Archaea, hardy single-celled organisms that form the third domain at the top of the universal tree of life, have survived for billions of years in some of the most extreme environments on Earth. Now, scientists have taken a big leap forward in explaining how that is possible, discovering how these organisms use hydrogen as a source of energy – something that never occurred to our species until recently.
“Humans have only recently begun to think about using hydrogen as a source of energy, but archaea have been doing it for a billion years,” said study author Dr Bob Leung of Monash University in a statement.
Alongside archaea, the two other domains of life in the widely accepted model are the bacteria and the eukaryotes – the group that includes animals, plants, and fungi. Current thinking in the world of evolutionary biology suggests that the eukaryotes (yep, humans too) evolved from an ancient merger between archaeal and bacterial cells via the exchange of hydrogen gas. Understanding how archaea use hydrogen could therefore be central to understanding the very underpinnings of life on our planet.
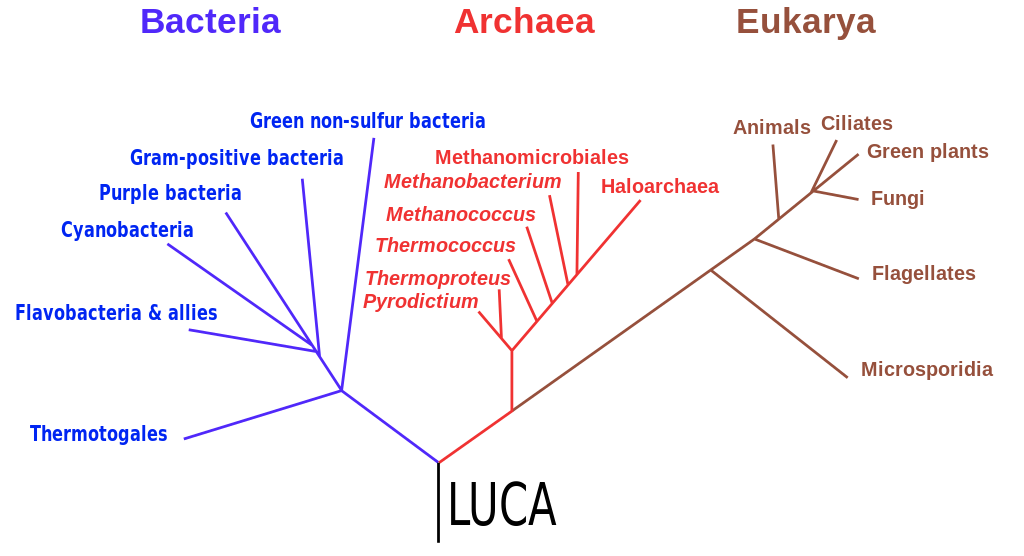
This widely accepted, simplified version of the phylogenetic tree of life shows the three domains extending out from LUCA, the last universal common ancestor.
“Our finding brings us a step closer to understanding how this crucial process gave rise to all eukaryotes, including humans,” Leung added.
The team combed through the genome sequences of over 2,000 archaeal species to find the genetic codes for hydrogen-producing enzymes, and they hit on 130 genomes with evidence of unusual enzymes called [FeFe] hydrogenases. These have previously been documented in other organisms, but not in archaea, making this result a world first.
In addition to this, they found evidence of hybridization between [FeFe] hydrogenases and another class of enzyme, [NiFe] hydrogenases, across 10 archaeal orders. “These findings revise our understanding of the distribution and evolution of microbial [hydrogen] metabolism, and have broad biological, chemical, and biotechnological ramifications,” the authors write.
The 130 genomes came from species in nine different phyla, living in some of the most inhospitable locations on the planet, from hot springs to deep beneath the ocean floor. By reproducing these [FeFe] hydrogenases in the lab, the scientists could see for themselves the huge diversity in their structures and functions.
It turns out that archaea not only possess some of the smallest hydrogenases of any lifeform, but they are also the most complex.
This ability to process hydrogen and generate energy is what has allowed these resilient microbes to thrive in places most living things wouldn’t dare to tread. But as well as helping us learn more about how they’ve survived down the millennia, which has implications for our own evolutionary story, there’s also the possibility that we can learn from archaea as we seek to transition to a more sustainable energy future.
“Biotechnologists now have the opportunity to take inspiration from these archaea to produce hydrogen industrially,” said Leung.
Hydrogen has been touted as a “fuel of the future”, though its production through chemical processes is not without an environmental impact – that’s why natural deposits of pure hydrogen gas are so highly prized. Learning from archaea to produce better hydrogen catalysts could help improve cost-effectiveness and sustainability.
Professor Chris Greening, first author on the paper, added, “Industry currently uses precious chemical catalysts to use hydrogen. However, we know from nature that biological catalysts function can be highly efficient and resilient. Can we use these to improve the way that we use hydrogen?”
The study is published in the journal Cell.
Source Link: World-First Discovery Reveals How The Third Domain Of Life Makes Energy In Earth’s Bleakest Corners