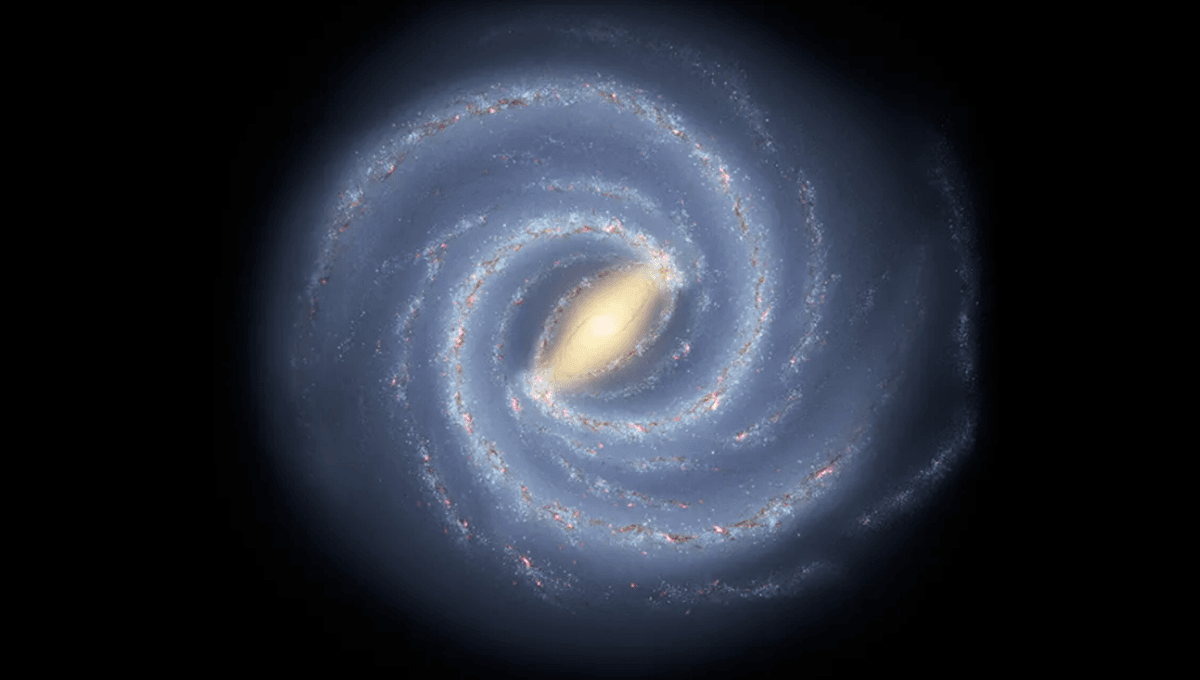
A former NASA analyst on TikTok has explained the (hopefully obvious) reason why photographs of our galaxy – the Milky Way – are not real.
Responding to the question “How do we take pictures of the Milky Way if we are in it?”, science communicator and former NASA space analyst Alexandra Doten explained that we simply do not have pictures of the Milky Way.
“Every full image you see of the Milky Way is an illustration,” Doten explained in the video (see below).
“We cannot see the Milky Way like this, and I don’t think humans ever will,” she added.
The reason for this is quite simple: we have never been able to view the Milky Way from any other vantage point than the edge of a spiral arm of our galaxy.
Think of it like with Earth, with a few added complications. We knew the shape of the Earth for a long time through mapping the surface, studying the motions and shapes of the planets and stars, and taking careful measurements of Earth’s gravity at different points. Through this, we determined the shape of the Earth, including that it isn’t perfectly round. But we could never have a complete image of the Earth until we left it and got far enough to photograph it all.
The first image of the whole Earth from space came in 1972, when astronaut Ron Evans or Harrison Schmitt took a photo from onboard Apollo 17 while headed to the Moon. This was the first time that an Apollo mission’s trajectory made such a photo possible, and the result was the iconic “Blue Marble” image.
Leaving the galaxy far enough to photograph it is a whole different undertaking for a species that has not yet left the Solar System.
“To get [images of the Milky Way] a spacecraft would have to travel either up or down from the disk of the Milky Way, and travel so incredibly far,” Doten explains.
But that doesn’t mean we don’t know what the Milky Way looks like. Most of the objects you see when you look up at the night sky are stars in our own galaxy, which we can map. We can see a good portion of the Milky Way in the night sky as well, and from this, we can map the stars within it and build up an impression of what it looks like. Doten compares it to trying to create an image of a Ferris wheel you are currently riding on.
We can see and image enough objects within our galaxy – including the supermassive black hole at the center of it – in order to get a pretty good idea of what it looks like. Mapping the stars within it, and looking at its shape, we can tell we are within the spiral of a barred spiral arm galaxy. Seeing other galaxies similar to our own helps too, just as seeing Jupiter’s bulge helped Isaac Newton figure out that the Earth bulges too.
The more we look at it, the better we can work out what is going on, including looking for collisions with other galaxies. But we will likely never see the Milky Way from far enough away to take a true photograph of its beauty, and certainly not within our lifetimes, or many, many generations to come.
An earlier version of this article was first published in August 2024.
Source Link: Why Aren't Full Photos Of The Milky Way Real? A NASA Analyst Explains The Obvious