The discovery of a vampire squid specimen from the Early Jurassic could help reveal the poorly understood ancestry of this unique species. The fact it was buried holding prey adds unusual additional insight into its place in the ecosystem.
Vampire squid are not true squid, being more closely related to octopuses than the creatures they were named after. Members of the family can be recognized in the fossil record because, along with their eight arms they have two filaments, rather than the more substantial tentacles squid have. Nevertheless, they remain very poorly understood.
Today, only one species of vampire squid survives, but for once this isn’t a reflection of humanity’s damage to the planet. As far as we can tell, there has only been one species for a very long time. More than a dozen ancestral species are known from times when they apparently lived in shallower waters, but they’re still enough to make every discovery precious.
A discovery unearthed in Luxembourg in 2022 and dating back around 180 million years is even more valuable than most. It’s a species we have not seen before, now named Simoniteuthis michaelyi. It’s also unusually complete, with the hard internal part known as the gladius and the tops of all eight arms visible. It would have been 38 centimeters (15 inches) long.
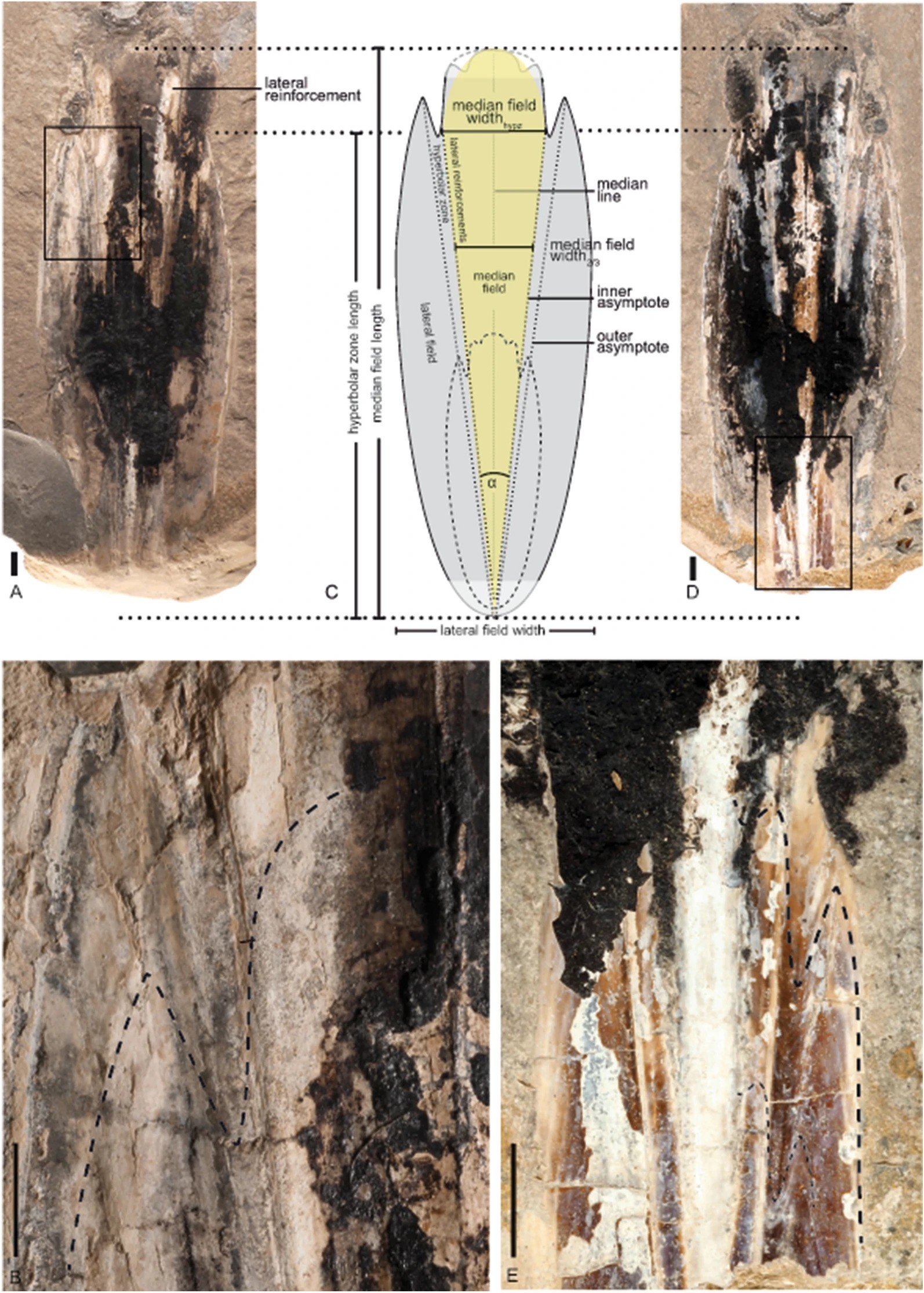
The gladius (hard mouthparts) of Simoniteuthis michaelyi as seen from different angles and represented schematically.
Two fishes are close to the specimen’s mouth, apparently being delivered by the arms. The scientists who described the fossil attribute its death to distraction sinking. This occurs when marine creatures are too busy feeding or fornicating to realize they are sinking into waters so depleted in oxygen (hypoxic) that they cannot survive or escape.
One author reporting this find previously described a case of distraction sinking involving two vampire squid of different species. One of these squid was feeding on the other when, it is suspected, both sank into hypoxic waters. Such waters were more likely to preserve a specimen. Nevertheless, the fact that such a substantial portion of ancient vampire squid fossils seem to have died in this process suggests it was something of a menace in the Early Jurassic. Vampire squids’ modern adaptation to hypoxic waters apparently came much later. Other cephalopods were prone to distraction sinking as well.
