For the first time, scientists have recovered the mummified, frozen body of a juvenile saber-toothed cat from the Arctic permafrost in Siberia. Despite being over 35,000 years old, the sub-zero temperatures have kept the specimen in a remarkable state of preservation, with its fur, head, torso, and limbs still intact.
The frozen carcass of the saber-toothed cat (Homotherium latidens) was discovered in 2020, buried within the permafrost near the Badyarikha River in the northeast of Yakutia, Russia.
Detailing the discovery in a new study, researchers from the Russian Academy of Sciences wrote: “For the first time in the history of paleontology, the appearance of an extinct mammal that has no analogues in the modern fauna has been studied.”
This individual was essentially a kitten, perishing just three weeks after its birth. Unfortunately, its extremely young age means it had not yet developed the exceptionally long upper canine teeth that are characteristic of the genus.
Scientists have long pondered the appearance of the saber-toothed cat, and this specimen is proving to be an invaluable resource for understanding these extinct animals.
The study authors note that the juvenile saber-tooth has “significant differences from a modern lion cub of similar age.” Compared to a lion of similar age, the saber-tooth cat has an “unusual” shape of the muzzle, a large mouth opening, small ears, elongated forelimbs, a chunky neck region, and a dark coat color. The researchers noted that these are all classic adaptations to living in cold climates.
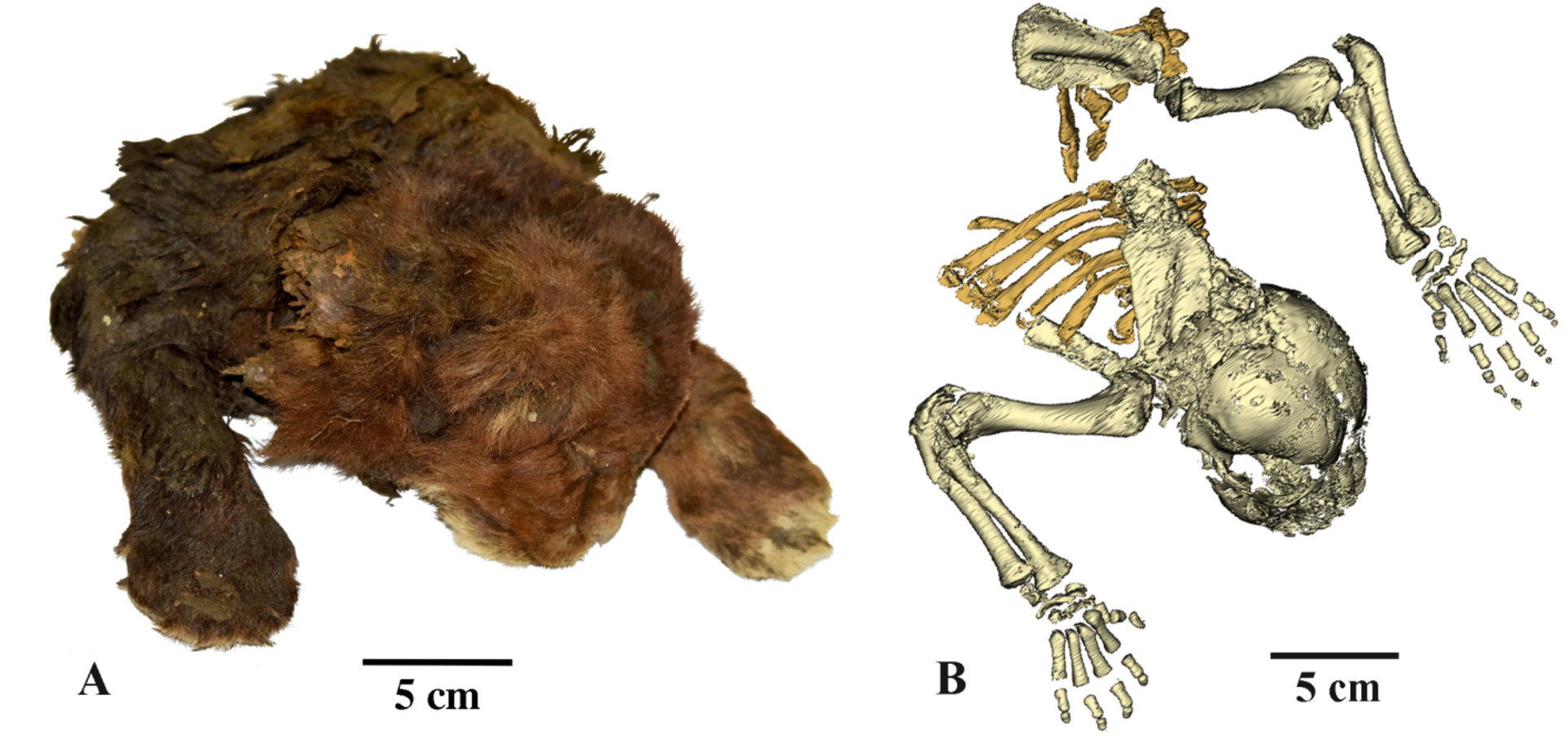
The external fur of the saber-tooth cat (left) and a CT scan of the specimen showing its bones (right).
Homotherium, an extinct genus of saber-toothed cats, was widespread during the Ice Age, inhabiting regions across Eurasia, Africa, and the Americas, with different species adapted to each region.
The recently discovered individual from Russia belongs to the species H. latidens, which lived in Eurasia until around 10,000 years ago when the last Ice Age came to a close.
It’s distinct from its counterpart that lived in North America, H. serum, as well as the African species, H. problematicum and H. africanum. Most Homotherium remains have been discovered in North America, making this latest find a valuable opportunity to shed light on the Eurasian branch of the genus.
“The discovery of H. latidens mummy in Yakutia radically expands the understanding of distribution of the genus and confirms its presence in the Late Pleistocene of Asia,” the study authors wrote.
In recent years, several other animal species have been excavated from the permafrost of Siberia, including woolly rhinoceros, mammoths, wolves, cave lions, and birds. Since Neanderthals and Denisovans also inhabited Eurasia during this period, it raises the question of whether we might one day discover an extinct human species preserved in permafrost.
The study is published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Source Link: World First 35,000-Year-Old Saber-Toothed Kitten Found Mummified In Permafrost