When we think about mummies, I’m willing to bet the first images that come to mind relate to Ancient Egypt. However, mummification has been practiced by many cultures across the world, and as you can imagine, each has developed their own embalming methods for this purpose. But not all of these various methods receive the same attention, and some are cruder and more inventive than you’d expect.
An incredible example of this is the little-known case of a mummy located in the church crypt of St Thomas am Blasenstein, in a small village in Austria. This mummy is remarkably well-preserved, but no one has known how it has survived so well for so long.
“The unusually well-preserved mummy in the church crypt of St Thomas am Blasenstein is the corps of a local parish vicar, Franz Xaver Sidler von Rosenegg, who died in 1746,” Dr Andreas Nerlich, a pathologist at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität explained in a statement.
Nerlich and colleagues examined the body using an array of techniques, including CT scanning, focal autopsy, and radiocarbon dating. They found that the mummy’s upper body fully intact but its lower portion and head showed greater degrees of post-mortem decay.
This is the first case of a mummified body that has been identified to have been ’embalmed’ by stuffing the abdominal and pelvic cavity with various substances through the anal canal.
Dr Andreas Nerlich
Interestingly, during their investigation they also found a variety of foreign materials stuffed into the abdominal and pelvic cavity. When they opened the body, they identified this material as wood chips from fir and spruce trees, pieces of branches, and fabrics like linen, hemp and flax. These materials would have been easily accessible to people at the time, and appear to have been used as a basic method of drying the otherwise soggy parts of the body soon after death.
“Clearly, the wood chips, twigs, and dry fabric absorbed much of the fluid inside the abdominal cavity,” Nerlich added.
This embalming method is pretty different to other known practices where the body is opened and prepared. Instead, whoever embalmed this vicar did so by stuffing the materials up the cadaver’s rectum, much like a turkey is prepared at Christmas.
“This is the first case of a mummified body that has been identified to have been ’embalmed’ by stuffing the abdominal and pelvic cavity with various substances through the anal canal,” Nerlich told IFLScience.
“This stuffing was undertaken in order to absorb fluid from the interior of the body and this has lead to an excellent preservation of the thorax and abdomen. If this body would have been buried in a usual soil burial, the abdominal wall would have disappeared after some time and any possible researcher would only have noted some wooden chips and cloths which might have also come from the body surface.”
During their examination, the researchers also found a small glass sphere, like a bead, with holes on either end. It is possible this addition was part of some of the fabric in the body, but as it is only a single piece, it may also have been lost during the body’s preparation (like the old joke about a surgeon losing his watch in a person during an operation).
This research not only explains the methods used to preserve this body, it also helped identify the person themselves. For a long time, the body was only assumed to have belonged to Sidler and was merely referred to as the “air-dried chaplain” in past research papers. However, this latest study has now confirmed it to have belonged to Sidler.
The analysis revealed that the person died between the ages of 35 and 45 and most likely lived between 1734 and 1780. This matches the dates for Sidler’s life. The team also found that this individual had a high-quality lifestyle, with a diet based on central European grains, animals products, and fish, while also showing very few signs of physical activity. This latter point would certainly suggest the lifestyle of a priest. There was also evidence of a long-term smoking habit and lung tuberculosis towards the end of their life.
According to Nerlich, there is evidence that cadavers were “prepared” for transport or elongated laying-out of the dead, but these reports all lack precise descriptions. As such, it is possible the vicar was planned for transportation to his home abbey, but may not have been sent there for some unknown reason.
For Nerlich and his colleagues, the case is an important for several reasons. Not only is it the first recorded example of this type of embalming process, but their overall analysis of the body stresses the need for future researchers to include specific techniques in their work.