At least partial traces of all eight arms are visible in the S. michaelyi fossil, but there is no sign of the two filament tentacles. Nevertheless, the team describing it are confident they have a vampire squid, not an unusual-looking octopus.
As one of the oldest vampire squid fossils known, the discovery could shed light on their evolution, but so far, if anything, just creates more confusion. In particular, we don’t know when the two filaments, used by modern vampire squid to scoop up small organisms and floating detritus known as “marine snow”, evolved. This specimen provides no answers.
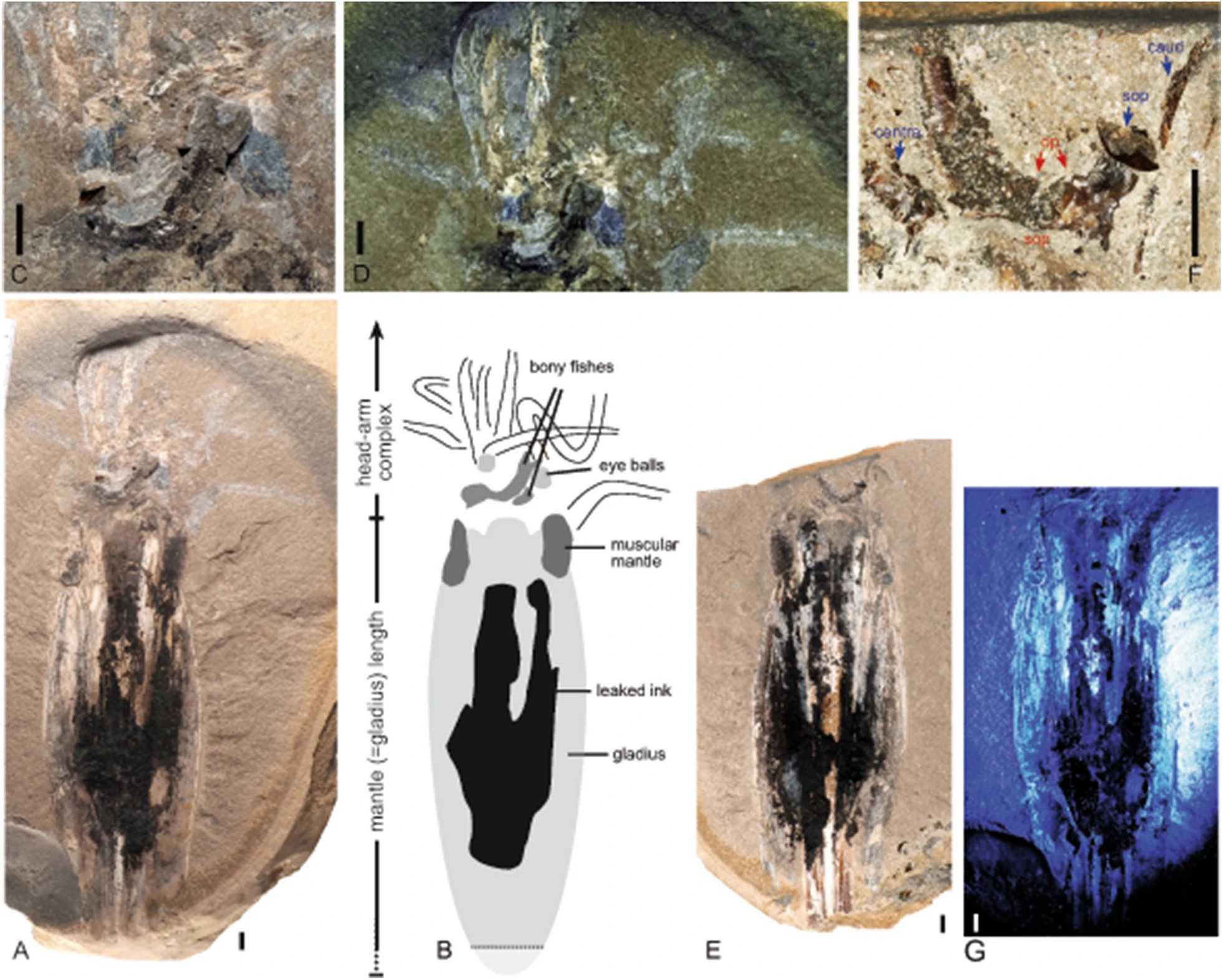
The slab (A–D) and counter-slab (E–G) of the vampire squid fossil in overview and close-ups of important parts, and under UV light, including the musculature of the arms (C and D) and the preyed on fish (F).
Given their origins as a breakaway from true squid, “taxa belonging to the vampyromorph clade should definitely display an arm crown consisting of either 10 well-developed arms, or eight arms plus a rudimental pair,” the authors write. However, like most of the other ancient vampire squid fossils, neither can be seen in this one.
The genus name honors Jo Simon, a volunteer at the Luxembourg National Museum of Natural History, while the species is named for the Museum’s director Patrick Michaely.
Vampire squid have some of the worst PR in the animal kingdom. Even the scientific name of the surviving species means “vampire squid from hell”. Having managed the remarkable feat of adapting to live in near oxygenless ocean depths, they get unfairly lumped with not only the vampire name but a totally spurious connection to extreme capitalism.
In truth, were you ever to encounter a living vampire squid they would pose no threat, let alone drink your blood or offer you an exploitative home loan. You’d probably have been crushed to death long before by the extreme pressure of their domain, but given their modest size they wouldn’t eat you anyway unless something else had dismembered you.
The findings are published in the Swiss Journal of Palaeontology.
Source Link: Newly Discovered Jurassic Vampire Squid Species Found "With Prey In Its Arms"