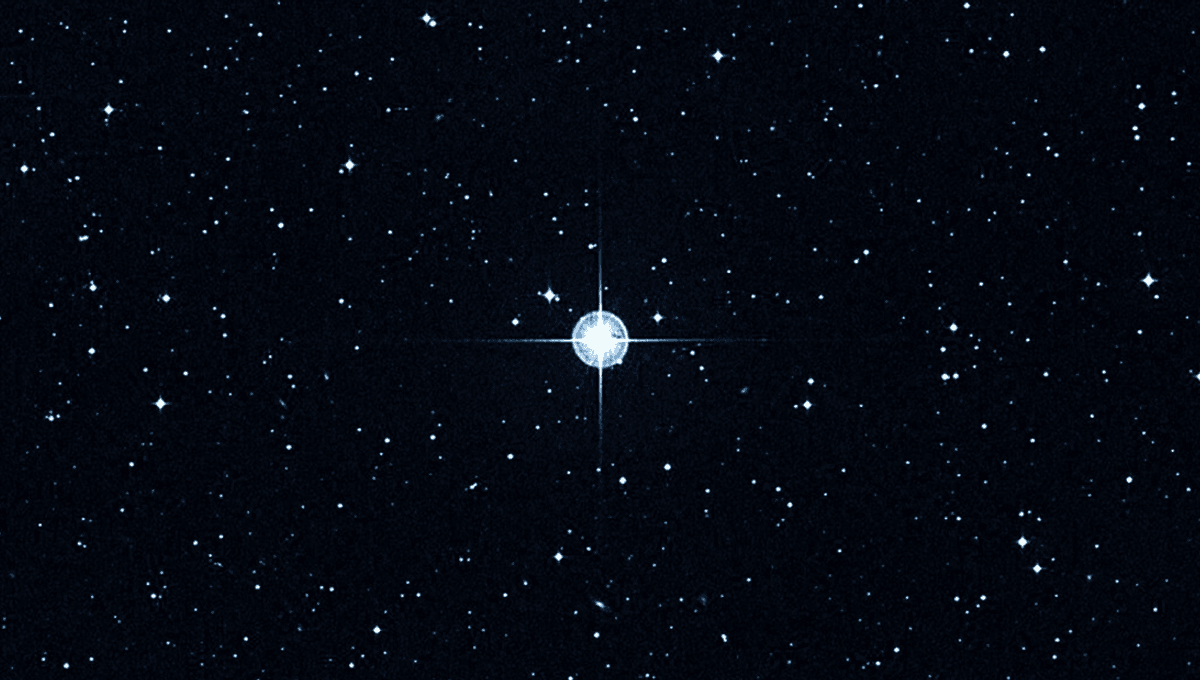
The Big Bang and the age of the universe have plenty of evidence behind them, from the temperature of the cosmic microwave background to the measured expansion of the universe. Through a lot of work over the last century, we now believe the universe to be around 13.8 billion years old.
But it would not take much to refute this idea. If we were to find a star that is definitively older than this, it would show that the universe was around before 13.8 billion years ago. Enter star HD 140283, looking suspiciously non-metallic.
HD 140283, better known as the Methuselah star, is around 200 light-years from Earth, in the constellation of Libra. It is known to be a high-velocity, sub-giant star, and one of the closest metal-poor stars to our Solar System.
“The high rate of motion is evidence that the star is simply a visitor to our stellar neighborhood,” NASA’s Hubble Mission team explains of the star. “Its orbit carries it down through the plane of our galaxy from the ancient halo of stars that encircle the Milky Way, and will eventually slingshot back to the galactic halo.”
In the 1950s, astronomers found HD 140283 to be very metal-poor compared to other stars in the neighborhood, suggesting that the star was formed earlier in the universe, before it had become “polluted” by heavier elements fused in the center of other stars. In the early 2000s, astronomers attempted to age it, and came up with an even more surprising result. According to their observations and analysis using stellar evolution models, the Methuselah star’s age was possibly around 16 billion years old.
The age of stars is pretty difficult to pin down, relying on measurements of their absolute brightness as well as their chemical abundances, and this was far from the final word on the topic.
“Maybe the cosmology is wrong, stellar physics is wrong, or the star’s distance is wrong,” Howard Bond of Pennsylvania State University in University Park and the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore said in a 2013 statement, after new measurements by the Hubble Space Telescope. “So we set out to refine the distance.”
That team refined distance measurements to the star, an important step in figuring out a star’s intrinsic brightness, which is fundamental in determining its age. Think of it like not knowing if you are seeing a torch held by an approaching stranger, or a very distant lighthouse. Placing the star’s distance at a refined 190.1 light-years, and finding that it had a higher-than-predicted oxygen to iron ratio, the team aged the star to be a much less universe model-breaking star.
“Put all of those ingredients together and you get an age of 14.5 billion years, with a residual uncertainty that makes the star’s age compatible with the age of the universe,” Bond said, adding, “This is the best star in the sky to do precision age calculations by virtue of its closeness and brightness.”
With uncertainty of around 0.8 billion years, at the lower end of the age estimate, it is at least not older than the universe is believed to be. Further studies have placed the star’s age between 13.7 billion and 12.2 billion years, with another suggesting between 11.5 billion years and 12.5 billion years.
The Methuselah star, named for the Biblical Noah’s grandfather, described as dying at the age of 969, is likely not older than the universe, nor evidence that we have the age of the universe horribly wrong. But it remains the oldest star we have found in the universe so far. There are other candidates, such as J22132050-5137385, which is thought to be around 13.6 billion years old, give or take 2.6 billion years. Further measurements of this and others could knock the Methuselah star off the top spot, or else refine the age estimate downwards.
Source Link: What's So Weird About The Methuselah Star, The Oldest We've Found In The Universe?