JWST images are nothing if not stunning, bringing incredible resolution to the infrared universe. Showcasing faint nebulae or distant galaxies has a curious side effect: usually, closer and definitely brighter stars appear to gain spikes, six big ones and two small ones. The effect is so iconic that you can use it to confirm at a glance that the picture was taken by JWST.
The reason behind the spikes is the architecture of the telescope – any modern observatory has to contend with this fact. Telescopes for advanced astronomy are no longer using lenses to magnify the distant features of the cosmos. They use mirrors instead. So the light is first reflected off the primary mirror and onto a secondary mirror. This secondary mirror is right in front of the primary and its location and how it is held can create peculiar patterns.
Let’s look at JWST specifically. Its secondary mirror is circular and it is held by three struts. The struts produce a phenomenon known as diffraction. It’s the way waves are affected by an obstacle in their path. In the case of the three struts of the secondary mirror, the light from the bright object produces diffraction spikes. Each strut produces two spikes at 90 degrees from the strut, and that adds up to six. But if you count them, there are definitely eight spikes in the image: six big ones and two small ones.
So what gives? Well, JWST also has another peculiar characteristic. Its primary mirror is segmented and made of 18 hexagonal pieces that also create diffraction features. Actually, the shape of the mirrors is what contributes the most to the spikes. The edges of the mirrors produce the most prominent spikes, which is why they are evenly spaced: the mirrors are regular hexagons.
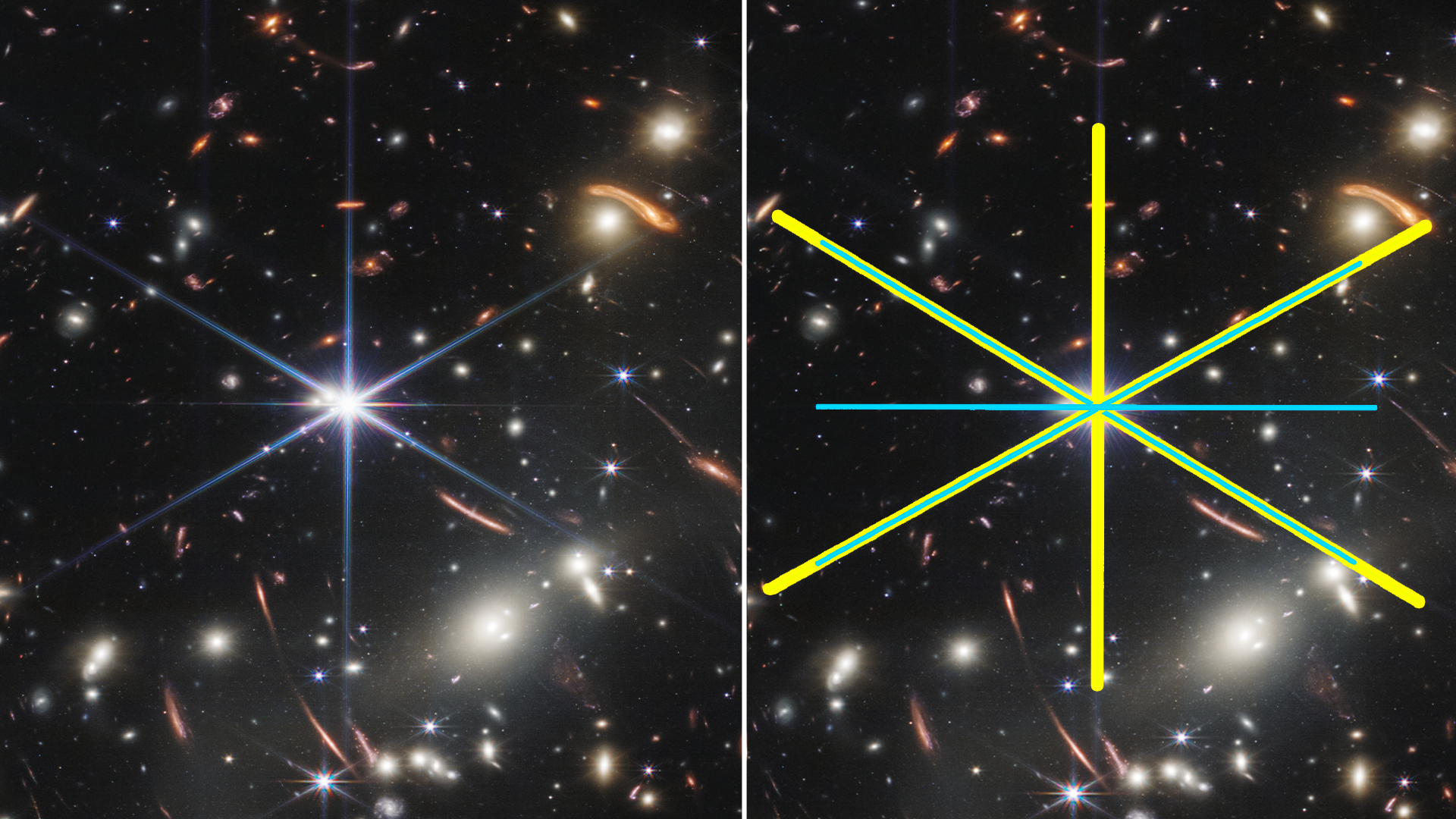
The cyan lines show the position of the spikes from the spurs, the yellow are the ones from the mirror.
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STSCI with modification from IFLScience.
So why are they not 12? Well, the team was clever enough to align four of the spikes of the mirror with four of the spikes of the struts so that you end up having a total of eight appearing. Paying close attention to the spikes (the brighter the star, the easier it is) you would see that the tips of them are often very faint and they might even look like a dashed line.
This is another effect that often follows diffraction known as interference, where light waves then cancel each other out or amp up each other depending on how they are overlapping.
JWST has been delivering some incredible science and even more has been teased to arrive in the coming months.
Source Link: Why Do Stars In JWST Images Have 8 Spikes?