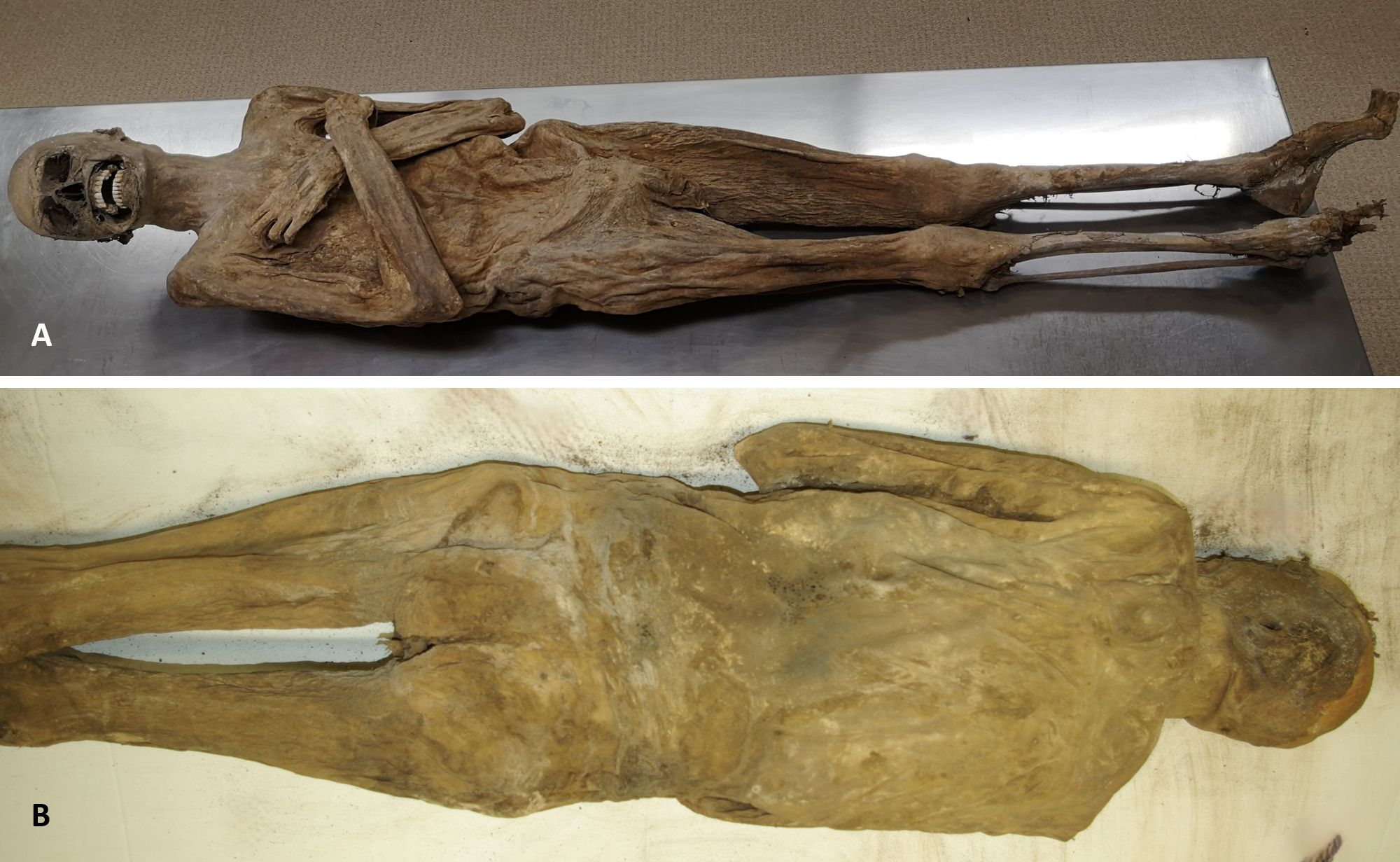
The external appearance of the mummy reveals the astonishing level of preservation.
Image credit: Andreas Nerlich
In 2000, the body was analyzed by Austrian pharmacologist Bernhard X. Mayer from the University of Vienna who conducted a detailed external examination and an X-ray with a portable X-ray machine. During his inspection, the X-ray picked up the bead in Sidler’s abdomen but nothing else, leading to the conclusion that the priest may have been poisoned. The rumors of which still persist even now. But through Nerlich’s assessment, we now know that this bead, although unusual, was added to the body post-mortem.
“The investigation of a well preserved mummy should always – if possible – include a CT scan investigation, since the X-ray analysis of [the] mummy in 2000 did not detect the stuffing,” Nerlich told IFLScience.
It seems any future research into crypt burials need to take a deeper look at the bodies they may contain, as unusual preservation practices can tell us a lot about how people lived and died in their respective time, as well as how others attempted to keep them from rotting.
The study is published in the journal Frontiers in Medicine.
Source Link: Exceptionally Well-Preserved Austrian Mummy Was Embalmed With Previously Unknown Method