Nutritionally speaking, tuna is an outstanding source of nourishment, offering high-quality protein, fatty acids for heart and brain health, and essential vitamins and minerals like vitamin D, B12, and selenium. However, not to mention its huge sustainability concerns, this nutrient-loaded fish has a major downside: it’s packed with mercury, a neurotoxic heavy metal.
How much mercury is in tuna?
Compared to most other seafood, the flesh of tuna has relatively high levels of mercury. A Food and Drug Administration (FDA) estimate suggests that tuna contains between 0.126 and 0.689 parts per million of mercury on average. These levels are up there with some of the worst offenders, which are sharks and swordfish.
Some forms of tuna are worse than others, though. For instance, canned albacore tuna, also known as white tuna, typically contains about three times more mercury than canned light tuna, like skipjack or yellowfin.
Why does tuna have so much mercury?
You’ll notice that most of the fish that are relatively abundant in mercury are apex predators, such as sharks, swordfish, marlin, king mackerel, etc. This is because of a process called bioaccumulation.
Inorganic mercury enters the natural environment through industrial pollution, which is converted into its organic form, methylmercury, by microorganisms in the marine ecosystem. Small levels of methylmercury can also be naturally formed by bacteria in waters and sediments.
The chemical is consumed by small aquatic organisms, which are then eaten by progressively larger predators in the food chain. Since mercury is absorbed quicker than it’s metabolized or excreted, higher concentrations of the metal build up at each trophic level of the food chain, with top predators consuming the most.
Mercury (or technically methylmercury) is so abundant in the environment that even tuna that live in the middle of the ocean will contain some amount of the chemical.
It’s apparent that mercury has become deeply embedded into these natural systems too. A 2024 study found that levels of mercury have remained unchanged in tuna despite an overall decline in global mercury emissions since the 1970s.
The researchers speculated that the stable mercury levels in tuna might result from the upward movement of “legacy” mercury from deeper ocean layers to the surface waters where tropical tuna typically feed. This legacy mercury, likely released into the environment years or even decades ago, may not yet show the impact of recent reductions in atmospheric emissions.
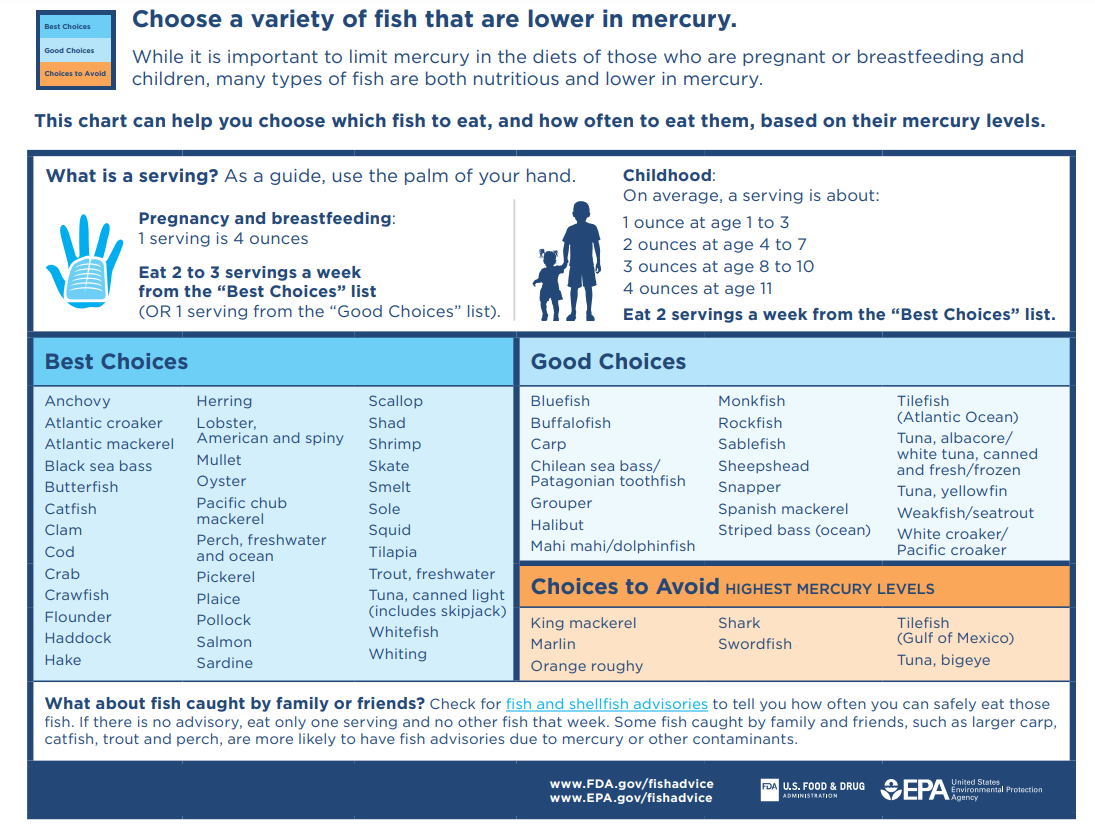
Advice on eating fish published by the US government.
Image credit: FDA/EPA
How much tuna is too much?
The quantities of mercury are minute, but they can build up, especially if consumed in high amounts for a long time. Since the metal is a neurotoxin, much of the concern is neurological.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), symptoms of methylmercury poisoning may include: peripheral vision problems; “pins and needles” feelings, usually in the hands, feet, and around the mouth; lack of coordination of movements; impairment of speech, hearing, and walking; and muscle weakness.
However, you have to consume a fair quantity of tuna for a considerable period to start worrying about mercury-related poisoning.
Under the FDA guidelines, adults can happily eat 2 to 3 servings of canned light tuna each week without any problems. Ideally, children and pregnant people should aim for this level of consumption too, if not less.
However, that’s a very conservative recommendation. Elsewhere, the FDA notes: “adverse short-term health effects for adults from consuming average amounts of seafood usually require a level of methylmercury not generally found in seafood products.”
Some scientists estimated that healthy adults can consume around 25 cans (containing ~95 grams) of tuna a week before running a significant risk of mercury poisoning.
That might sound like an unattainable level of tinned fish consumption, but you’d be surprised. A 2019 study looked at the tuna-eating habits of students at the University of California and found that 7 percent of study participants ate more than 20 tuna meals every week.
Lo and behold, hair samples showed many of the students had levels of mercury that were at ” a level of concern.”
All “explainer” articles are confirmed by fact checkers to be correct at time of publishing. Text, images, and links may be edited, removed, or added to at a later date to keep information current.
The content of this article is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of qualified health providers with questions you may have regarding medical conditions.
Source Link: Why Is Tuna So High In Mercury, And How Much Tuna Is Too Much?