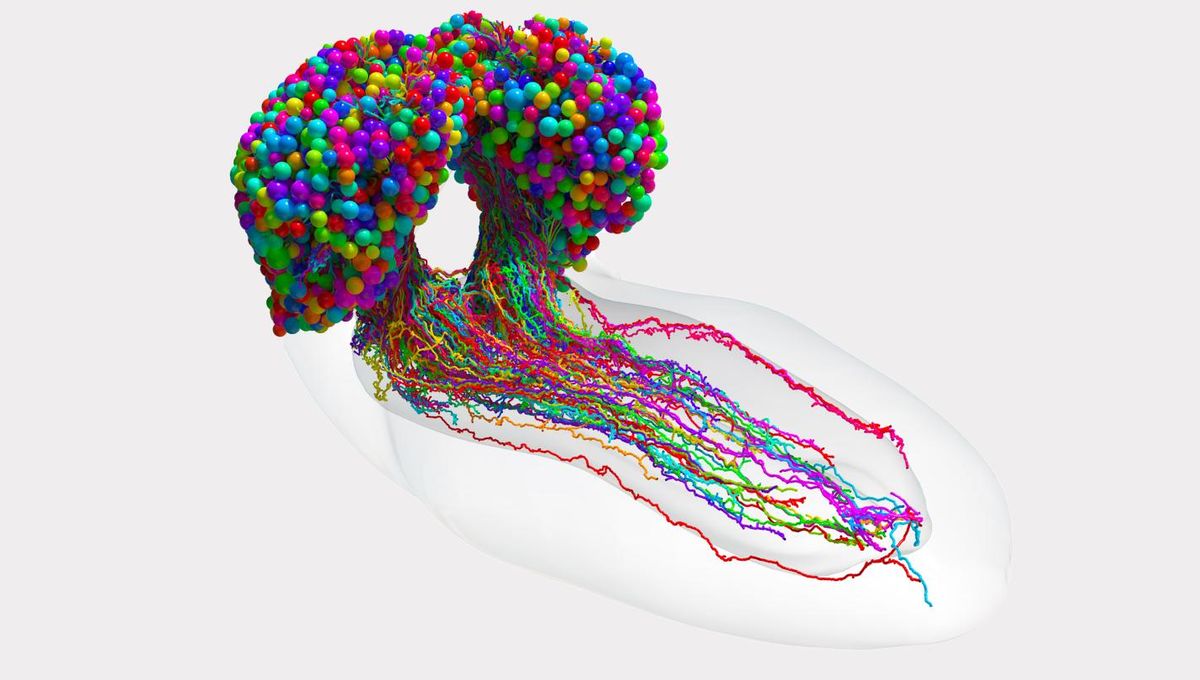
The most complex brain map ever created has been released by scientists, depicting the intricate inner workings of the insect mind. They state that the new map could be a crucial step into actually beginning to understand how the brain works, including how thoughts originate.
“If we want to understand who we are and how we think, part of that is understanding the mechanism of thought,” said senior author Joshua T. Vogelstein, a Johns Hopkins biomedical engineer, in a statement.
“And the key to that is knowing how neurons connect with each other.”
Created by a collaboration between Johns Hopkins University and the University of Cambridge, the map depicts a diagram of the neural connections in a larval fruit fly, which bear a lot of similarities with human brains and are regularly used as a model organism. It is the most complete diagram to date, with most other “connectomes” (a map of synapse connections within a brain) only showing a small region and not the entire organ.
To do so, the researchers had to go through the painstaking process of slicing the brains into tiny segments of tissue, before using electron microscopy to reconstruct the connections within those tissue slices. No modern advances have managed to take the intricate work out of this reconstruction, making it an incredibly slow process – this model took over a decade. For each individual neuron in the diagram, it took an entire day.
The fruit fly is perfect for the job because much of its underlying mechanisms and genetics are similar to those of humans, whilst also having a much smaller and less complex brain.
Why is it so hard to do this with humans? A mouse brain is around a million times larger than that of a baby fruit fly, and a human brain is orders of magnitude larger than that. If it takes 10 years to do a fruit fly larva, imagine how long it could take for a primate or human brain; according to researchers, it probably won’t be within our lifetimes.
Once imaged, the Johns Hopkins team used proprietary software to analyze the data and group neurons together according to predicted patterns, as well as categorizing each neuron. They discovered the densest regions were those around the learning centers of the brain.
The team hope the research can influence and inspire future brain models, but also potential machine learning architecture that can learn from the brain’s layout.
“What we learned about code for fruit flies will have implications for the code for humans,” Vogelstein said.
“That’s what we want to understand – how to write a program that leads to a human brain network.”
The research was published in Science.
Source Link: Incredible Complete Map Of Insect Brain Released After 12 Years' Work