When animals are killed by predators on land in the wild, there’s a good chance scavengers will descend upon the carcass pretty quickly, saving everybody the problem of burial.
The same is true in the ocean. Essentially, if there are predators out there who do not finish the whole meal, you better believe something will come to fit the “I’ll just take the scraps” niche. But some carcasses are more difficult to scavenge than others, which (along with mermaids) was the surprising subject of a viral X (Twitter) thread on Tuesday.
After whales die, they begin to decompose. Gases during decomposition can sometimes float the animal to the surface, where birds and sharks will attempt to tear out chunks, over the course of weeks or even over a month. But it isn’t easy for the animals. Despite using techniques such as vigorous head thrashing and shaking, and body rolling.
Generally, as noted by Kairo, who runs a popular science-based Instagram account, the methods are ineffective are getting to the tastiest parts of whales.
The thread suggests (for fun) that one mythical animal could perfectly fit this niche, and have itself an easy life opening up whales and scavenging on the gooey bits inside.
“MERMAIDS” They have hands! And teamwork! And tools!” Kairo suggests. “There is this unrealized potential to take on this deeply lucrative role of top scavenger that nobody else in the ocean seems to be able to fill.”
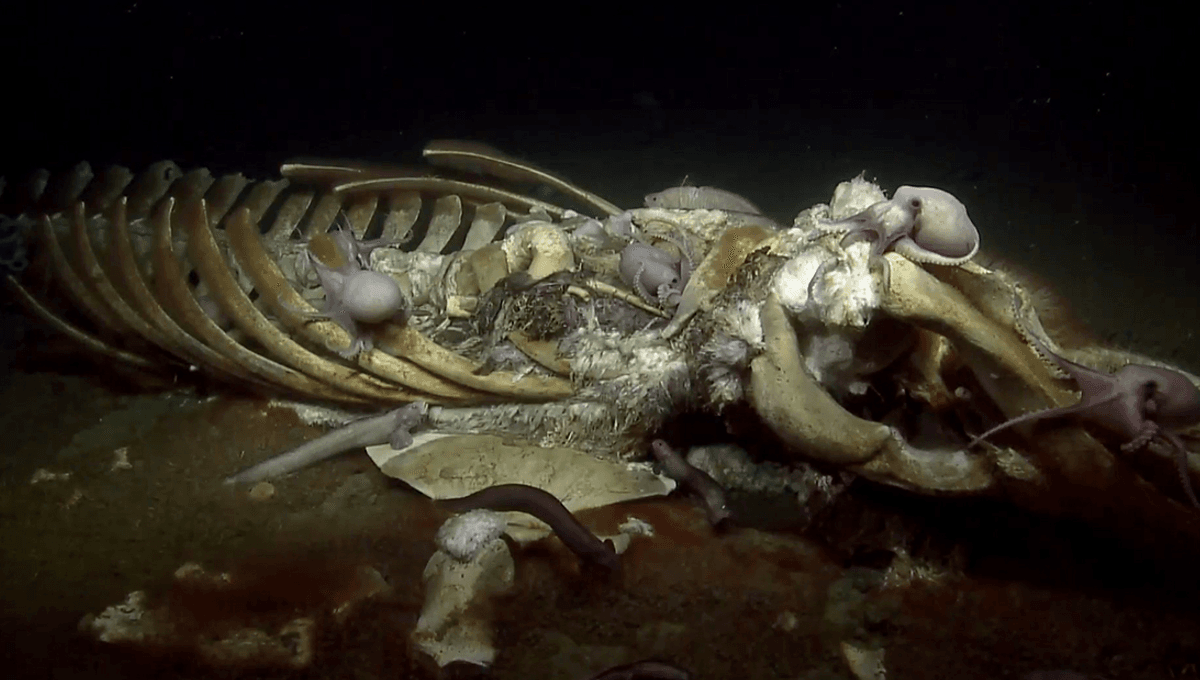
While a fun idea, whale carcasses are not going to waste as it is (other than the occasional time they are scattered for miles by overenthusiastic officials using way too much TNT). After weeks of bobbing around, they sink and can fall to the bottom of the ocean, where their decaying body will feed an ecosystem, known as a “whale fall”.
Scavengers tend to consume the soft tissues of the animal within months, while fragments of flesh feed nearby critters for over a year.
“The whale skeleton can support rich communities for years to decades, both as a hard substrate (or surface) for invertebrate colonization and as a source of sulfides from the decay of organic compounds of whale bones. Microbes live off of the energy released from these chemical reactions and form the basis of ecosystems for as long as the food source lasts,” the National Ocean Service explains. “At deep sea levels this forms a new food web and provides energy to support single- and multi-cell organisms and sponges, thus adding to the ocean’s food chain.”
While scavengers at the surface may struggle to get a share of the carcass, scavengers down below sure finish the job.
Source Link: Whale Falls: How Dead Whales Go On To Feed An Entire Ecosystem