The star cluster NGC 4755 is popularly known as the Jewel Box because its stars look like sapphires with the occasional ruby and diamond through a small telescope. There are, however, no emeralds. That’s not just an omission of this collection of 100 or so stars. Irrespective of the achievements of environmentally active celebrities or building metering systems, when it comes to space, no stars are green.
To the naked eye, at least for most people, stars look either red or white. Using telescopes to increase brightness some of those apparently white stars turn out to be orange or blue and some are arguably yellow. The absence of stars in the middle of the rainbow says more about our eyes than a gap in stellar physical properties.
Most of the colors we see on Earth are caused by objects’ surface chemistry, which determines which wavelengths of light are reflected and what gets absorbed. Stars are different, however. Their color is determined by their temperature.
Cool stars (3,700 Kelvin and below) emit light mostly in the red part of the spectrum (longer than 625 nanometers), as well as the infrared we can’t see. In contrast to our association of blue with cold and red with hot, as stars get hotter they emit shorter wavelengths of light, which is why the hottest stars, such as Sirius, look quite blue.
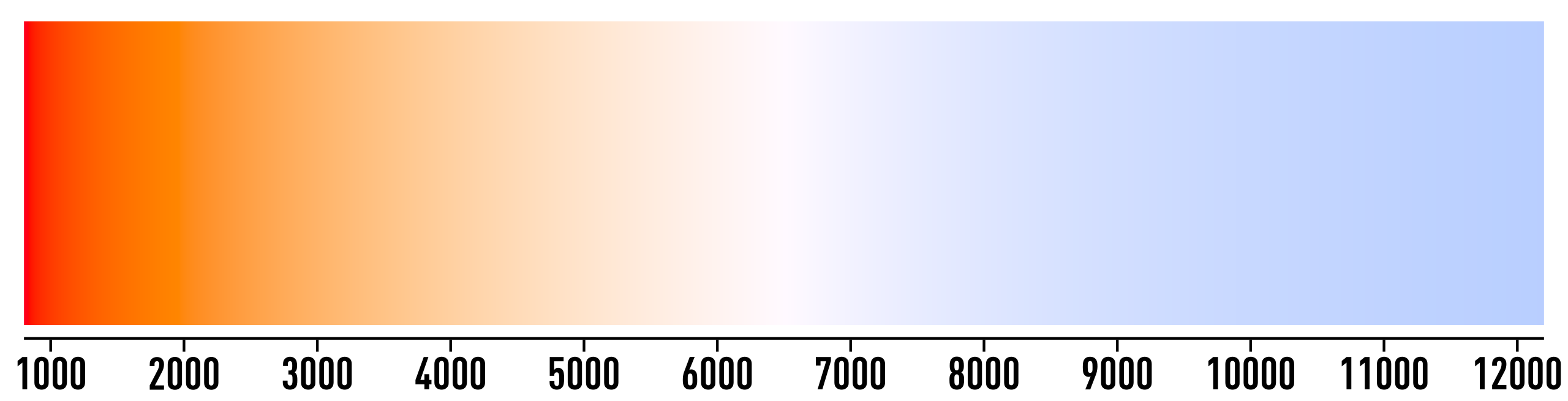
The relationship between temperature and peak wavelength is defined by Wein’s displacement law. Based on its formula, a star with a temperature of 5,500 K will emit its peak radiation at 527 nanometers, almost in the center of the green part of the spectrum.
Put like this, the absence of green stars seems even more puzzling. There certainly are stars with that temperature – indeed the Sun’s photosphere, which determines the light it emits, is not far off at 5,72 K – so why aren’t they green?
Crucial to the answer is that stars don’t emit light only at their peak like a plucked string producing a single wavelength of sound. The peak is just the peak, stars always produce plenty of longer wavelength photons, and a few shorter ones.
If our eyes concentrated purely on the peak wavelength we would see Sun-like stars as green, but that is not how they work. Confronted with a mix of greens and yellows, with a small amount of red and blue thrown in, we see the mix as white.
