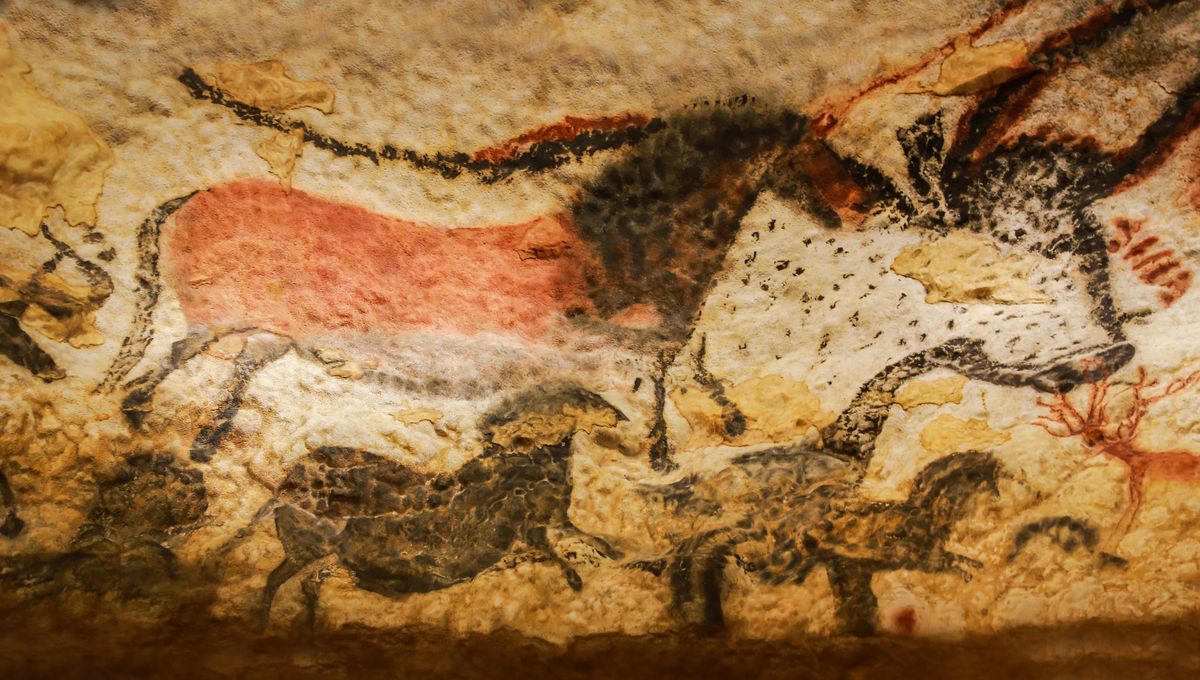
Human evolution is complex and fascinating, but it is filled with various terms and names related to past humans and hominin species that can get quite confusing. One example of this is the famous Cro-Magnon people who lived in Europe around the time of the last Ice Age (c. 40,000 to 10,000 years ago). Although they were initially named after the Cro-Magnon rock shelter in France where their skeletons were discovered in during the 1860s, scientists now refer to these people as Early Modern Humans (EMH) or Anatomically Modern Humans (AMH). So, who were they?
Discovery, naming, and renaming
The bones of the first five Cro-Magnon specimens were discovered in in 1868 while road construction was taking place in the Dordogne Valley in southwestern France. The remains identified at the site related to four adults and an infant. The rock shelter they were found in showed clear signs of occupation, including the placement of ornaments that included pendants and necklaces made from shells and animal teeth.
The inclusion of these features led researchers to initially believe the occupants had been deliberately buried in the shelter as if it was a single grave.
During this early research, scientists compared the skeletons to those of Neanderthals that had been discovered at sites in England and later in France. Through this comparison, they came to the conclusion that the Cro-Magnon specimens were distinct enough from these archaic humans to warrant their own designation. However, advances in anthropology and a shift in our understanding of human evolution and genetics eventually established that these people were fully modern humans and were indistinguishable from people today.
As such, the term “Cro-Magnon” was slowly phased out by the end of the 20th century as they were recognized as one group in a larger population of early modern humans who migrated across Europe, Asia, and Africa during the Upper Palaeolithic era.
Another reason why the name was changed was because the term “Cro-Magnon” did not refer to a specific taxonomy; it was the name of a cave and was considered too imprecise for palaeontology.
Physiology
Cro-Magnon individuals were anatomically similar to people living today. They had high foreheads, strong prominent chins, and slight brow ridges. They were generally taller than Neanderthals (in some cases the latter were up to 0.3 meters or 1 foot shorter) and their skeletons indicate they lived tough, physically demanding lifestyles.
Analysis of the skeletons found at the first rock shelter suggested these humans endured harsh environmental conditions. Cro-Magnon 1, the skull of an adult man found at the cave, shows signs of a fungal infection, while some of the others had fused vertebrae in their necks, which would have likely come from traumatic injuries. There is even one female found at the site who appears to have lived with a fractured skull.
Lifestyle
Despite living through extremely difficult conditions, the Cro-Magnon people lived in complex social structures and had vibrant cultural and artistic expression. Archaeologists have recovered sophisticated tools made from bone, stone, and antler, as well as artistic creations in the form of cave paintings, jewelry, decorated artifacts, and carvings. They are particularly recognized for creating some of the earliest depictions of animals and human figures, as well as abstract patterns.
These artistic representations provide valuable insights into the beliefs, rituals, and daily lives of these ancient humans. The evidence they left behind indicates how humans evolved in Europe and showcases some of the behaviors and traits that would continue to be distinct feature of our species today.
Source Link: Who Were The Cro-Magnon People?