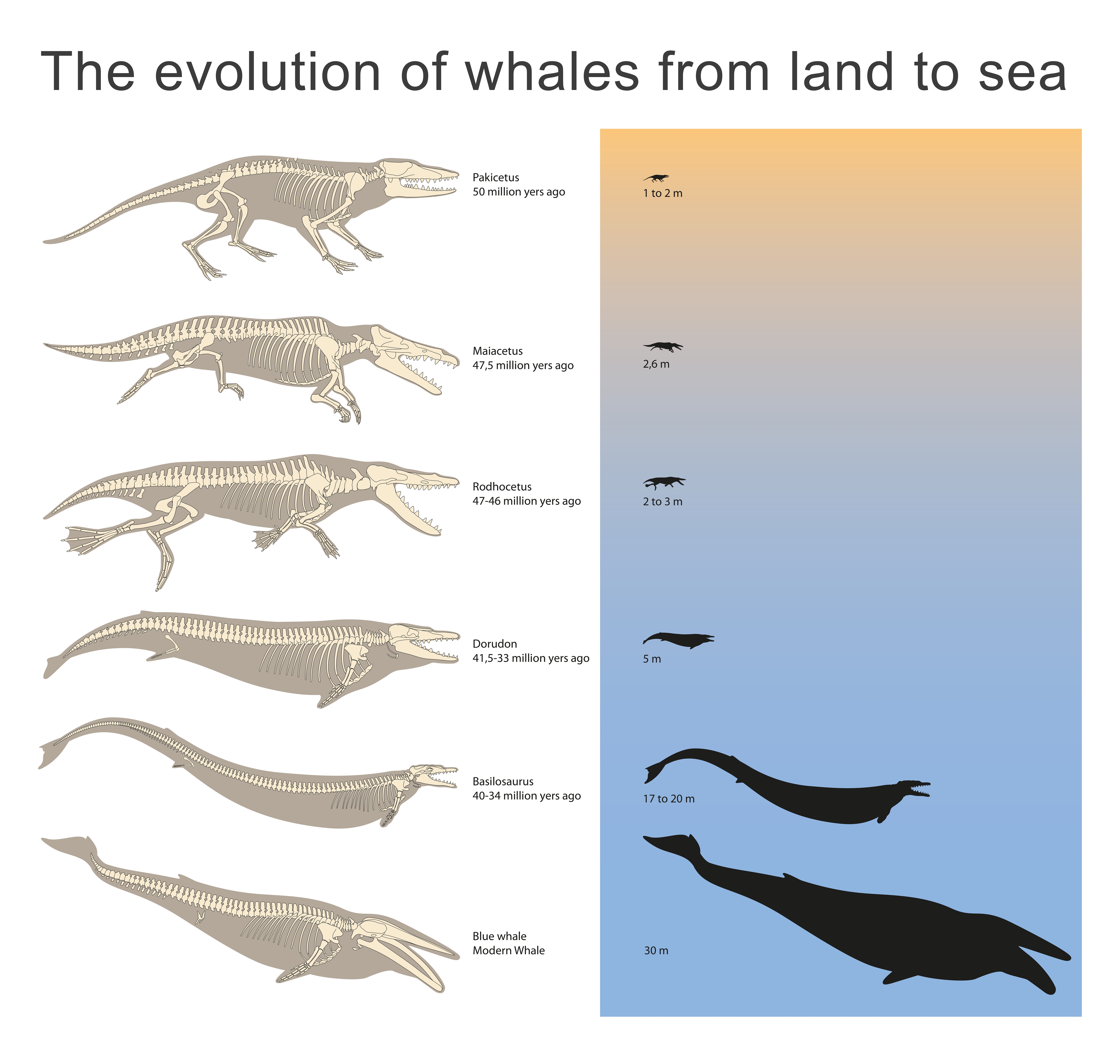
It took several hundred million years, but whales went from small, four-legged land mammals, to the giants of the sea we know today.
Image credit: Aldona Griskeviciene/Shutterstock.com
“Within eight million years, the ancestors of whales go from being fully terrestrial, such as the four-legged, furry Pakicetus which lived around the edge of the Tethys Sea, to fully aquatic,” explained cetacean researcher Dr Ellen Coombs in a 2022 statement about a study investigating whale evolution. “This is super quick in evolutionary terms.”
ADVERTISEMENT GO AD FREE
Dorudon’s descendants became modern whales. The baleen whales began to develop their filter-feeding with flatter skulls around 34 million years ago, while others retained their teeth and became the orcas, sperm whales, and dolphins of today. This was the split into the toothed whales, Odontoceti, and the baleen whales, Mysticeti, undergoing changes in their noses and faces to accommodate different diets.
Genetic research has revealed that alongside hind limbs and physical changes that can be seen in the fossil record, cetaceans lost a lot more than just legs when they transitioned back into water dwellers. Among other things, researchers have discovered that cetaceans have lost the gene to make saliva, which makes sense given their aquatic diets. Furthermore, they’ve found that toothed whales have lost most of their genes for smelling and taste.
Genetics can also help explain how modern whales became quite so big, a far cry from the goat-sized, land-dwelling ancestors they evolved from.
Source Link: Whale Ancestor Crawled Out Of The Sea 400 Million Years Ago – And Then Crawled Back In