The southern tip of Africa is slowly lifting out of the water by up to 2 millimeters each year. Now, scientists think they’ve finally figured out why.
GPS devices in South Africa have long hinted that something unusual might be happening to the landmass. These instruments can determine both their horizontal position and elevation with millimeter-level precision using satellite signals. In recent years, it’s suggested the landmass has risen significantly since 2012.
“This data showed an average rise of 6 millimeters between 2012 and 2020,” Dr Makan Karegar, author of the study from the Institute of Geodesy and Geoinformation at the University of Bonn, said in a statement.
Scientists previously hypothesized that the rise was due to mantle flow in the Earth’s crust. Although Earth’s mantle can look like solid rock, it behaves like a super-thick syrup that gently oozes and flows over extremely long periods of time. The uplift of South Africa, they speculated, could be a result of this mantle pushing upwards in the region, causing Earth’s crust to bulge.
However, Dr Karegar and other scientists at the University of Bonn have put forward another explanation. They argued that the rising landmass might be more closely associated with drought.
When land loses water, it starts to lift up, like a foam ball expanding back to shape after being squeezed. Normally, underground water weighs the land down, so when it disappears, the ground rebounds and swells upward.
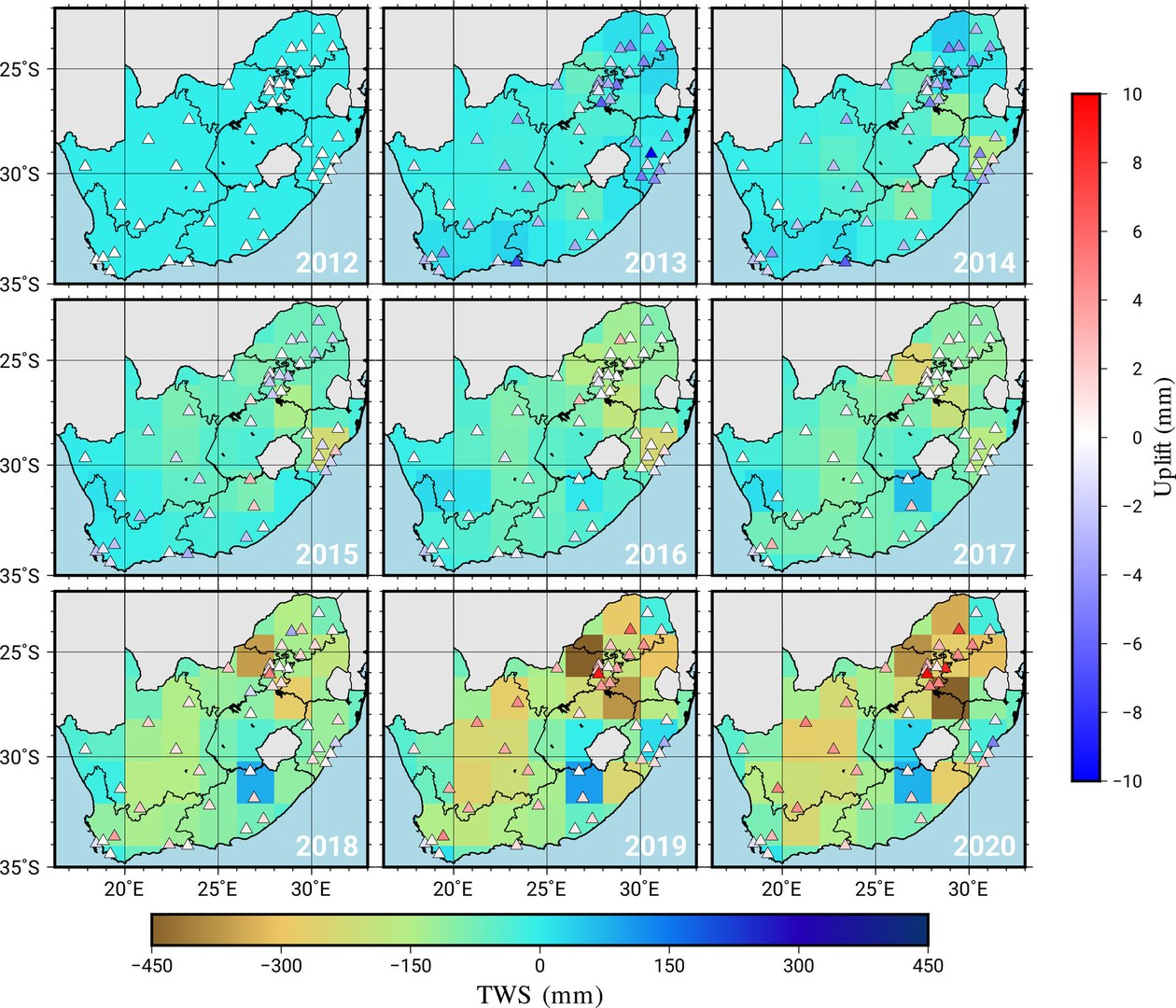
The graph shows the water losses and gains in South Africa between 2012 and 2020. The browner the region, the higher the water loss. The triangles represent GPS stations. A red triangle means that this station has risen in height since 2012.
Image credit: © AG Kusche / University of Bonn
This is what the team thinks is happening in South Africa. They found that areas in South Africa with the biggest drops in groundwater and surface water were also the ones rising the most.
“This data also showed that the land uplift could primarily be explained by drought and the associated loss of water mass,” explained Christian Mielke, lead author on the study, also from the University of Bonn.
Much has been made of South Africa’s water crisis in the past decade, especially in the Western Cape region and the City of Cape Town. The earlier part of the drought in 2015 was blamed on the El Niño weather pattern, but experts are now pointing towards poor city management, a growing urban population, increasing agriculture, and climate change.
The problem became so severe in 2018 that Cape Town authorities warned they could soon be approaching “Day Zero”, a time when the city would literally run out of water. Fortunately, the crisis never reached this point, but the problem continues to loom – and, surprisingly, it’s still affecting the country’s physical landscape.
The new study is published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth.
Source Link: Why South Africa Has Been Lifting Out The Ocean By Up To 2 Millimeters Each Year