To study the rapidly changing ecosystems of Antarctica, researchers have recently created the first continent-wide map of its plant life.
You might expect the color palette of Antarctica to be bright white with the odd icy blue and cold grey, but a surprising amount of green can also be found thanks to mini pockets of photosynthetic life. In the face of climate change and warming temperatures, it’s likely the ice-capped continent will witness the growth of even more vegetation – a worrying trend that scientists are keen to keep an eye on.
An international team of scientists, led by the University of Edinburgh with the Norwegian Institute for Nature Research, British Antarctic Survey (BAS), and Scottish Association for Marine Science, searched for Antarctica’s green spaces using satellite data from ESA, as well as field studies carried out over several summer seasons.
Their work detected almost 45 square kilometers (17.3 square miles) of vegetation, around 80 percent of which was located within the Antarctic Peninsula and neighboring islands. That may sound like a fair amount, but green space accounts for just 0.12 percent of Antarctica’s total ice-free area.
“Our continent-scale map provides key information on vegetation presence in areas that are rarely visited by people. This will have profound implications for our understanding of where vegetation is located across the continent, and what factors influence this distribution,” Charlotte Walshaw, PhD researcher from the University of Edinburgh, who led the study, said in a statement.
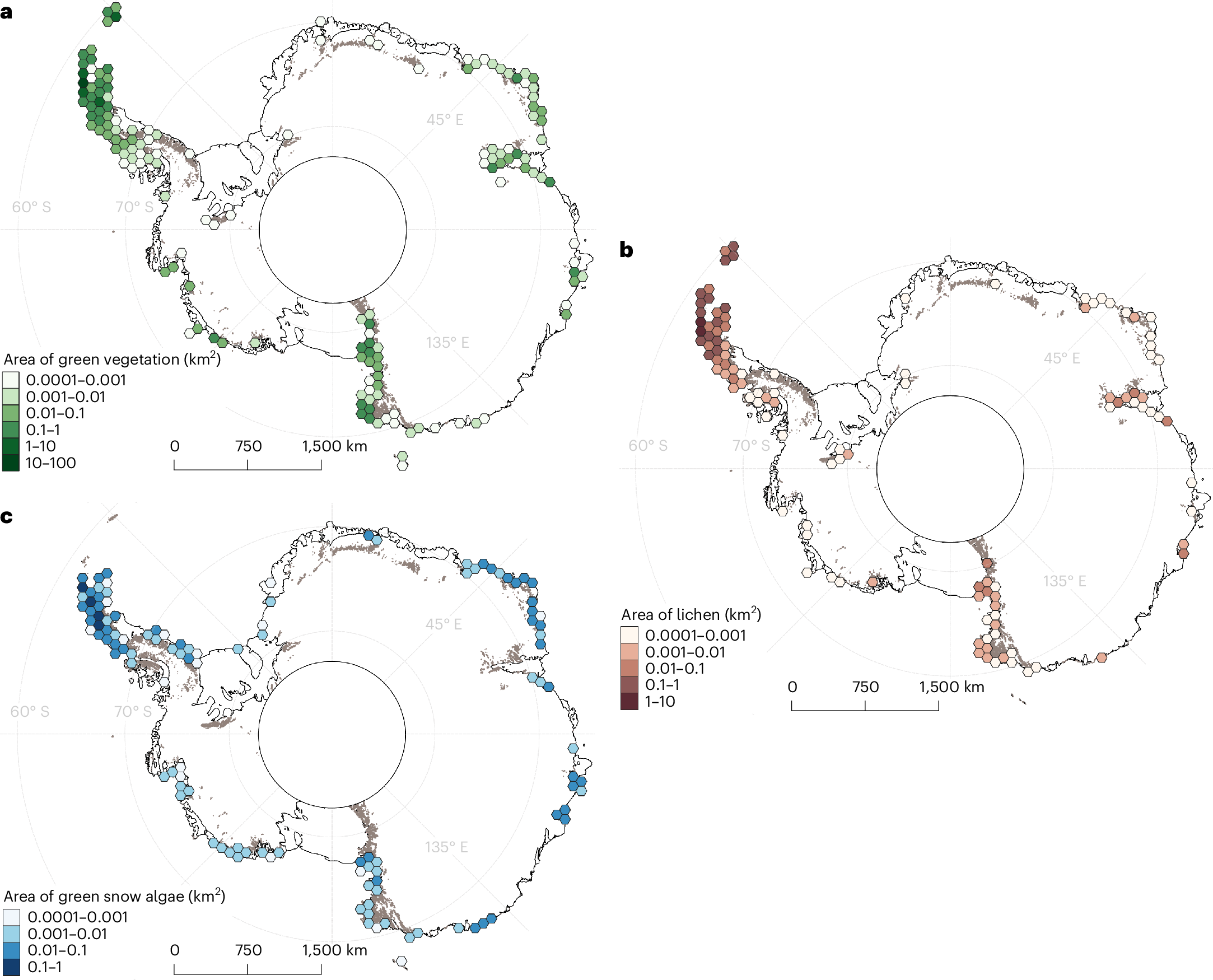
Maps of Antarctica show the distribution of (a) green vegetation, (b) lichens, and (c) green snow algae.
It isn’t easy for plant life to colonize new land in the harsh wilderness of Antarctica, although the long-standing natural order is starting to be disrupted.
Writing for the Conversation, study author Claudia Colesie from the University of Edinburgh explains how plant colonization in Antarctica typically unfolds through several stages. First, pioneering algae and cyanobacteria settle on the land and live between soil and sand particles, where they create a surface for other organisms to grow upon. Lichens and mosses use the surface to establish themselves and grow. Larger planets can then lay their seeds within this soft and moist mossy cushion
However, warming temperatures and shifting landscapes now mean it’s much easier for plant life to establish itself here. Just two vascular plants are native to the continent: Antarctic hair grass and Antarctic pearlwort. While these two species were once relatively rare on the ice-dominated continent, they’ve become increasingly common in the past couple of years due to rising temperatures.
Furthermore, over 100 plant species have recently invaded Antarctica, including common lawn grass that has rapidly spread over sub-Antarctic Islands and appears to be working its way down the Antarctic Peninsula.
“Getting an accurate map of the photosynthetic life of the continent gives us a baseline for assessing future change. As the continent warms and ice melts, we expect that areas of rock outcrop will expand, and vegetation will colonize more ground. This new map enables us to monitor these consequences of climate change,” added Peter Fretwell, remote sensing expert at BAS and co-author of the paper.
The new study is published in the journal Nature Geosciences.
Source Link: World First Map Of Antarctica's Plant Life Shows Rapidly Sprouting Continent Under Climate Change