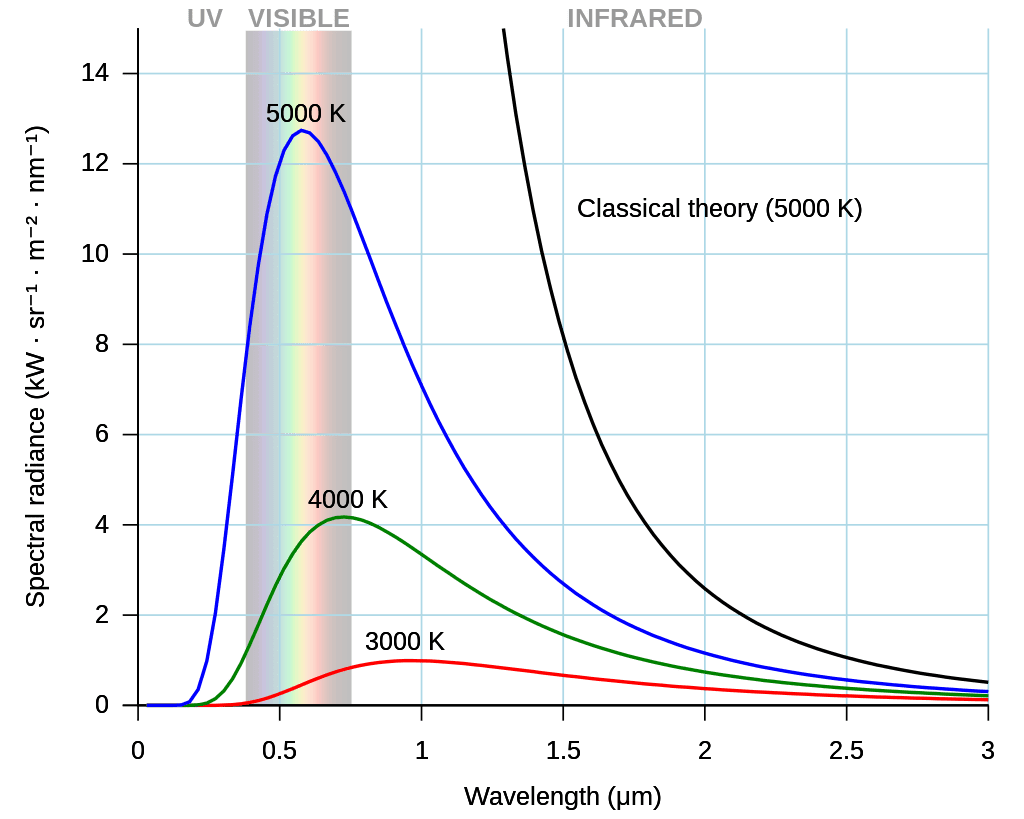
The curves of light emitted at different wavelengths for three temperatures. As things heat up more light is emitted, and the peak gets shorter, but there is always a wide range. The black line indicates what was thought to happen prior to Plank launching the quantum revolution. Image credit: Darth Kule – Own work, Public Domain
We see the same process when heating an object on Earth. First, it glows red hot, then orange, and then white. If we have a powerful enough source of heat it may even glow blue, but never green.
We can see stars as green if we put the light through a filter that takes out some of the other wavelengths, but that’s just cheating really. Nevertheless, the universe also has a few tricks up its sleeve.
Popular optical illusions have us stare at colored shapes and see a ghostly contrasting residue after looking away because the cones in our eyes become fatigued from color overload. Stars can do the same thing. Antares is a star so bright and red its name literally means the rival to Mars (Ares in Greek). Its much fainter companion Antares B is white. However, when seen in the same field of view, Antares B looks green by contrast. Similar descriptions have been given to other white companions of brighter red stars.
Grass or living leaves look green to us because that is pretty much the only wavelengths of sunlight they are reflecting to us. Some objects in space are similar – such as the occasional green comet.
Besides the smooth curves of thermal radiators like the Sun, individual elements release specific spectral lines as a result of their electrons’ energy transitions. Some of these, such as calcium, are particularly bright in the green. However, there is usually enough light of other colors to create an overall white effect if the light is not split up into its constituents.
Source Link: Why There Are No Green Stars