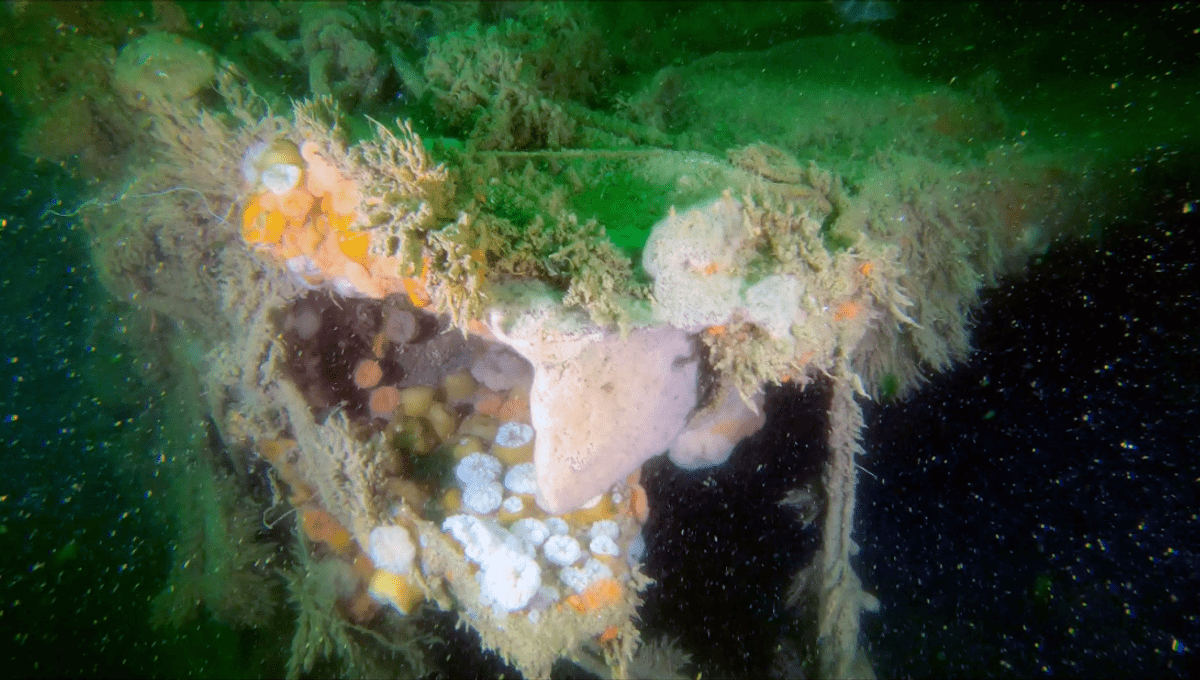
At IFLScience we love a good shipwreck, but while these fallen vessels can act like artificial reefs for a host of marine species (they went mad for Shackleton’s Endurance), new research has uncovered the negative impact they can have on the environment. A World War II (WWII) German shipwreck that has sat on the seabed for 80 years has been leaking pollutants as it stewed on the seafloor, releasing hazardous heavy metals all the while.
The shipwreck is the V-1302 John Mahn vessel that sank in the Belgian part of the North Sea. Initially, it was a German fishing trawler, but it was later redeployed during WWII as a patrol boat, during which time it was attacked by the British Royal Airforce in 1942 and sank.
WWI and WWII shipwrecks across the world are thought to collectively contain around 2.5 million and 20.4 million tons of petroleum products, demonstrating that though they be spooky, they be chockfull of pollutants.
To ascertain how these pollutants might be impacting the environment, scientists took sediment samples from the ship and the sea floor immediately around it. Analyses revealed that the shipwreck had leaked several toxic pollutants into the environment, including heavy metals (like nickel and copper), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (chemicals found in coal, crude oil, and gasoline), arsenic, and explosive compounds.
“We wanted to see if old shipwrecks in our part of the sea (Belgium) were still shaping the local microbial communities and if they were still affecting the surrounding sediment,” explained lead author and PhD candidate Josefien van Landuyt of Ghent University in a statement. “This microbial analysis is unique within the project.”
That microbial analysis revealed that not only was the leaking shipwreck altering the pollutants in its immediate vicinity, but it was also changing the microbiome of the seabed. This is because there are some freaky microbes that are hot for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (such as Rhodobacteraceae and Chromatiaceae), and so these were found in higher concentrations among the most polluted areas.
Another group of microbes, the sulfate-reducing bacteria like Desulfobulbia, were living it up on the shipwreck’s hull and contributing to its corrosion.
“While wrecks can function as artificial reefs and have tremendous human story-telling value, we should not forget that they can be dangerous, human-made objects which were unintentionally introduced into a natural environment,” van Landuyt continued. “Today, new shipwrecks are removed for this exact reason.
“The general public is often quite interested in shipwrecks because of their historical value, but the potential environmental impact of these wrecks is often overlooked.”
Perhaps it’s time we turned to an eco-friendlier brand of ghost story.
The study was published in Frontiers in Marine Science.
Source Link: WWII Shipwreck Leaking Explosives For 80 Years Reveals How They Can Shape Ocean Ecosystems